MP Board Class 12th Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 14 Biomolecules
Biomolecules Important Questions
Biomolecules Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Choose the correct answer :
Question 1.
Which protein transports oxygen in blood flow :
(a) Haemoglobin
(b) Insulin
(c) Albumin
(d) Myoglobin.
Answer:
(a) Haemoglobin
Question 2.
Enzyme which enhances the conversion of glucose to ethanol is :
(a) Zymase
(b) Invertase
(c) Maltase
(d) Diastase.
Answer:
(a) Zymase
Question 3.
In human body carbohydrate is stored :
(a) In the form of glucose
(b) In the form of glycogen
(c) In the form of starch
(d) In the form of fructose.
Answer:
(b) In the form of glycogen
![]()
Question 4.
Change in optical rotation of a freshly prepared solution of sugar after some time is called :
(a) Optical activity
(b) Inversion
(c) Specific rotation
(d) Mutation.
Answer:
(b) Inversion
Question 5.
Formula of most familiar disachharide is :
(a) C10H18O9
(b) C10H12O10
(c) C18H22O11
(d) C12H22O11.
Answer:
(d) C12H22O11.
Question 6.
The following statement is false in relation to Ribose :
(a) It is a polyhydroxy compound
(b) It is a aldehydic sugar
(c) It contain 6 carbon atoms
(d) It has optical rotation.
Answer:
(c) It contain 6 carbon atoms
Question 7.
How many subunits are present in haemoglobin :
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 4
(d) 5.
Answer:
(b) 3
Question 8.
Starch is polymer of :
(a) Glucose
(b) Sucrose
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Glucose
Question 9.
Which sugar is present in maximum amount in human blood :
(a) Fructose
(b) d – glucose
(c) Sucrose
(d) Lactose.
Answer:
(b) d – glucose
Question 10.
Element present in vitamin B12 is :
(a) Pb
(b) Zn
(c) Fe
(d) Co.
Answer:
(d) Co.
Question 11.
Amount of glucose in blood is determined by :
(a) Tollen’s reagent
(b) Benedict’s solution
(c) Alkaline iodine solution
(d) Bromine water.
Answer:
(b) Benedict’s solution
Question 12.
Vitamin B, is : (MP2014)
(a) Riboflavin
(b) Cobaltamine
(c) Thiamine
(d) Pyrimidine.
Answer:
(c) Thiamine
Question 13.
Deficiency of Vitamin C leads to :
(a) Scurvy
(b) Rickets
(c) Pyorrhoea
(d) Anaemia.
Answer:
(a) Scurvy
Question 14.
Most effective energy reservoir in all living cells is :
(a) A.M.P.
(b) A.T.P.
(c) A.D.P.
(d) U.D.P.
Answer:
(b) A.T.P.
Question 15.
Disaccharide present in milk is :
(a) Sucrose
(b) Lactose
(c) Maltose
(d) Cellulose.
Answer:
(b) Lactose
![]()
Question 16.
Which is not glyceroid : (MP2018)
(a) Fat
(b) Oil
(c) Phospholipid
(d) Soap.
Answer:
(d) Soap.
Question 17.
Which is not found in R.N.A.: (MP 2016)
(a) Thymine
(b) Uracil
(c) Adenine
(d) Guanine.
Answer:
(a) Thymine
Question 18.
Deficiency of which vitamin causes Rickets :
(a) Vitamin C
(b) Vitamin B
(c) Vitamin A
(d) Vitamin D.
Answer:
(d) Vitamin D.
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks :
- By the oxidation of glucose ……………… molecules of ATP are produced.
- The breaking of complex molecules in organisms is known as ………………
- In hyperglycemia the amount of ……………… in blood increases.
- Deficiency of ……………… leads to eye disease.
- Deficiency of iodine leads to ……………… disease.
- Blood ……………… the temperature of the entire body.
- ……………… hormone balances the amount of sugar in blood.
- ……………… is responsible for the clotting of blood.
- Denaturation does not affect the ……………… structure of protein.
- Protein is a polymer of ……………… (MP 2018)
- ……………… is the basic unit of protein.
- ……………… is not present in D.N.A.
- Haemoglobin is a ……………… compound of iron.
- Oils and fats obtained from plants and animals (organisms) are called ………………
Answer:
- 38
- Catabolism
- Sugar
- Vitamin A
- Goitre
- Balance
- Insulin
- Vitamin K
- Primary
- Amino acids
- Amino acid
- Uracil
- Complex
- Lipids.
Question 3.
(A) Match the following :
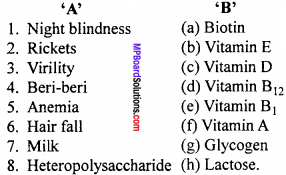
Answer:
- (f)
- (c)
- (b)
- (e)
- (d)
- (a)
- (h)
- (g)
Question 4.
Answer in one word/sentence :
- Write the chemical name of Vitamin C.
- Tell the source of Vitamin K.
- Is responsible for clotting of blood?
- Which bond links amino acids together?
- How many amino acids are synthesized by human body?
- Cellulose is a linear polymer of which glucose?
- In RNA molecule which pyrimidine is present in place of Thymine?
- Lactose on hydrolysis gives.
- Glucose contains Pyranose ring whereas Fructose contain.
- In polysaccharides, monosaccharide units are linked to each other by which bond?
- Which protein helpful for clotting of blood known as? (MP 2018)
- Write one example of Monosaccharide Carbohydrate.
- What is the name of Disaccharides sugar present in milk?
Answer:
- Ascorbic acid
- Green leafy vegetables
- Vitamin K (Phylloquinone)
- Peptide bond
- Ten
- β – glucose
- Uracil
- Glucose and Lactose
- Furanose ring
- Glycosidic
- Fibrinogen
- Glucose or fructose
- Lactose.
Biomolecules Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write the reaction of hydrolysis of sucrose.
Answer:
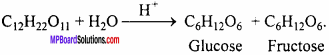
Question 2.
What type of compounds are bases?
Answer:
Bases are heterocyclic compounds.
Question 3.
What is the formula of peptide bond?
Answer: Formula of peptide bond is – CO – NH -.
Question 4.
Which are the main biomolecules found in the biological system?
Answer:
Carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids and lipids etc. are found in the biological system.
![]()
Question 5.
What are oligosaccharides?
Answer:
Carbohydrates that yield 2 to 10 oligosaccharides monosaccharide units are called oligosaccharides.
Question 6.
Write two examples of fibrous protein.
Answer:
Keratin and myosin are the examples of fibrous protein.
Question 7.
What are biomolecules?
Answer:
Molecules which take part in the formation of living system are known as bio – molecules. Like : Proteins, carbohydrates.
Biomolecules Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Where does the water present in the egg go after boiling the egg? (NCERT)
Answer:
When egg is boiled, the denaturation of protein and then coagulation takes place probably through H – bonding. Water present in the egg gets absorbed or adsorbed during denaturation and disappears. In this process, the globular protein in egg changes to insoluble fibrous protein.
Question 2.
Why cannot vitamin C be stored in our body? (NCERT)
Answer:
Vitamin C is soluble in water. It cannot be stored in our body because it is easily excreted in urine.
Question 3.
What are proteins?
Answer:
The word protein is derived from the Greek word protious (Protious = to take the first) i.e. first or very important. Proteins are high molecular mass nitrogen containing complex organic compounds found in the protoplasm of all animal and plants.
Chemically protein is the condensation polymer of α – amino acid.
Question 4.
What are essential and non – essential amino acids? Give two examples of each type. (NCERT)
Answer:
Essential amino acids:
The amino acids which our body cannot make and must be obtained through diet.
Examples : Valine, Isoleucine, Arginine, Lysine, Threonine etc.
Non – essential amino acids:
These are the amino acids which our body can make.
Examples : Glycine, Alanine, Glutamic acid, Aspartic acid, Glutamine, Serine etc.
Question 5.
What are the common types of secondary structure of proteins? (NCERT)
Answer:
The conformation of polypeptide chain assumed as a result of hydrogen bonding is called secondary structure of proteins. The two types of secondary structures are α – helix and β – pleated sheet structure. (For detail refer your NCERT text – book.)
Question 6.
What is the effect of denaturation on the structure of proteins? (NCERT)
Answer:
During denaturation, 2° and 3° structures of proteins are destroyed but 1° structure remains intact. As a result of denaturation, the globular proteins (soluble in H2O) are converted into fibrous proteins (insoluble in H2O) and their biological activity is lost. The coagulation of egg white on boiling is a common example of denaturation.
Question 7.
Differentiate between globular and fibrous proteins. (NCERT)
Answer:
Differences between globular and fibrous protein :
Globular protein:
- They have coiled ball like structure.
- They have three – dimensional structure.
- They are soluble in water and aq. solution of salt and base.
- These proteins are inactive towards temperature and pH value.
Fibrous protein:
- These molecule have long threads like structure.
- They have sheet like structure.
- These are insoluble in water.
- Fibrous protein are active towards temperature and pH value.
Question 8.
What are monosaccharides? (NCERT)
Answer:
Monosaccharides are the carbohydrates which cannot be hydrolysed further to give simpler units of polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones.
Question 9.
What are disaccharides? Write general formula of disaccharides.
Answer:
Disaccharides are sugar which are formed by combination of two monosaccharides by removal of one molecule of water. Both monosaccharides are of hexose type in which one unit is glucose. Thus, disaccharides are of aldose – aldose or aldose – ketose type. General formula of disaccharides is C12H22O11.
Example : Sucrose, maltose, lactose etc.
Question 10.
What is the basic structural difference between starch and cellulose? (NCERT)
Answer: Starch consists of two components : amylose and amylopectin. Amylose is a long linear polymer of 200 – 1000 α – D – (+) glucose units held by C1 – C4 glycosidic linkage. It is soluble in water. Amylopectin is a branched chain polymer of α – D – (+) glucose linkage whereas branching occurs by C1 – C6 glycosidic linkage. It is insoluble in water.
On the other hand cellulose is a straight chain polysaccharide composed only of β – D – (+) glucose units which are formed by glycosidic linkage between C1 of one glucose unit and C4 of next glucose unit.
Question 11.
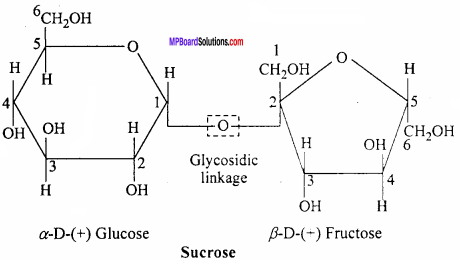
What do you understand by the term glycosidic linkage? (NCERT)
Answer:
The oxygen (ethereal) linkage through which two monosaccharide units are joined together by the loss of a water molecule to form a molecule of disaccharide is called glycosidic linkage. For example, sucrose (a disaccharide) is composed of C1 of α – glucose and C2 β – fructose through the glycosidic linkage.
Question 12.
What is glycogen? How is it different from starch? (NCERT)
Answer:
1. The carbohydrates are stored in animal body as glycogen. It is present in liver, muscles and brain. Enzymes break the glycogen down to glucose when the body needs glucose.
2. Glycogen is more highly branched than amylopectin (starch) glycogen chain consist of 10 – 14 glucose units, whereas amylopectin (starch) glycogen chain consist of 20 – 25 glucose units.
![]()
Question 13.
Write two Differences between α – Amino acid and Protein.
Answer:
Differences between α – Amino acid and Protein :
α – Amino acid:
- They are simple compounds having amino and Carboxylic acid group.
- On combining amino acid gives dipeptide, polypeptide and then protein. example glucose, lysine etc.
Protein:
- Proteins are complex nitrogenous compounds.
- Protein on hydrolysis gives amino acid. example Haemoglobin, casein etc.
Question 14.
What are carbohydrates? Which unit of carbohydrate provide energy to human body?
Answer:
Carbohydrates are compound of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. General formula of carbohydrate is where x and y are integers. These compounds have ratio of hydrogen and oxygen 2 : 1 like water (H2O). Therefore the name of these compounds is given carbohydrates. Examples of carbohydrates are glucose (C6H12O6), fructose (C6H12O6), sucrose (C6H12O6) etc.
Glucose is the unit of carbohydrates which is responsible to provide energy. Glucose decomposes slowly with the help of oxydase enzyme present in the body into CO2 and water. Energy is released in this process.
![]()
Question 15.
Define polysaccharides. Give examples also.
Answer:
Polysaccharides are natural isomers which have molecular weight upto many lacks, general formula of polysaccharides is (C6H10O5)nwhere value of n is from 12 to thousands. These are complex material which are formed by condensations of mono-saccharides. These compounds contain glycocydic bonds.
Example : Starch, cellulose etc.
Question 16.
What is invert sugar?
Answer:
Cane – sugar is dextro – rotatory [D or +] which gives equimolar mixture of monosaccharides. This mixture is laevorotatory [L or -]. Hence the mixture of glucose and fructose obtained as a result of hydrolysis of cane sugar is called as invert sugar.
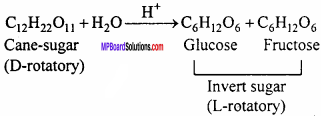
Question 17.
Define the following as related to proteins :
- Peptide linkage
- Primary structure and
- Denaturation.
Answer:
1. Peptide linkage:
A peptide bond is an amide linkage formed between – COOH group of one α – amino acid and NH2 group of the other α – amino acid by loss of a molecule of water. It units two amino acids unit in a peptide bond (molecule).
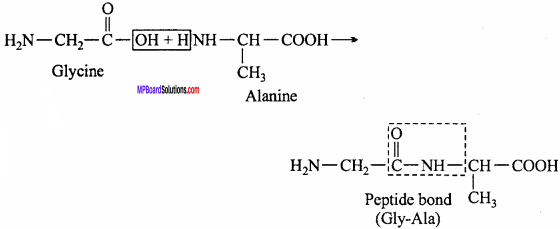
2. Proteins are the polymers of aramino acids. These polymers (also known as polypeptide) consist of amino acids linked with each other in a specific sequence. This sequence of amino acids is known as the primary structure of proteins. Any change in this sequence of amino acids (i.e., primary structure) creates a different proteins.
3. A process that changes the physical and biological properties of proteins without affecting the chemical composition of proteins is called denaturation. The denaturation is caused by certain physical and chemical treatment such as changes in pH, temperature, presence of somegalts or certain chemical agents.
Question 18.
Give the names and functions of any four proteins.
Answer:
Proteins and their functions :
- Haemoglobin : Transport of oxygen from lungs to different tissues of body.
- Myosin : For motion of muscles
- Pepsin : As a catalyst in bio-chemical reactions
- Keratin : Present in hairs, nails and teeth.
Question 19.
What are nucleic acids? Mention their two important functions. (NCERT)
Answer:
Nucleic acids are long chain polymers of nucleotides. They are also called poly-nucleotides. Nucleic acids are mainly of two types, the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA).
Functions :
1. DNA is responsible for transmission of hereditary effects from one generation to another. This is due to unique property of replication, during cell division and two identical DNA strands are transferred to the daughter cells.
2. DNA and RNA are responsible for synthesis of all proteins needed for the growth and maintenance of our body. Actually, the proteins are synthesized by various RNA molecules (m – RNA and f – RNA etc.) in the cell but the message for the synthesis of a particular protein is present in DNA.
Question 20.
What is the difference between a nucleoside and a nucleotide? (NCERT)
Answer:
A nucleoside contains only basic component of nucleic acids namely a pentose sugar and a nitrogenous base. A nucleotide contains all the three basic components of nucleic acids namely a phosphoric acid group, a pentose sugar and a nitrogenous base.
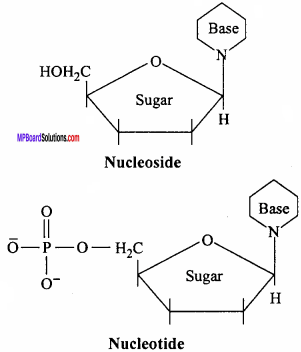
Question 21.
The two strands in DNA are not identical but are complementary. Explain. (NCERT)
Answer:
The two strands in DNA molecule are held together by hydrogen bonds between purine base of one strand and pyrimidine base of the other and vice – versa. Because of different sizes and geometries of the bases, the only possible pairing in DNA are G (guanine) and C (cytosine) through three H – bonds i.e., (C = G) and between A (adenine) and T (thiamine) through two H – bonds i.e., (A = T) (for figure refer your NCERT text – book). Due to this base pairing principle, the sequence of bases in one strand automatically fixes the sequence of bases in the other strand. Thus, the two strands are complimentary and are not – identical.
Question 22.
Write the important structural and functional differences between DNA and RNA. (NCERT)
Answer:
Differences between DNA and RNA:
DNA :
- Occurs mainly in the nucleus of the cell.
- It contains the sugar deoxyribose.
- Does not contain nitrogenous base, uracil.
- It has a double strand helix.
- It is responsible for the transmission of heredity character.
- Alkaline hydrolysis is quite slow.
- Ratio A/T = 1 and G/C = 1.
RNA:
- Occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell.
- It contains the sugar ribose.
- Does not contain nitrogenous base thymine.
- It has double as well as single strand helix.
- It helps in protein biosynthesis.
- Alkaline hydrolysis takes place readily.
- Such ratio is not present.
Question 23.
How are vitamins classified? Name the vitamin responsible for the co – agulation of blood. (NCERT)
Answer:
On the basis of solubility in water or fat, the vitamins are generally classified into two types:
1. Water soluble vitamins:
These include vitamin B – complex. (B1, B2, B3, B4, B6, B12 and nicotinic acid etc.) and vitamin C etc.
2. Fat soluble vitamins:
These include vitamins A, D, E and K. Liver cells are rich in fat soluble vitamins. Vitamin K is responsible for coagulation of blood.
![]()
Question 24.
What happens when protein is denatured ?
Or, Explain the denaturation of protein. (MP 2016)
Answer:
Denaturation of Protein:
Disruption of tertiary structure of protein is called denaturation. These reactions take place by heating in in presence of acids or highly concentrated salts or heavy metals. Denauration does not affect the primary structure of protein. Denaturation takes place in the rearrangement of secondary and tertiary structures. As a result of this, protein losses its biological actvity.
During denaturation the protein molecule uncoils fro an ordered and specific conformation into a more disordered conformation. Denaturation takes place when proteins are heated or treated with acids, bases, alcohols, KI, urea, acetone etc. or when exposed to UV or X – ray radiations. Denaturation is of two types :
- Reversible and
- Irreversible.
Reversible denaturation of proteins takes place in presence of denaturating agents like salts. But on removal of denaturating agent protein acquires its original structure. In irreversible denaturation protein cannot change to its original state. For example, white of example, i.e., yolk is a globulin and soluble protein. On putting it into boiling water it changes to white rubber like solid which is insoluble in water. Similarly, addition of an acid generally lemon juice to milk results in denaturation and milk coagulates to form cheese.
Question 25.
Write functions and sources of the following bio – molecules/elements : (MP 2011)
- Protein
- Carbohydrates
- Fat
- Calcium.
Answer:
1. Protein : Formation of new tissues and their repairing with the body.
Source : Milk, egg, meat, cheese, fish.
2. Carbohydrates : Carbohydrates provides energy to the body.
Source : Rice, potato, fruits, cane sugar etc.
3. Fats : They provides energy to the body.
Source : Ghee, oils, milk, egg. etc.
4. Calcium : Increase the bones and teeth.
Source : Green leafy vegetables, milk.
Biomolecules Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write a note on Nucleic acid.
Answer:
Nucleic acid:
It is found in nucleus of the cell. It has large amount of phosphorus. Nucleic acid are polynucleotides which is formed by the combination of various nucleotide units.
Each nucleotide is formed by three chemical components:
- Phosphate group
- Pentose ribose sugar or De – oxyribose
- Heterocyclic base : Like derivative of pyrimidine (Thiamine, uracil, cytosine) and derivatives of purine (Adenine and Guanine).
Nucleic acids are of two types :
- DNA : De – oxyribonucleic acid.
- RNA : Ribonucleic acid.
Components of DNA:
(a) De – oxyribose sugar molecule
(b) Phosphoric acid molecule
(c) Nitrogenous base : It is of two types :
- Pyrimidine base : It includes Cytosine (C) and Thymine (T)
- Purine base : It includes Adenine (A) and Guanine (G)
Components of RNA:
RNA contains Ribose and nitrogen base like Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Uracil (U) and Cytosine (C).
Question 2.
What are carbohydrates? Write its classification and four main functions.
Answer:
Definition:
Optically active polyhydroxy aldehydes or ketones or substances which yield these on hydrolysis are known as carbohydrates.
Example : Glucose, starch, cellulose, sucrose etc.
Classification of Carbohydrate:
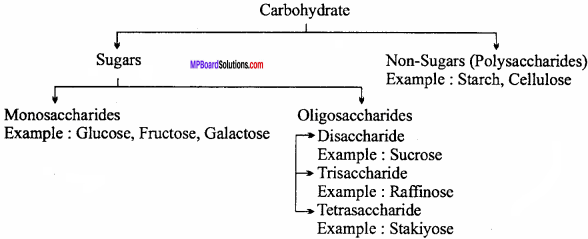
Functions of Carbohydrates:
1. It is the main structural component of cell.
2. It acts as a bio – fuel and provides energy to organisms for doing work.![]()
3. Carbohydrate is stored in the liver as glycogen, which hydrolysis to provide the energy required.
4. Cellulose is found in grass and plants which provide energy to animals grazing grass because these animals possess specific enzymes which hydrolyses cellulose to glucose.
![]()
Question 3.
Write the functions of the following vitamins : (MP 2014)
- Vitamin – A
- Vitamin – D
- Vitamin – E
- Vitamin – K.
Answer:
Functions caused by the above Vitamins :
- Vitamin – A : For vision and growth develops resistance against diseases.
- Vitamin – D : For bones, control of metabolism of calcium and phosphorus.
- Vitamin – E : Virility in man and reproduction.
- Vitamin – K : Coagulation of blood.
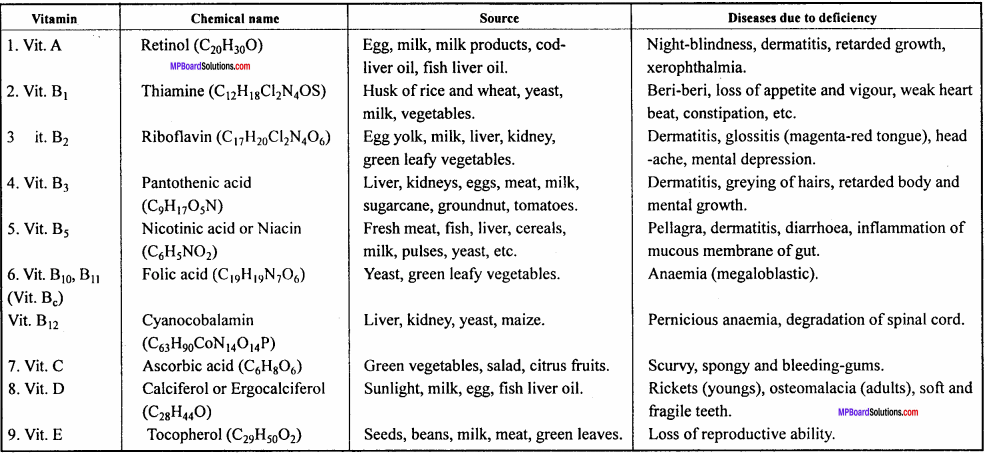
Question 4.
Give the diseases caused by ascorbic acid, thiamine retinol and nicotinic
Or,
Give the source and diseases caused by Vitamin A, B, C and D.
Answer:
Name of Vitamins deficiency diseases are given in the ahead chart:
Chemical names of Vitamins , their sources and diseases due to deficiency:
Question 5.
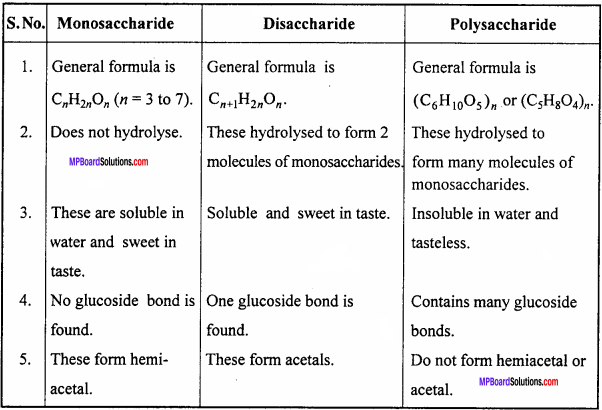
Give differences between monosaccharide, disaccharide and polysaccharide.
Answer:
Difference between monosaccharide, disaccharide and polysaccharide :