MP Board Class 12th Chemistry Important Questions Chapter 13 Amines
Amines Important Questions
Amines Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Choose the correct answer :
Question 1.
A compound which gives oily nitrosoamine with nitrous acid at low temperature:
(a) Methyl amine
(b) Dimethyl amine
(c) Trimethyl amine
(d) Triethyl amine.
Answer:
(b) Dimethyl amine
Question 2.
Which of the following has strongest basic character :
(a) C6H5NH2
(b) (CH3)2NH
(c) (CH3)3NH
(d) NH3.
Answer:
(b) (CH3)2NH
Question 3.
Benzene diazonium chloride gives on hydrolysis :
(a) Chlorobenzene
(b) Phenol
(c) Alcohol
(d) Benzene.
Answer:
(b) Phenol
![]()
Question 4.
In the reaction C6H5CHO + C6H5NH2 → C6H5N = CHC6H5 + H2O + C6H5N = CHC6H5 is known as :
(a) Aldol
(b) Schiff’s reagent
(c) Schiff’s base
(d) Benedict reagent.
Answer:
(c) Schiff’s base
Question 5.
Nitrobenzene gives N – phenyl hydroxyl amine when it reacts with :
(a) Sn/HCl
(b) C6H5CH2NH – CH3
(c) Zn/NaOH
(d) Zn/NH4Cl.
Answer:
(c) Zn/NaOH
Question 6.
Which of the mixture when reacts with ale. KOH known as Carbylamine reaction :
(a) Chloroform and Ag powder
(b) Trihalogenated methane and primary amine
(c) Alkyl trihalide and primary amine
(d) Alkyl cyanide and primary amine.
Answer:
(b) Trihalogenated methane and primary amine
Question 7.
Which of the following gas is responsible for Bhopal gas tragedy in 1984 :
(a) CH3 – N = C = O
(b) CH3 – N = C = S
(c) CHCl3
(d) C6H5COCl.
Answer:
(a) CH3 – N = C = O
Question 8.
Aniline reacts with cold nitrous acid (NaNO2 + HCl) and gives :
(a) C6H5 – OH
(b) C6H5 – N, – Cl
(C) C6H5 – NO2
(d) C6H5 – Cl.
Answer:
(b) C6H5 – N, – Cl
Question 9.
The product of mustard oil reaction is : (MP 2013,16)
(a) Alkyl isothiocyanate
(b) Dithiocarbonamide
(c) Dithioethyl acetate
(d) Thioether.
Answer:
(c) Dithioethyl acetate
Question 10.
A nitrogen containing compound, on heating with chloroform and alcoholic KOH gives vapours of disagreeable odour, the compound can be :
(a) Nitrobenzene
(b) Benzamide
(c) N, – N – dimethyl aniline
(d) Aniline.
Answer:
(d) Aniline.
Question 11.
Ethyl amine reacts with nitrous acid to form :
(a) Ammonia
(b) Nitrous oxide
(c) Ethane
(d) Nitrogen.
Answer:
(d) Nitrogen.
Question 12.
Oil of mirbane is :
(a) Aniline
(b) Nitrobenzene
(c) p – Nitroaniline
(d) p – Aminoazobenzene.
Answer:
(b) Nitrobenzene
Question 13.
Aniline is purified by :
(a) Steam distillation
(b) Vacuum distillation
(c) Simple distillation
(d) Solvent extraction.
Answer:
(a) Steam distillation
![]()
Question 14.
Amine which will not react with acetyl chloride is :
(a) CH3 – NH2
(b) (CH3)2NH
(c) (CH3)3N
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) (CH3)3N
Question 15.
![]()
(a) Gattermann’s reaction
(b) Sandmeyer’s reaction
(c) Wurtz’s reaction
(d) Frankland reaction.
Answer:
(b) Sandmeyer’s reaction
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks :
- With transition metal ion amine establish co – ordination and form …………….
- By reduction cyanides form ……………. and isocyanides form
- Benzoic acid reacts with hydrazoic acid to form …………….
- All aliphatic amines are more ……………. than ammonia.
- 1° and 2° amine react with Grignard reagent to form …………….
- C6H6 – COOH + ……………. → C6H5NH2 + N2 + CO2
- Trinitrotoluene is an ……………. substance. (MP 2011)
- Methyl amine is ……………. basic than ammonia. (MP 2011,15)
- Aromatic amines are ……………. in water.
- Amines are benzolate in presence of NaOH. This reaction is called …………….
- By reaction with nitrous acid 1° amine forms alcohol and 2° amine form …………….
- Reaction of 2° amine with nitrous acid represent …………….
- Basic nature of amine is due to presence of ……………. on nitrogen atom. (MP 2009)
- Primary amine on heating with ……………. and ……………. form alkyl isocyanides. (MP 2009)
- Mixture of T.N.T. and ammonium nitrate is known as …………….
- On reacting aniline with HCl and NaNO2 at 0°C temperature benzene diazonium chloride is formed. This is called ……………. reaction.
- On heating alkyl isocyanide at 250°C ……………. is formed. (MP 2014)
Answer:
- Complex ion
- Primary amine, secondary amine
- Aniline
- Basic
- Alkane
- N3H
- Explosive
- More
- Insoluble
- Schotten Baumann
- Nitrosamine
- Libermann nitroso test
- Lone electron pair
- Chloroform and caustic soda
- Amatol
- Diazotisation
- Alkyl isocyanate
Question 3.
Match the followings:
I.
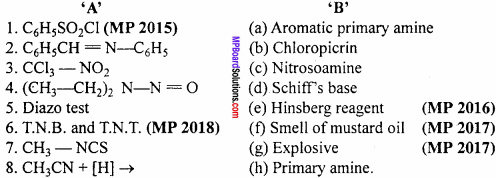
Answer:
- (e)
- (d)
- (b)
- (c)
- (a)
- (g)
- (f)
- (h)
II.

Answer:
- (e)
- (d)
- (a)
- (c)
- (b)
III.
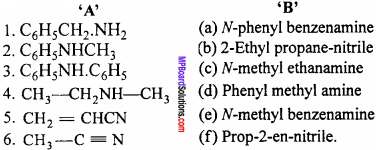
Answer:
- (d)
- (e)
- (a)
- (c)
- (f)
- (b)
Question 4.
Answer in one word/sentence:
- Why aniline turns blackish brown in open air? (MP 2013)
- Tertiary amine does not acetanilised, why?
- Which isomer of C3H9N is least basic and having lowest b.p.?
- Which amine gives diazotization reaction?
- The compound obtained when primary aromatic amine when heated with CHCl3 and ale. KOH.
- Secondary amine can be identified by.
- Primary nitroalkane reacts with nitrous acid to form which compound?
- What is the nature of amines? (MP 2010)
- Write the name and formula of Hinsberg’s reagent. (MP 2011)
- What is nitrating mixture?
- Nitrobenzene is known as.
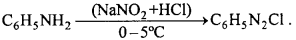
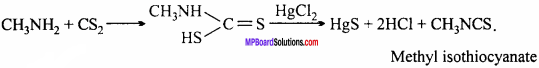
Write the name of reaction.- What is the name of reaction for preparation of methyl isocyanide?
- What do 1° and 2° amine form on reaction with phosgene?
- Write the name of reaction :
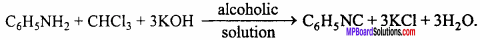
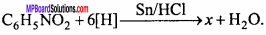
- What is obtained by reacting amine with chloroform?
- In which form is amine used in organic synthesis ?
- What does ethylamine form on oxidation in the presence of KMnO4?
- On adding Br2 water in aqueous solution of C6H5NH2 which precipitate is obtained?
- Which amine is obtained by the reduction of cyanide in the presence of Pt or Ni?
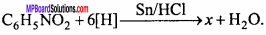
Write the formula of x.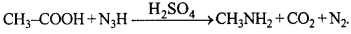
Write the formula of x.- Write the formula of Benzene diazonium chloride.
Answer:
- Aniline gets oxidised by air
- Active hydrogen is absent
- Tertiary amine
- All primary aromatic amines
- Phenyl isocyanide
- By Liebermann’s nitroso test
- Nitrolic acid
- Basic
- Benzene sulphonyl chloride (C6H5SO2Cl)
- Conc. HNO3 + conc. H2SO4
- Oil of mirbane
- Diazotisation
- Carbyl – amine reaction
- Substituted urea
- Carbylamine reaction
- Sand – meyer’s reaction
- Alkyl isocyanide
- Reagent alkane
- Aldehyde
- Symmetrical tribromoaniline
- 1°amine
- C6H5NH2
- Schmidt reaction
- C6H5 – N2 – Cl.
Amines Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is Hinsberg reagent?
Answer:
Aryl sulphonyl chloride like Benzene sulphonyl chloride (C6H5SO2Cl) is called Hinsberg reagent.
Question 2.
Which group linked in Aniline increases basic strength?
Answer:
Groups like – OCH3, – CH3 etc. linked in aniline increases the basic strength.
Question 3.
Write the structure of Phthalimide.
Answer:
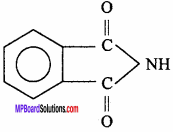
Question 4.
How is the structure of amines and why?
Answer:
Structure of amines is pyramidal because of the presence of lone electron pair on nitrogen.
![]()
Question 5.
What is the use of Benadryl? Tell the functional group present in it.
Answer:
Benadryl is used as an antihistamine and tertiary amine group is present in it.
Question 6.
Why are amines soluble in dilute mineral acids?
Answer:
Amines form ionic crystalline salts in dilute mineral acids.
R – NH2 + HCl > [R – \(\overset { + }{ N }\) H3s]Cl–
Question 7.
Write the formula and IUPAC name of Sulphonic acid.
Answer:

Question 8.
In what are amines found in nature?
Answer:
In nature, amines are found in proteins, vitamins, alkaloids and hormones.
Question 9.
What is the bond angle in trimethyl amine?
Answer:
Bond angle in trimethyl amine (CH3)3N is 108°.
Question 10.
Write the equation of formation of iodobenzene from aniline.
Answer:
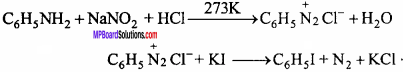
Amines Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Aniline is insoluble in water but soluble in HCl. Explain.
Answer:
Being basic nature, aniline forms soluble salts with strong acids like HCl while with water no such salt is formed. Therefore, aniline is insoluble in water but soluble in HCl.
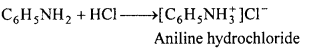
Question 2.
Write a short note on Schotten Baumann reaction.
Answer:
Aromatic acid chloride reacts with phenol and aniline in presence of aqueous NaOH or pyridine. The reaction is known as Schotten Baumann reaction.

Question 3.
How will you convert: (NCERT)
(i) Benzene into aniline
(ii) Benzene into N, N – dimethylaniline
(iii) Cl – (CH2)4 – Cl into hexane – 1, 6 – diamine.
Answer:
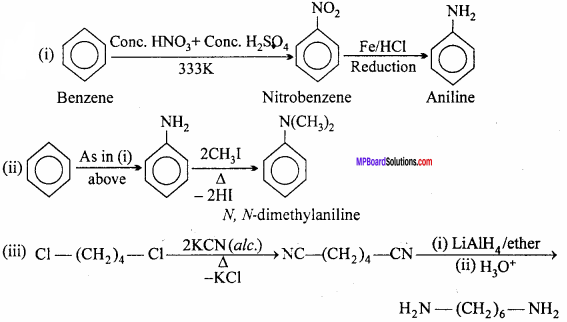
Question 4.
Arrange the following in increasing order of their basic strength: (NCERT)
- C2H5NH2,C6H5NH2,NH3,C6H5CH2NH2 and (C2H5)2NH
- C2H5NH2,(C2H5)2NH,(C2H5)3N, C6H5NH2
- CH3NH2, (CH3)2NH, (CH3)3N, C6H5NH2, C6H5CH2NH2.
Answer:
- C6H5NH2 < NH3 < C6H5CH2NH2 < C2H5NH2 < (C2H5)2NH
- C6H5NH2 < C2H5NH2 < (C2H5)3N < (C2H5)2NH
- C6H5NH2 < C6H5CH2NH2 < (CH3)3N < CH3NH2 < (CH3)2NH.
![]()
Question 5.
Describe a method for the identification of primary, secondary and tertiary amines. Also write chemical equations of the reactions involved. (NCERT)
Answer:
Hinsberg’s test:
This is a excellent test for distinguishing between primary, secondary and tertiary amines. The amine is treated with benzene sulphonyl chloride (Hinsberg’s reagent) in presence of excess of aqueous potassium hydroxide solution. (Refer text for details)
Question 6.
What is Mendius reaction?
Answer:
Reduction of alkyl cyanides by sodium and alcohols yield primary amine. This reaction is called Mendius reaction.
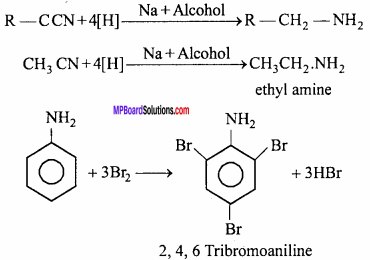
Question 7.
Ethyl amine is more basic than ammonia, why?
Answer:
The value of Ka = 4.5 x 10-4 for ethyl amine and for ammonia it is 1.8 x 10-5. Larger is the Kb value, more basic is the amine and vice – versa. In ethyl amine the availability of lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom increases due to the +I inductive effect of the ethyl group. Hence, this lone pair of electrons can easily accept a proton. This explains why ethyl amine is more basic than ammonia.
Question 8.
Write short notes on :
- Chmidt reaction
- Mustard oil reaction.
Answer:
1. Schmidt reaction:
When hydrazoic acid dissolved in chloroform or benzene, react with mono carboxylic acid in presence of H2SO4 at 55°C, primary amine is obtained.
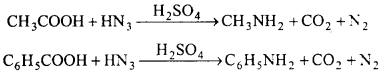
Mustard oil reaction:
When aliphatic primary amine is heated with carbon disulphide and HgCl2, alkyl isothiocyanate is formed, which has smell like mustard oil. Therefore, this reaction is called mustard oil reaction.
Question 9.
Give a Hinsberg method to identify primary, secondary and tertiary amines.
Answer:
Hinsberg method:
This method is capable to differentiate primary, secondary and tertiary amines. Amines are heated with benzene sulphonyl chloride (Hinsberg reagent) and various products are obtained.
1. Primary amine : These form sulphonamide which are soluble in KOH.
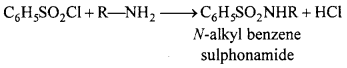
2. Secondary amine : Secondary amine also form sulphonamide which are insoluble in KOH.
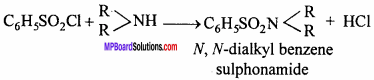
3. Tertiary amine : Tertiary amine does not react.
C6H5SO2Cl + R3N → No reaction.
Question 10.
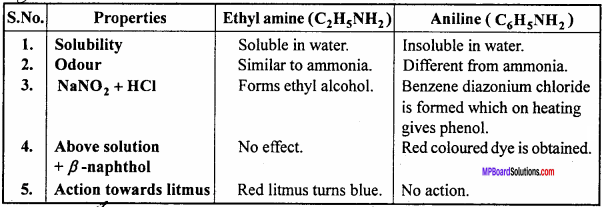
Write the points of difference between Ethyl amine and Aniline.
Answer:
Differences between Ethyl amine and Aniline:
Question 11.
Why aniline is less basic than ethyl amine?
Answer:
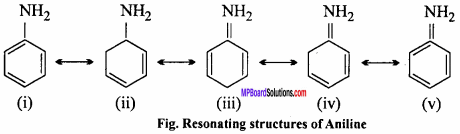
Aniline is less basic than ethyl amine as due to resonance of benzene nucleus, the lone pair of electron of nitrogen atom is attracted towards nucleus and gets delocalised in the ring Thus, electron pair is liberated with difficulty in aniline than ethyl amine. Hence, its basic property is less than ethyl amine.
The delocalisation of electron as a result of resonance is shown as follows :
Question 12.
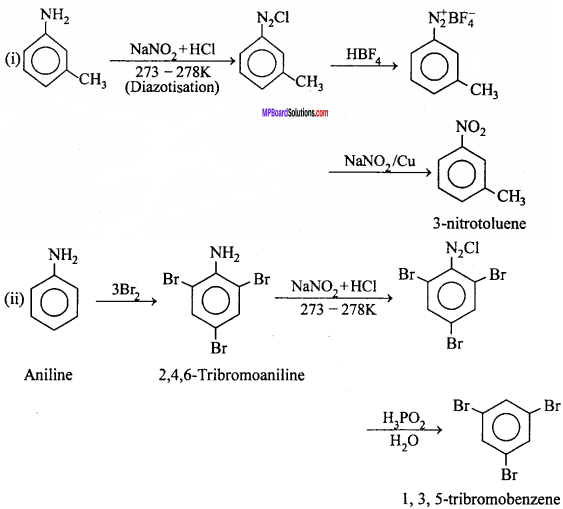
Convert: (NCERT)
- 3 – Methylaniline into 3 – nitrotoluene
- Aniline into 1,3,5 – tribromobenzene.
Answer:
Amines Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write reduction reactions of nitro – benzene :
- In acid medium
- Neutral medium
- In basic medium.
Or,
Describe reduction reactions of nitro – benzene in different conditions.
Answer:
Reduction of Nitro – benzene:
Nitro – benzene is readily reduced. This gives different compounds under different conditions depending upon the pH of the medium and the nature of the reducing agent. The reduction takes place in three steps :
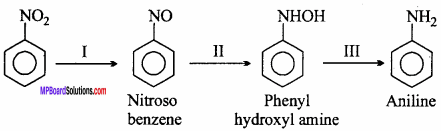
(a) Acidic medium : When reduced with Sn + HCl or Fe + HCl, gives aniline.
![]()
(b) Neutral medium : When reduced with aluminium mercury couple or zinc dust and ammonium chloride, phenyl hydroxyl amine is formed.
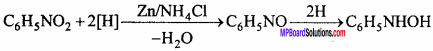
(c) In basic medium (Alkaline medium):
(i) Reduction with alkaline sodium arsenite : Azoxy benzene is formed.
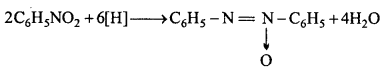
(ii) Reduction with zinc dust and caustic soda : Hydrozo benzene is formed.
![]()
Question 2.
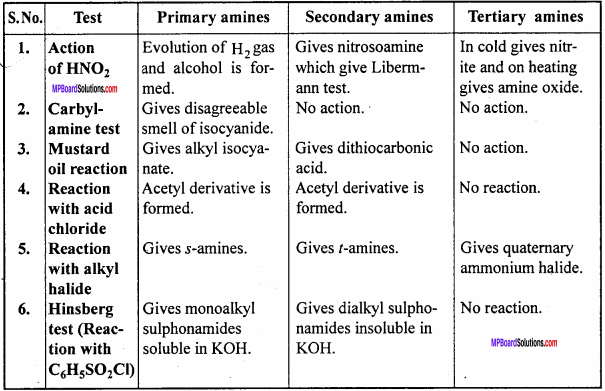
Distinguish among p, s and t amines under the following points:
- Reaction with HNO2
- Carbyl amine reaction
- Mustard oil reaction
- Reaction with acid halide
- Reaction with alkyl halide
- Reaction with C6H5SO2Cl
Answer:
Differences among p, s and t amines :
Question 3.
Explain the laboratory method of preparation of ethyl amine under the following heads:
- Procedure
- Equation of reaction
- Diagram
- Physical properties.
Answer:
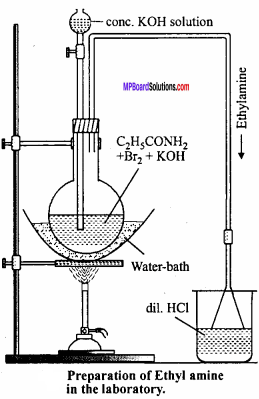
Laboratory method of preparation of ethyl amine:
In laboratory ethyl amine is prepared by Hofmann Bromoamide reaction. In this process reaction of propanamide with bromine and caustic potash solution takes place. All steps in the process are following:
C2H5CONH2 + Br2 → C2H5CONHBr + HBr
KOH + HBr → KBr + H2O
C2H5CONHBr + KOH → C2H5NCO + KBr + H2O
C2H5NCO + 2KOH → C2H5NH2 + K2CO3
C2H5CONH2 + Br2 + 4KOH → C2H5NH2 + 2KBr + K2CO3 + 2H2O
Procedure:
In a round bottom distillation flask equivalent quantities of bromine and propanamide is taken and 10% KOH solution is added in it. Now 50% KOH solution is added in excess and the flask is heated on water bath upto 57.67°C. When the solution becomes colourless, ethyl amine starts to be distilled which is absorbed in dil. HCl.
Physical properties:
It is a colourless liquid with an odour like ammonia which is soluble in water and organic solvent. It is a combustible substance. Its boiling point is 19°C.
![]()
Question 4.
Write laboratory method of preparation of aniline. Give all chemical equations of this process.
Or,
Describe commercial method of preparation of aniline.
Answer:
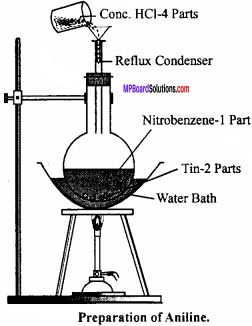
Laboratory Method for the Preparation of Aniline:
Aniline is prepared in the laboratory by the reduction of nitro – benzene with tin and hydrochloric acid.
C6H5NOZ +6[H] → C6H5NH2 + 2H2O
Experiment:
Nitrobenzene (20 g) and granulated tin (40 g) are taken in a round – bottom flask and a reflux condenser is fitted. Now hydrochloric acid (100 ml) is added in small amounts (10 ml at a time). The flask is shaken after each addition of acid and the temperature is not allowed to rise above 90°C. The flask is heated on a water bath till the smell of nitro – benzene disappears. On cooling the flask, a solid mass of molecular formula
(C6H5NH2.HCl)2.SnCl4 separates out.
Sn + 4HCl → SnCl4 +4H
C6H5NO2 + 6[H] → C6H5NH2 + 2H2O
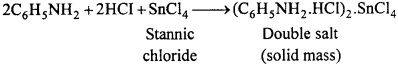
The solid mass is treated with concentrated NaOHsolution. So that a clear alkaline solution is obtained. Aniline is liberated and floats as a dark brown coloured oil.
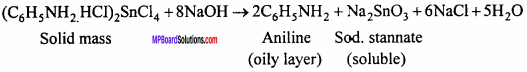
From this aniline is obtained by steam distillation.
Question 5.
Write down the chemical equation representing preparation of nitrobenzene in laboratory and give the following chemical reaction of nitrobenzene:
- Nitration
- Sulphonation.
Answer:
Preparation of nitrobenzene in laboratory : Nitrobenzene is prepared in laboratory by treating benzene with a mixture of cone. HNO3and cone. H2SO4at 60°C.
![]()
Reaction of nitrobenzene:
1. Nitration : Nitrobenzene forms m – dinitrobenzene when heated with fuming HNO3 and cone. H2SO4.
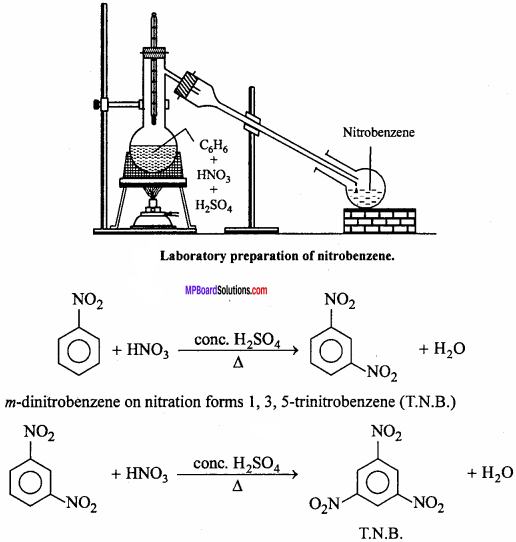
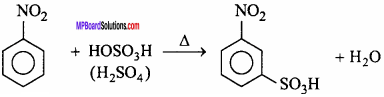
2. Sulphonation : Nitrobenzene forms m – nitrobenzene sulphonic acid on heating with fuming H2SO4.
Question 6.
Write short notes on the following : (NCERT)
- Carbylamine reaction
- Diazotisation
- Hofmann’s bromamide reaction,
- Coupling reaction
- Ammonolysis
- Acetylation
- Gabriel phthalimide synthesis.
Answer:
1. Carbylamine reaction:
Primary aliphatic amine or aniline when warmed with chloroform in presence of alcoholic KOH gives isocyanide or carbylamine, a compound with disagreeable odour. This reaction is known as Carbylamine reaction.
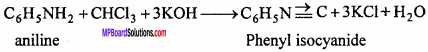
2. Diazotisation:
By action of NaNO2 solution in ice cooled solution of aromatic amine formed inorganic acid, diazonium salts are obtained.
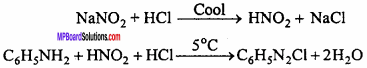
Diazonium salt contains diazo group (- N = N -) therefore, this process is called diazotization.
3. Hofmann’s bromamide reaction:
Primary aliphatic and aromatic amines can be prepared from amides by treatment with Br2 and KOH. The amine formed contains one carbon atom less than the parent amide. Therefore, this method is used for stepping down the series in organic conversion. Due to this reason it is also known as Hofmann degradation.
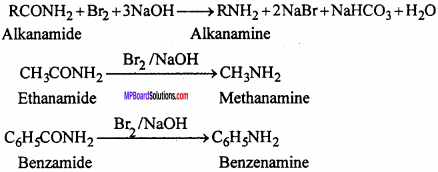
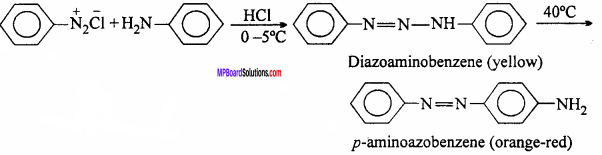
4. Coupling reaction:
Aniline reacts with diazonium chloride at ice cold temperature to giveoright orangered dye.
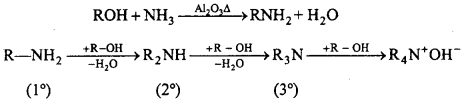
5. Ammonolysis:
It is a process of replacement of either halogen atom in alkyl halides (or aryl halides) or hydroxyl group in alcohols (or phenols) by amino group. The reagent used for ammonolysis is alcoholic ammonia. Generally, a mixture of primary, secondary and tertiary amine is formed.
6. Acetylation:
Aliphatic and aromatic primary and secondary amines react with acid chlorides, anhydrides and esters by nucleophilic substitution reaction. This reaction is considered as replacement of hydrogen atom of – NH2 or >NH group by acyl group.
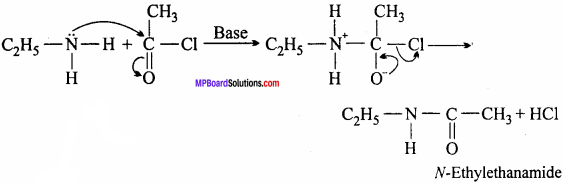
This reaction is known as acylation. The reaction is carried out in the presence of a base stronger than amine like pyridine, which removes HCl so formed and shift the equilibrium towards right hand side. The product obtained by acylation reaction is known as amides.
7. Gabriel phthalimide synthesis:
In this reaction, potassium phthalimide react with alkyl halide to form N – methyl phthalimide which on hydrolysis give primary amine.
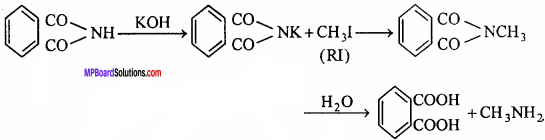
Question 7.
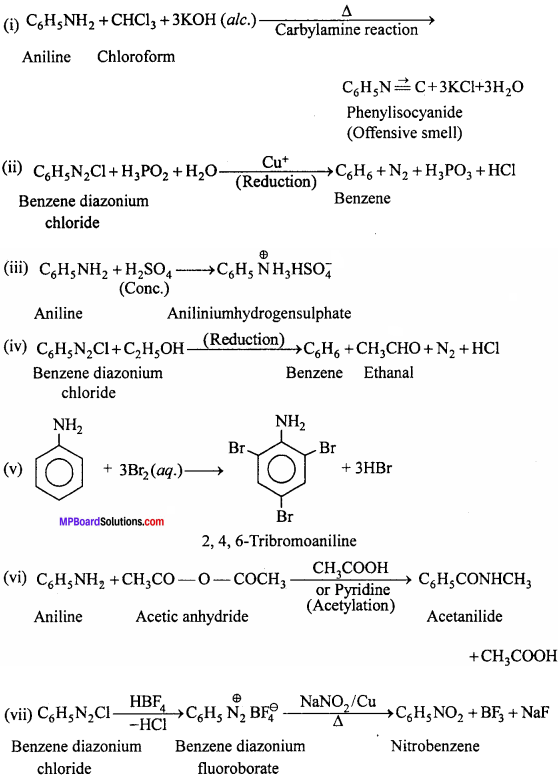
Complete the following reactions
(i) C6H5NH2+ CHCl3+ (alc.)KOH →
(ii) C6H5N2Cl + H3PO2+H2O →
(iii) C6H5NH2+ H2SO4(Conc.) →
(iv) C6H5N2Cl + C2H5OH →
(v) C6H5NH2+Br2(aq) →
(vi) C6H5NH2+ (CH3CO)2O →
(viii) ![]()
Answer: