MP Board Class 12th Economics Important Questions Unit 4 Form of Market and price Determination
Micro Economics Form of Market and price Determination Important Questions
Micro Economics Form of Market and price Determination Objective Type Questions
Questions 1.
Choose the correct answers:
Question 1.
Main feature of perfectly competitive market is:
(a) Uniform price
(b) Homogeneous product
(c) Large number of buyers and sellers
(d) All of the above.
Answer:
(d) All of the above.
Question 2.
The market in which there is free entry and exit is:
(a) Monopolistic competition market
(b) Imperfect competition market
(c) Perfect competitions market
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Perfect competitions market
Question 3.
There is inverse relation between demand and price of goods in:
(a) Only monopoly
(b) Only monopolistic competition
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Only perfect competition.
Answer:
(d) Only perfect competition.
Question 4.
According to which economist “Price of a commodity is determined by the forces of demand and supply”:
(a) Jevons
(b) Valros
(c) Marshall
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Marshall
Question 5.
Not a condition of equilibrium of monopoly firm:
(a) Average revenue = Marginal revenue
(b) Marginal revenue = Marginal cost
(c) Marginal cost curve cuts marginal revenue curve from downwards.
(d) Both (b) and (c).
Answer:
(a) Average revenue = Marginal revenue
Question 6.
Market price is found in:
(a) Short period market
(b) Long period market
(c) Very long period market
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Short period market
Question 7.
Demand curve of a firm is perfectly elastic in:
(a) Perfect competition
(b) Monopoly
(c) Monopolistic competition
(d) Oligopoly.
Answer:
(a) Perfect competition
![]()
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks:
- The price on which demand and supply are equal, is called ………………..
- Price discrimination is possible in ……………….. market.
- Increase in total revenue by the sale of additional unit of the commodity is called ………………..
- If the supply of any good remains unchanged, and with the increase in demand its ……………….. increases.
- In perfect competition market, a firm is a ………………..
- Price ceiling is done by the ………………..
- In the ………………..period demand force is more effective.
- In ………………..market there should be two or more two firms.
- A group of firms is called ………………..
- The market for petrol is ………………..
Answer:
- Normal
- Monopolistic
- Marginal revenue
- Increase
- Price takes
- Government
- Short period
- Oligopoly
- Industry
- International.
![]()
Question 3.
State true or false:
- Market of bricks is provincial.
- Normal price is imaginary.
- Imperfect competition is a practical approach.
- The forces of demand and supply remains in the state of equilibrium for a long period.
- Among the forces of demand and supply, either of the two determines the price of the goods.
- Under perfect competition firms themselves determine the price.
- Under monopolistic competition demand curve is uncertain.
Answer:
- False
- True
- True
- False
- False
- False
- True.
Question 4.
Match the following:

Answer:
- (c)
- (a)
- (e)
- (d)
- (b).
Question 5.
Answer the following in one word / sentence:
- The market was Tomatoes is known as?
- Market price revolves around?
- A perfectly competitive firm in the long period earns which type of profit?
- Who has given importance to time in the determination of price?
- Unusual gain or loss is found in which market competition?
- In practical life which competition is not found?
Answer:
- Very short period
- Normal price
- Normal profit
- Prof. Marshall
- Imperfect competition
- In case of perfect competition.
![]()
Form of Market and price Determination Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is equilibrium price?
Answer:
The price at which the demand and supply of product is equal is called equilibrium point.
Question 2.
What is the effect on equilibrium price when demand and supply change?
Answer:
Changes in demand and supply is a normal process. It directly affects the equilibrium price sometimes demand is more than the supply, and supply sometimes exceeds the demand. Increase or decrease in both can cause a fall in equilibrium price.
Question 3.
What are the causes of changes in demand?
Answer:
Changes in demand can be of many reasons:
- Change in income of the consumer.
- Change in population.
- Change in habits, interest and income of the consumer.
- Change in availability of substitute goods.
- Change in price of related goods.
Question 4.
What are the causes of changes in the supply?
Answer:
Following causes can be responsible for the changes in the supply of a goods.
- Change in the price of raw material. .
- Change in availability of raw material.
- Change in the wages of the laborious
- Change in price of machinery.
- Change in the laws of production.
- Change in the techniques of production.
Question 5.
Define perfect competition.
Answer:
According to Prof. Marshall:
“The more nearly perfect market is the stronger, the tendency for the same price to be paid for the same thing at the same time in all parts of the market.”
Question 6.
What is market price?
Answer:
Market price is also known as short period price which is determined by temporary interaction of demand and supply. It is also known as temporary price.
Question 7.
What is normal price?
Answer:
Normal price is a long-term price of any commodity. It is determined with the interaction of demand and supply. It is an imaginary price and is not found in actual life.
![]()
Question 8.
What is perfect competition?
Answer:
Perfect competition refers to market situation where there are large numbers of ‘buyers and seller’s. They have perfect knowledge about the market. Goods are homogeneous, perfect mobility of the factors of production and one price prevails in the market.
Question 9.
What is the effect of large number of buyers and sellers?
Answer:
In perfect competition, the number of buyers and sellers are very large. Each buyer buys a very small part of the product and is unable to influence the price output or price prevailing in the market. Likewise the supply of an individual seller is Very small in comparison to total supply and thus, he is unable to affect the price policy of the product alone by changing his supply.
Question 10.
Write three features of Monopolistic competition.
Answer:
- There are large number of buyers and sellers selling closely related, but not homogeneous products. Each firm has a limited share/control over the market. Large number of firms leads to competition in the market.
- The products of the sellers are differentiated but are close substitute of one another. The products produced by one firm is different from products produced by other firms.
- There is free entry and exit of firms.
![]()
Question 11.
Why there are very few firms in Oligopoly market?
Answer:
Following reasons show that why few firms exist in Oligopoly:
- Huge set-up costs,
- Patent rights,
- License requirements,
- Control over raw materials, etc,
- Presence of cut throat competition among firms.
Question 12.
In perfect competition situation sellers and buyers have full knowledge about the market. What is its effect?
Answer:
In perfect competition buyers and sellers both have perfect knowledge about the prevailing market condition. Due to homogeneous product, the sellers can not sell the goods on different prices. This is the reason that the buyers and sellers accept the same price.
Question 13.
What do you mean by supply?
Answer:
Supply refers to the quantity of goods available for sale at a given price in a given market at a given time.
Question 14.
What do you mean by contraction of supply?
Answer:
Other factors remaining constant when a decrease in price causes fall in supply, it in called contraction of supply.
Question 15.
What do you mean by price control?
Answer:
Price control means fixation of price by law. At the controlled price quantity demanded in not equal to quantity supplied. The price is fixed by the government below the equilibrium price. Its aim is to make the goods available to poor.
![]()
Question 16.
What do you mean by equilibrium price?
Answer:
The equilibrium price is that price at which its two determinants: Demand and supply are balanced or equal. Thus,
S = D.
Question 17.
What do you mean by explicit cost?
Answer:
Explicit cost refers to all those expenses made by a firm to buy goods directly. They include payment of raw material, taxes, wages, etc.
Question 18.
What do you mean by supported price?
Answer:
The government fixes the prices of several goods higher than their equilibrium price to protect the interest of farmers.
Question 19.
Define Monopoly market or Explain Monopoly.
Answer:
Monopoly is a market situation in which there is a single seller of a single, commodity. In this way, he can control the supply of the goods and also fixes the price according to his own choice.
Question 20.
What to you mean by Oligopoly?
Answer:
In oligopoly, there are few two or three producers or sellers. They deal in either homogeneous or different products. They compromise and form organization. The person or the organization who produces the maximum generally fix the prices.
Question 21.
What do you mean by dumping?
Answer:
When there are excess production the monopolist starts selling his goods at lower rate in other countries or dispose off, the goods it is called dumping.
Question 22.
What do you mean by monopolistic competition?
Answer:
It is the market situation in which there are many sellers of a particular product, but the product of each seller is in same way, differentiated in the minds of consumer from the product of every seller. It is the midway situation between perfect competition and monopoly.
![]()
Form of Market and price Determination Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Distinguish between Market Price and Normal Price.
Answer:
Differences between Market Price and Normal Price:
Market Price:
- Market price is a short term price.
- Market price always fluctuates.
- Market price may be less or more than the cost of production.
- Market price is the real price.
- Demand has got more impact on the determination of price.
- Market price can be fixed for both productive and reproductive goods.
Normal Price:
- Normal price is the long term price.
- Normal price remains stable.
- Normal price is always equal to the cost of production.
- Normal price is imaginary price.
- Supply has more importance in the determination of price.
- Normal price is fixed for reproductive goods only.
Question 2.
Write the characteristics of Market price?
Answer:
It has the following characteristics:
1. Short period price:
Market price is also known as short period price. In it prices will always be fluctuating. It will be of perishable goods and the demand will always influence the price. In this supply will be rigidly fixed. This will be very short period to meet the demand of the goods. Therefore, it is known as short period price.
2. Demand is active:
In the market price only demand will be. active. On the other hand there will be no effect of supply on it because it is passive. If demand increases price will go up and its vice versa. So, the supply is rigidly fixed in it. In other words supply is inelastic. So, in short period the effect of only demand can be seen on the price line.
3. Proportional relation between demand and supply:
Thirdly, there is proportionate relationship between demand and market price. If the demand increases two times,the price will too go double because the supply is rigidly fixed. Similarly will happen in the case of the fall of the demand. So, it can be said that there is direct relationship between the demand and the market price.
4. Market price is more or less to marginal cost:
Due to passiveness of the supply the market price may be more or less to marginal cost. It is because supply is inelastic. It never be increased. If the demand increases again and again the price will be very high and the marginal cost remain constant. So, it will be lower to price line. The same will be in the case of decrease of demand i.e., it will be high. So, market price can be more or less to marginal cost.
5. Market price is practical:
In our day-to-day life this market price can be seen. In market this price actually we get in our daily life. So, it is true to say that market price is practical and can be realized in our real life. Hence, it is said market price is practical. It can be visualized in our day to day economic life.
![]()
Question 3.
Write features of normal price.
Answer:
Normal price is long term price determined by the interactions of demand and supply.
- Normal price is long term price of durable goods. This price is determined by the interaction of demand and supply.
- In normal price both demand and supply are active. So, it has permanent equilibrium. Here, demand and supply both can be increased in due course of time.
- Normal price is imaginary price and is not found in actual market.
- Normal price is long term price, because it is determined by the permanent forces of demand and supply.
- In the determination of normal price, supply has got more importance because the producer has got enough time to meet the demand.
- Normal price is generally related with reproductive goods, because it relates with long term period.
Question 4.
Market for a goods is in equilibrium. Explain the chain of reaction in the market if the prices are.
Answer:
1. Higher than an equilibrium price:
When price prevailing in the markets is higher than that of equilibrium price, demand will be less than supply i.e., there is excess supply in the market. Excess supply will force the market price to slide down causing extension of demand and contraction of supply. This process will continue till equilibrium between supply and demand is stuck.
Thus, equilibrium price will be restored through the free play of market forces of demand and supply.
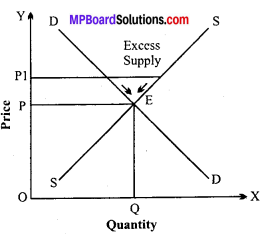
2. Market price lower than equilibrium price:
In a situation of excess demand consumers are willing to buy greater amount of commodity than what the producers are willing to sell. Accordingly, price of the commodity will be pushed up. This will cause expansion of supply and contraction of demand. This process will continue till demand becomes equal to supply and equilibrium is stuck in the market.
Question 5.
Explain the effect of changes in demand and supply on equilibrium price?
Answer:
If there is a change in demand and supply, the demand curve and supply curve will also shift from their original position and as a result, the equilibrium price will change. This change can take place in three ways:
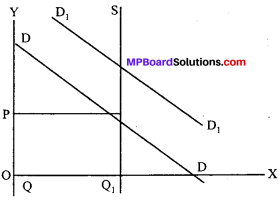
1. When the supply is fixed but the demand is changed:
If the supply does not change but there is a change in demand, the increase in demand will result in rise, in price and the decrease in demand will result in fall in price. It is clear from the diagram. Here, the DD curve is shifted to D1 D, the price will rise from QP to Q1 P and the quantity sold will be increased from OQ to OQ1. Conversely if the D1 D1 curve is shifted to DD or the demand is decreased, the price will full form Q1 P1 to QP and the quantity sold will fall from OQ1 to OQ.
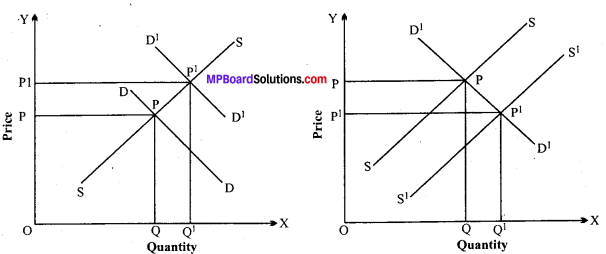
2. When the demand is fixed but the supply is changed: When the demand for a commodity is fixed but this is changed in supply, the supply curve will shift.The rise in supply will result in fall in price and the fall in supply will which result in rise in price. In the case of rise in supply, the supply curve will shift towards the right. If the supply falls, the supply curve will shift towards the left.
This can be explained with the help of diagram. Here, SS is shifted to S1S1 whereas DD curve is unchanged, hence the price is reduced from QP to Q1 P1 and the quantity sold is increased from OQ to OQ1. Conversely, the fall in supply i.e., from S1S1 to SS, the price will rise from Q1 P1 to QP and the quantity sold will reduce from OQ1 to OQ.
Question 6.
“When equilibrium price of a good is less than its market price, there will be competition among the sellers.” Give reasons.
Answer:
When equilibrium price of a goods is less than its market price, there will be competition among the sellers. At a price lower than market price, there will be excess supply, i.e. supply will be more than demand.
Question 7.
“In monopoly in the long period the equilibrium of a firm may reach to zero.” Why?
Or
Why can a firm not earn abnormal proof its or zero under perfect competition in the long run?
Answer:
A firm under perfect competition can earn abnormal profit in the short-run and not in the long-run. When a firm is earning abnormal profit in the short-run. Then new firms will be motivated to enter the industry. With the entry of new firms in the industry, the total supply will increase. With the increase in the supply and total demand remaining same. The price will start decreasing as a result abnormal profits earned by the existing firms will start disappearing. This process will continue until all the firms earn only normal profit, i.e., zero abnormal profit.
![]()
Question 8.
When is a firm called a price accept-or?
Answer:
A firm is able to accept the price when price of a good is determined by the forces of demand and supply, and at this price firm can sell any amount of goods in the market and no firm can influence the price. The reasons are:
- The large number of buyers and sellers cannot affect the supply in the market.
- Goods are homogeneous. If any firm changes price higher then the price prevailing in the market, then the buyers will switch on to other firms in the market.
- The buyers and sellers have complete knowledge about the market, so each firm is a price taker.
Question 9.
What is the effect of free entry and exist of firms in perfect competition?
Answer:
Implication of freedom of entry and exit of a firm under perfect competition: In perfect competition, there is free entry of new firms and exit of existing firms. New firms induced by large profit can enter the industry whereas in case of loss insufficient firms leave the industry. The implication of this feature of perfect competition is that no firm can earn abnormal profit in the long-run. The firm earns normal profit or minimum profit to remain in business.
Question 10.
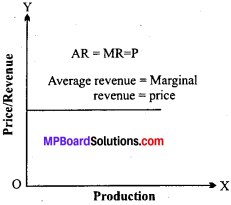
What is the relation between market price and marginal revenue for a price taking firm?
Answer:
For a price taking firm, marginal revenue is equal to price:
If we decrease or increase a unit than the total revenue also changes. It is called marginal revenue.
Formula: MR = TRN — TRN-1 A price taking firm always accept the market price. So far its average revenue, marginal revenue and market price is equal. By totaling all the marginal revenues, total, revenues can be calculated.
Question 11.
What will happen if the price prevailing in the market is.
(a) Above the equilibrium price?
(b) Below the equilibrium price?
Answer:
(a) In this case, many more firms will enter the market realizing that they can earn higher profit here than elsewhere. As a result, at prevailing price there will be excess supply in the market. This excess supply will lower the market price and the market price will be equal to equilibrium price.
(b) In this case many firms who are incurring losses will exit the industry. As a result, at a prevailing price, there will be excess demand. The excess demand will raise the market price and the market price will be equal to equilibrium price.
Question 12.
Suppose the demand and supply curves of a commodity X in a perfectly competition market are given by,
qd = 700 – P
qs = 500 + 3P for P ≥ 15
= 0 for 0 ≤ P ≤ 15.
Assume that the market consists of identical firms. Identify the reason behind the market supply of commodity X being zero at any price less than ₹ 15. What will be the equilibrium price for this commodity? At equilibrium, what quantity of X will be produced?
Answer:
In the question qd and qs denote the demand and supply respectively and P denotes the price of commodity X. From the market supply curve, we come to know that below ₹ 15 the market supply is zero. This means that no producer produces commodity X, when its price is below ₹ 15. We know that the firm produces positive quantity of output only when the price of the goods is at least equal to minimum average variable cost of the firms. When the price is below minimum AVC, they produce nothing. Therefore, the minimum average cost of producing commodity X is ₹ 15.
Here, the price is ₹ 15. At equilibrium from the supply curve we get quantity of supply. At equilibrium price,
qd = qs
700 – P = 500 + 3p
– 4 P = – 200
P = 50
Hence, equilibrium price = ₹ 50
Equilibrium quantity = 700 – P
= 700 – 50 = 650
Question 13.
Suppose, the demand and supply curves of salt are given by;
qd = 1000 – p
qs = 700 + 2p.
(i) Find equilibrium price and quantity.
(ii) Now suppose that the price of an input used to produce salt increases so that the new supply curve is:
Qs = 400 + 2p.
How does an equilibrium price and quantity change?
(iii) Suppose, that the government has imposed a tax of ₹ 3 per unit of sale. How does it affect the equilibrium price and quantity?
Answer:
(i) At equilibrium price: qD -qs
1000 – p = 700 + 2 p
1000 – 700 = 2p + p
3p = 300
or
p = 100
Equilibrium price = ₹ 100
Equilibrium quantity qD = 1000 – p = 1000 -100 = 900 units
qs = 700 + 2p = 700 + (2 x 100) = 900 units
(ii) New supply curve is: qs = 400 + 2p
At equilibrium price qD = qs
1000 – p = 400 + 2p
1000 – 400 = 2p + p
3p = 600
or
p = 200
Equilibrium price = ₹ 200
Equilibrium quantity
qD = 1000 – p = 1000 – 200 = 800 units
qs = 400 – 2p = 400 + (2 x 200) = 800 units
(iii) New supply curve equation after tax of ₹3 per unit on sale is imposed.
qs = 700 + 2 (p – 3) = 700 + 2p – 6 = 694 + 2p
At equilibrium price: qD =qs
1000 – p = 694 + 2p
1000 – 694 = 2+p + p
3p = 306
or p = 102
Equilibrium price has increased from ₹ 100 to ₹ 102.
Equilibrium quantity:
q D = 1000 – p = 1000 – 102 = 898 units
qs = 694 + 2p = 694 + (2 x 102) = 694 + 208 = 898
units Equilibrium quantity has decreased from 900 to 898 units.
![]()
Question 14.
Suppose the price at which equilibrium is attained above the minimum average cost of the firms constituting the market. Now if we allow the free entry and exit of firms, how will the market price adjust to it?
Answer:
When equilibrium price at equilibrium quantity is more than the minimum average cost:
When the price at the equilibrium quantity is more then minimum average cost than there will be abnormal profit. In this case, immediately many more firms will enter the market realizing that they can earn higher profit here than elsewhere. As a result at this price there would be excess supply in the market.
This excess supply will lead the firms to lower their prices so that they can sell off their entire output. If at this lowered price, the abnormal profit is still positive more firms will enter the market, but the entry will not stop. The entry of new firms will continue as long as the existing firms are earning abnormal profit at the lower price. Entry of new firms will stop when the price is equal to minimum average cost of each firm.
Question 15.
Will a profit maximizing firm in competitive market ever produce a positive level of output in the range where the marginal cost is falling? Give and explanation.
Answer:
A profit maximizing firm in a competitive market will produce a positive level at output in the same where marginal cost is falling. Falling MC means, the cost producing an additional unit of output trends to reduce. Here price is constant as the firm is working in a competitive market in this case, the difference be ween firm’s total revenue and TVC (TVC = Σ MC) tends to increase. It means firm’s profit increases with the increase in the level of output. Then a competitive firm increases output when gross profit is rising.
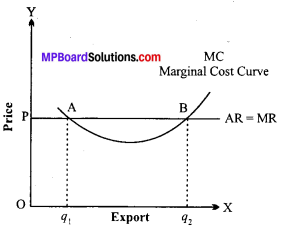
Question 16.
Explain the role of time in determining the price.
Answer:
To get balance between demand and supply. Time is very important. On the basis of time market is divided into four types:
1. Very short period market:
This is also called daily market where supply is very limited. Supply cannot adjust demand. This means demand of the commodity determines price. This market is of perishable commodities like milk, green vegetables, meat, fish, curd, egg etc.
2. Short period market:
The duration of short period market is more than very short period and supply can be increased to some extent. This means that use of factors of production can be increased or decreased.
3. Long period market:
Long period market is a market where, there is sufficient time to increase the supply. In other words, the producer have enough time to increase his production capacity as well as he can employ new factors of production. And he can also decrease the supply. So, supply plays a major role in price determination.
4. Very long period market:
This is a market where there is maximum change in demand supply. In demand side, there may be changes due to increase in population change in taste, preference or fashion. There can be a drastic change in demand due to these factors. Similarly, supply can be changed due to changes in technique of production.
![]()
Form of Market and price Determination Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are the main features of perfect competition?
Answer:
Following are the main features of perfect competition:
1. Large numbers of buyers and sellers:
In perfect competition, the number of buyers and sellers are very large so that none of the individual buyers or sellers are able to influence the price output policy of the industry (Price prevailing in the market).
2. Homogeneous product:
The second characteristics of a perfectly competitive market is that the product produced by each firm of the industry is homogeneous i. e., all the units of that product produced by different firms are perfect substitutes to each others. Salt, cotton, coal and wheat are homogeneous and the different sellers dealing in such goods cannot increase their prices as the customers (buyer) will leave him and would buy from the other sellers, selling at a lower price. As the goods are identical in all the respects, it is immaterial to the buyer as to who has produced it and he does not have any preference for the product of an individual seller.
3. Uniform price:
Under perfect competition all the units of a commodity are sold at the same price.If a producer tries to sell his products at a higher price than the ruling market price then he will not succeed. This is so, due to the condition of homogeneity of the products, and buyers will not be willing to pay a higher price for this products. They will buy that product from some other producer, who is willing to sell his products at the ruling market price.
4. Free entry or exit of firms:
There must be full freedom for the entrance of the firm. If the industry is gaining profit, the new firms can enter that industry. On the other hand, if the industry is incurring losses, some firms can freely leave the industry, thus enabling other firms to make normal profits.
5. Normal profit:
Under perfect competition all the firms get normal profit only. The marginal cost of the firms equals the marginal revenue. Thus, in the long run a perfectly competitive market gains only normal profit.
6. Uniformity in quality, shape and weight: There should be uniformity in the commodities to be sold in the market. There should not be any change in shape, color, quality and weight of the commodities. If the uniformity will be there, then only same price will be determined for the same type of units.
Question 2.
Explain determination of equilibrium price with the help of an example.
Answer:
Equilibrium price:
Under perfect competition price is determined by the interaction of demand and supply. The price at which both buyer and seller is ready to do the transaction of goods, that price is known as equilibrium price. At this price both demand and supply are equal, neither there is excess demand neither excess supply.
This can be explained with the help of an example.
The price at which the demand and supply remains same is called equilibrium price.
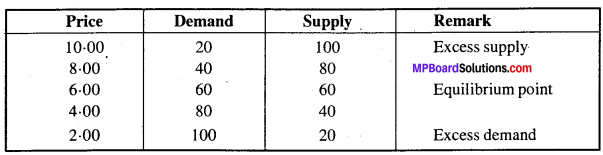
In the diagram, DD is the demand curve and SS is the supply curve. P is the point where price is determined. It is the equilibrium point, where demand and supply are equal. It is known as equilibrium price. Under perfect competition, the market price of a commodity is determined at a point where the demand and supply of the commodity are equal.
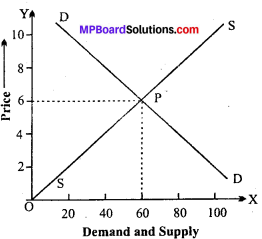
Question 3.
What is market price? Explain the effect of short period market in determining the price?
Answer:
Meaning of market price:
Market price is also known as short period price. This is the period in which the supply cannot be increased due to lack of time, So, this is the price which is determined by temporary interaction of demand and supply.
Price determination in the short period:
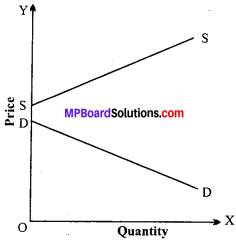
Market price is short period price of goods. In it the price will be determined by temporary equilibrium of demand and supply. That is why it is also known as temporary price. The reason is that the supply is fixed in short period. So, no change can be made in it. In this situation if demand increases price will go up and its vice versa. Hence, it can be said that the market price of perishable goods.like rice, tomato, fish, and other vegetables. In this period no adjustment is made between demand supply. In this way in it the role of demand is important. It can be shown with the help of a diagram.
In this figure SS is supply curve which is inelastic. It means there will be no effect of supply in the determination of the price. In this figure quantity is OS. From the figure it is evident that when the demand is DD Price is P or N. But when demand increases from DD to D1 D1 It means the price will increase i.e., from P or N to P1 or N1. Similarly
again when the demand falls from DD to D2 D 2 the price comes down from P or N to P2 or N2. It means the Price varies with the variation in demand. So, it can be said that in short period price only demand is active and supply is passive.
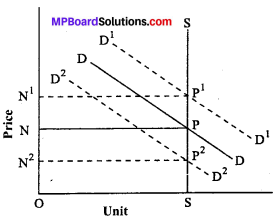
Question 4.
With the help of diagram explain price determination under perfect competition.
Or
Explain price determination under perfect competition on the basis of following points:
- Demand for a commodity
- Supply of a commodity
- Equilibrium of demand and supply.
Answer:
Dr. Marshall has explained price determination under perfect competition in a systematic way. He said that prices in perfect competition are neither determined by cost nor by utility, but the interaction of both. There are two factors necessary for determined price of a commodity. There are demand for the goods and supply of goods. The demand for goods is from consumer.
On the other hand supply of a commodity is through the purchasers and sellers. Every producer or sellers desires to sell this commodity over and above its cost. If he sells it below the marginal cost it would not be profitable for him. Therefore, marginal cost will be the minimum limit of the produce goods. Marshall’s theory can be divided into three parts:
- Demand for commodity
- Supply of commodity
- Equilibrium of demand and supply.
1. Demand for commodity:
Demand for a commodity is done by consumers. The consumer pays the price according to the utility he gets from the commodity. But it is too a fact that with every increase in quantity, the utility diminishes. So, the consumer will pay the maximum price for a commodity equals to its marginal utility. In the words of Dr. Marshall “Marginal utility is utility derived from the last unit consumed.”
In a perfect competition the price will always be equal to its marginal utility.This is the maximum price which a consumer will pay for a commodity. This is the upper hand or maximum limit which will be determined by the demand side. Dr. Marshall has compared it with the upper blade of a scissor. So, demand determines the maximum limit of the price. It is a upper hand or maximum point of the demand..
2. Supply of commodity:
Supply of the commodity is done by producer. Production is done with the help of factors. They get their remuneration. It makes the cost. No producer will be ready to sell its products less than the price. Hence, supply side is determined by the manufacturing cost of the product of the commodity.
3. Equilibrium of demand and supply:
From the above analysis of demand and supply it is clear that in perfect competition price is determined by the interaction of demand and supply. At one place the demand and supply will be equal at a particular price. This point is known as equilibrium point. At this equilibrium price the demand and supply quantity will be equal. This can be explained with the help of a figure.
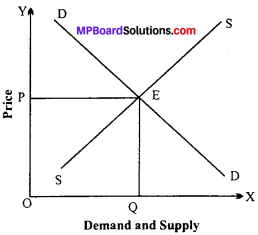
In the figure along the X-axis demand and supply is shown and along Y-axis prices is shown. SS is the supply curve and DD is the demand curve. Both the curves intersect each other at P. This is the equilibrium point. At this point OQ quantity is demand at OP price. The tendency of the demand curve is that it slopes from left to right that is as price increases demand will fall. On the other hand, supply curve slopes from left to right. It shows that every fall in price will cause increase in supply and vice – versa. This is how price is determined by the interaction of demand and supply at a point of intersection which is called Equilibrium price.
![]()
Question 5.
Define perfect competition. Is perfect competition a myth?
Or
“Perfect competition is an imaginary concept” Explain.
Or
“Is perfect competition imaginable “. State the main reason.
Answer:
Mrs. J. Robinson “Perfect competition prevails when the demand for output of each producer is perfectly elastic. This entails first, that the number of sellers is so large so that the output of anyone seller is a negligible, small proportion of the total output of the commodity and second that buyers are alike in respect of their choice of rival sellers so that the market is perfect”.
In real life, we do not find either free competition or full knowledge in markets. So, perfect competition is just an imaginary condition. In practice, perfect competition is a myth and it cannot be seen anywhere. In agricultural products, such as wheat, rice, cotton it can be seen to some extent. Many farmers cultivate wheat, rice etc. in their farms, similarly a number of buyers come to the mantis to purchase goods. But other things and conditions are not found in practice. So, perfect competition is a myth. It is due to the following reasons:
- Firstly, for the perfect competition huge number of sellers and buyers are needed. But in practice there are limited number of sellers and buyers. Especially market is ruled by the sellers.
- Secondly, there is lack of perfect competition between sellers and buyers. It is because and only a few sellers. Further market is always dominated by the sellers.
- Thirdly, the availability of substitution goods are another obstacle in the way of perfect competition. As soon as price increases people change their consumption due to substitution.
- Lastly, sometimes the prices of essential goods are determined by the Government of the nations. So, the free operation of law of demand and supply does not play its role in the market.
- Expenditure is done transport and advertisement when in perfect competition.such type of expenditure should not occur.
- Buyers are not aware of market and so they have not full knowledge of product and its price. On the basis of the above points it is true to say that perfect competition is imaginary and is not easy to be located.
It is theoretical and only on certain assumptions we can assume it. In our daily life we never see the perfection in the market. That is why economists have called it myth.
Question 6.
How is price determined under perfect competition in the long period? Explain.
Answer:
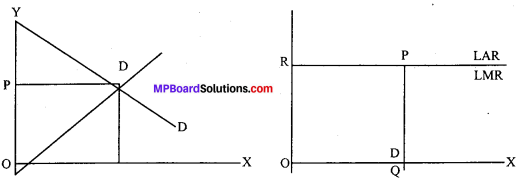
Long period:
Long period is a period of time in which, there is sufficient time to increase the supply. The producer has enough time to increase his production capacity as well as he can employ new factors of production. He can also decrease the supply. Under long period, there is an adequate time and so the supply of a commodity can be adjusted according to its demand. There is no scope for abnormal profit or loss. The price will be determined by the equilibrium of marginal cost, marginal revenue, average cost and average revenue.This can be explained with the help of the figure.
In the figure demand and supply of a firm determines OP price at point E, and OQ quantity of goods are bought and sold. OP price is accepted by the firm. This price is long term price where average cost (LAC) and Marginal Cost (LMC) is same. Firm is in equilibrium at point E where firm sells Ok quantity and produces OR quantity at minimum average cost. Firm earns normal profit. Here, P = LAC = LMC = LAR = LMR. In this period price depends on production cost, which is itself based on laws of production.
Question 7.
What is the effect of change in demand on equilibrium price?
Answer:
Increase in demand:
As we know, the demand for a commodity changes not only due to change in its own price but also due to change in other factors, such as consumer’s income, tastes and preferences, price of related goods, etc. When the demand changes on account of the factors other than change in price, there will be a shift in the demand curve. This situation is termed as change in demand.
Demand curve may shift either rightwards or leftwards. When, due to change in factors other than price, there is reduction in demand, it is called decrease in demand. Demand curve in such a case will shift left wards, conversely, when, due to change in factors other than price of the commodity, more quantity of the commodity is demanded, it is technically called increase in demand. The demand curve will shift upwards to the right. These types of changes in demand have been shown below diagrammatically.
Increase in demand:
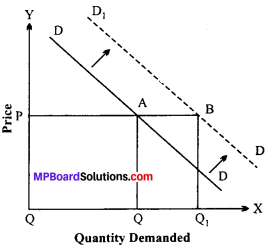
Fig. represents the situation of increase in demand. This shows how more quantity of the commodity is demanded even at the same price. OPis the original price at which quantity p demanded was OQ. Now due to increase in demand 8 (as reflected by demand curve D1 D1), demand p increases to OQ1 at the same price of OP. The increase in demand.
Decrease in demand:
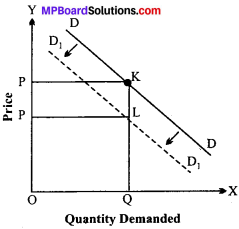
In the figure, DD is the original demand curve. OP and OQ are the original price and quantity demanded respectively. Now Quantity Demanded demand decreases (as indicated by leftward shift in the demand curve D1, D1 a given quantity of demand i.e„ OQ is demanded only at a price lower than OP. In other words, consumers buy the same amount of the commodity (OQ) only at a lower price, i. e., OP1 The fall in price (from OP to OP)1 for the same quantity of demand here is due to decrease in demand.