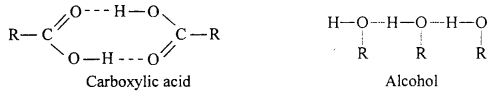MP Board Class 12th Chemistry Solutions Chapter 12 Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids NCERT Intext Exercises
Question 1.
Write the structures of the following compounds:
(i) a-Methoxypropionaldehyde
(ii) 3-HydroxybutanaI
(iii) 2-Hydroxycyclopentane carbaldehyde
(iv) 4-Oxopentanal
(v) Di -sec. butyl ketone
(vi) 4-Fluoroacetophenone.
Answer:
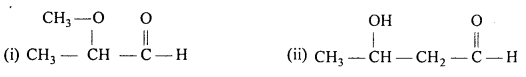
Question 2.
Write the structures of products of the following reactions :
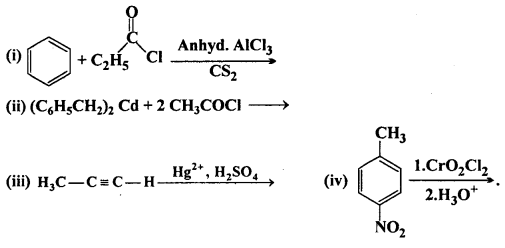
Answer:
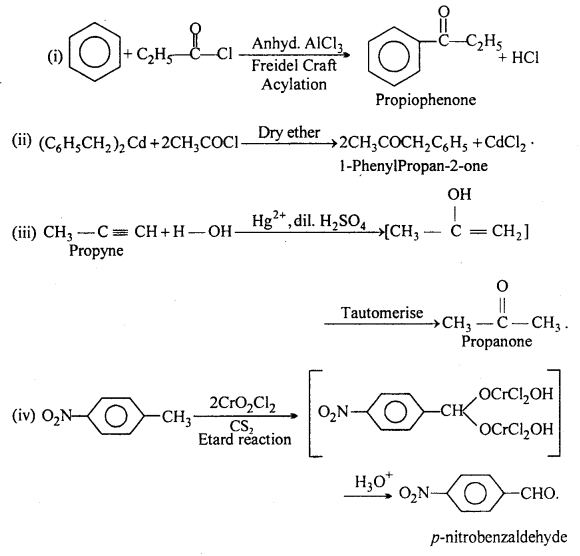
![]()
Question 3.
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their boiling points:
CH3CHO,CH3CH2OH, CH3OCH3, CH3CH2CH3.
Answer:
CH3CH2CH3 < CH3OCH3 < CH3CHO < CH3CH2OH.
This order can be predicted on the basis of inter-molecular force operating between them, these are having comparable molecular mass. CH3CH2OH undergoes the strongest H- bonding. In CH3OCH3 and CH3CHO dipole-dipole attraction is more in CH3CHO, since CH3CHO is more polar than CH3OCH3 therefore its boiling point is more than CH3—O—CH3. Propane being non-polar therefore, weak van der Waals’ forces exist between them.
Question 4.
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their reactivity in nucleophilic addition reactions :
(i) Ethanal, Propanal, Propanone, Butanone.
(ii) Benzaldehyde, p-Tolualdehyde, p-Nitrobenzaldehyde, Acetophenone.
Hint: Consider steric effect and electronic effect.
Answer:
(i) Butanone < Propanone < Propanal < Ethanal.
This order is predicted on the basis of two factor : (a) + I effect (Electron releasing effect) and (b) Steric effect.
(ii) Acetophenone < p-tolualdehyde < Benzaldehyde < p-nitrobenzaldehyde.
This order is predicted on the basis of inductives, resonance and hyperconjugation effect.
Question 5.
Predict the products of the following reactions:
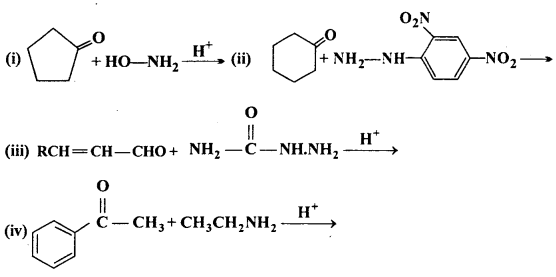
Answer:
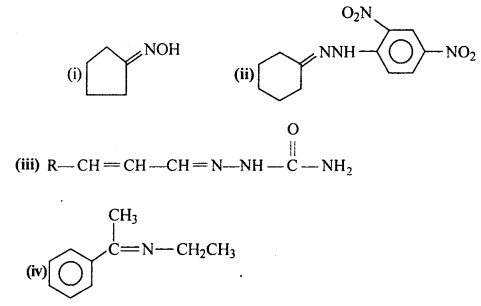
Question 6.
Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds:
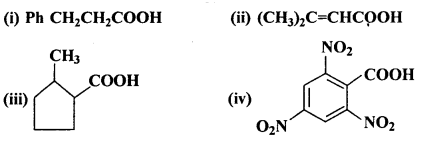
Answer:
(i) 3-Phenylpropanoic acid
(ii) 3-Methylbut-2-en-l-oic acid
(iii) 2-Methylcyclopentanecarboxylic acid
(iv) 2,4,6-Trinitrobenzoic acid or 2,4,6-Trinitrobenzenecarboxylic acid.
![]()
Question 7.
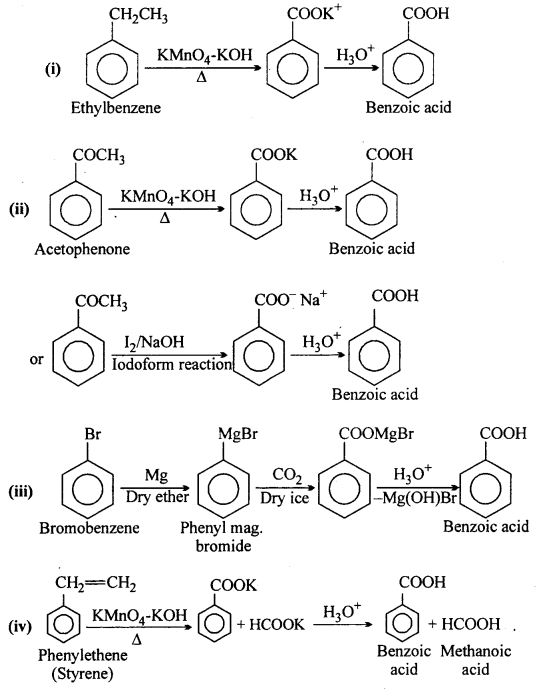
Show how each of the following compounds can be converted to benzoic acid:
(i) Ethylbenzene
(ii) Acetophenone
(iii) Bromobenzene and
(iv) Phenylethene (Styrene).
Answer:
Question 8.
Which acid of each pair shown here would you expect to be stronger ?
(i) CH3CO2H or CH2FCO2H
(ii) CH2FCO2H or CH2ClCO2H
(iii) CH2FCH2CH2CO2H or CH3CHFCH2CO2H
Answer:
(i) FCH2COOH (due to -I effect of F)
(ii) FCH2CO2H (due to much stronger -I effect of F over Cl)
(iii) CH3CHFCH2COOH (Inductive effect decreases with distance i. e. 3-fluorobutanoic acid is stronger than 4-fluorobutanoic acid)
![]()
![]()
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids NCERT Textbook Exercises
Question 1.
What is meant by the following terms ? Give an example of the reaction in each case:
(i) Cyanohydrin
(ii) Acetal
(iii) Semicarbazone
(iv) Aldol
(v) Hemiacetal
(vi) Oxime
(vii) Ketal
(vii) Imine
(ix) 2,4-DNP-derivative
(x) Schiff’s base.
Answer:
(i) Cyanohydrin: Cyanohydrins are organic compounds having the formula RR’C(OH)CN, where R and R’ can be alkyl or aryl groups.
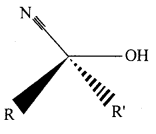
Aldehydes and ketones react with hydrogen cyanide (HCN) in the presence of excess sodium cyanide (NaCN) as a catalyst to field cyanohydrin. These reactions are known as cyanohydrin reactions.
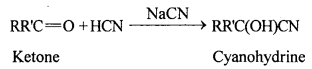
Cyanohydrins are useful synthetic intermediates.
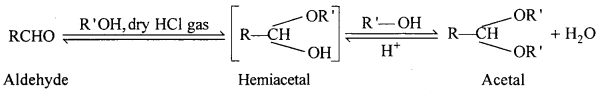
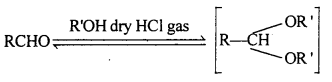
(ii) Acetal: Acetals are gem-dialkoxy alkanes two alkoxy groups are present on the terminal carbon atom. One bond is connected to an alky l General structure group while the other is connected to a hydrogen atom.
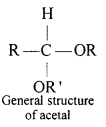
When aldehydes are treated with two equivalents of a monohydric alcohol in the presence of dry HCl gas, hemiacetals are produced that further react with one more molecule of alcohol to yield acetal.
(iii) Semicarbazone : Semicarbazones are derivatives of aldehydes and ketones pro¬duced by the condensation reaction between a ketone or aldehyde and semicarbazide.
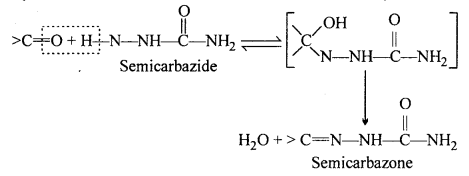
Semicabazones are useful for identification and characterisation of aldehydes and ktones.
(iv) Aldol condensation : Two same or different molecules of carbonyl compounds containing a-hydrogen atom in presence of dilute alkali like NaOH, Ba(OH)2, combined to form an addition compound which exhibits properties of aldehyde and ketone both. This reaction is called aldol condensation.
For example, in presence of dilute alkali NaOH or potassium carbonate, two molecules of acetaldehyde condensed and form β-hydroxybutanaldehyde or ‘aldol’.
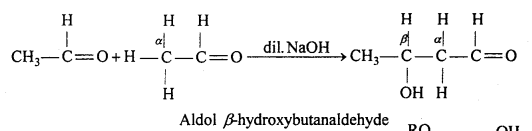
(v) Hemiacetal: Hemiacetals are a-alkoxyalcohols.
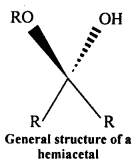
Aldehyde reacts with one molecule of a monohydric alcohol in the presence of dry HCl gas.
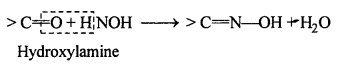
(vi) Oxime: Oximes are a class of organic compounds having the general formula RR’CNOH, where R is an organic side chain and R’ is either hydrogen or an organic side chain, If R’ is H, then it is known as aldoxime and if R’ is an organic side chain, it is known as ketoxime.
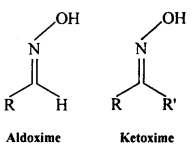
On treatment with hydroxylamine in a weakly acidic medium, aldehydes or ketones formaximes.
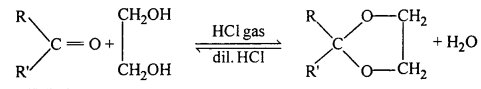
(vii) Ketal: Ketals are gem-dialkoxyalkanes in which two alkoxy groups are present on the same carbon atom within the chain. The other two bonds of the carbon atom are connected to two alkyl groups.
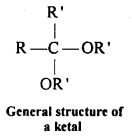
Ketones react with ethylene glycol in the presence of dry HCl gas to give a cyclic product known as ethylene glycol ketals.
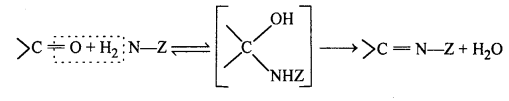
(viii) Inline : Imines are chemical compounds containing a carbon nitrogen double bond.
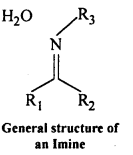
Imines are produced when aldehydes and ketones react with ammonia and its derivatives.
(ix) 2,4-DNP-derivative: 2,4-dinitrophenyIhydrazones are 2,4- DNP- derivatives, which are produced when aldehydes or ketones react with 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine in a weakly acidic medium.
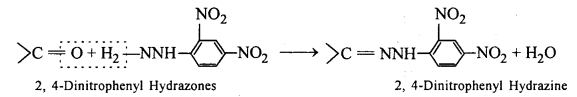
To identify and characterize aldehydes and ketones, 2,4-DNP derivatives are used.
(x) Schiff’s base : SchifFs base (or azomethine) is a chemical compound containing a carbon-nitrogen double bond with the nitrogen atom connected to an aryl or alkyl group but not hydrogen. They have the general formul R1R2C = NR3. Hence, it is an imine. It is named after a scientist, Hugo Schiff.
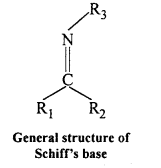
Aldehydes and ketones on treatment with primary aliphatic or aromatic amines in the presence of trace of an acid yields a Schiff’s base.
Question 2.
Name the following compounds according to IUPAC system of nomenclature :
- CH3CH(CH3)CH2CH2CHO
- CH3CH2COCH(C2H5)CH2Cl
- CH3CH=CHCHO
- CH3COCH2COCH3
- CH3CH(CH3)CH2C(CH3)2COCH3
- (CH3)3CCH2COOH
- OHCC6H4CHO-p.
Answer:
- 4-Methylpentanal
- 6-Chloro-4-ethylhexan-3-one
- But-2-en-l-al
- Pentan-2, 4-dione
- 3,3,5-Trimethylhexan-2-one
- 3,3-Dimethylbutanoic acid
- Benzene-1,4-dicarbaldehyde.
Question 3.
Draw the structures of the following compounds :
(i) 3-MethylbutanaI
(ii) p-Nitropropiophenone
(iii) p-Methylbenzaldehyde
(iv) 4-Methylpent-3-en-2-one
(v) 4-Chloropentan-2-one
(vi) 3-Bromo-4-phenylpentanoic acid
(vii) p, p’-Dihydroxybenzophenone
(viii) Hex-2-en-4-ynoic acid.
Answer:
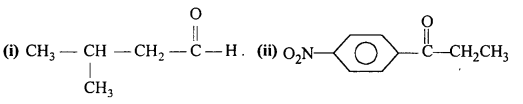
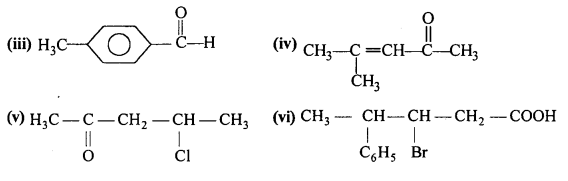
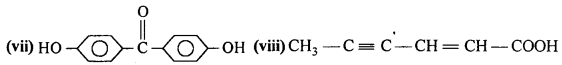
Question 4.
Write the IUPAC names of the following ketones and aldehydes. Wherever possible, give also common names :

Answer:

![]()
Question 5.
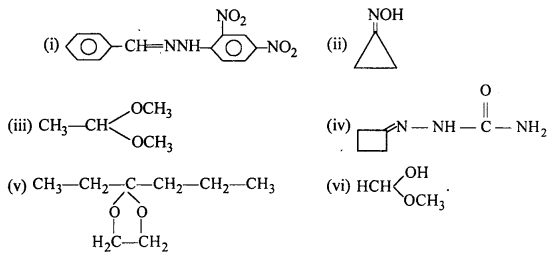
Draw structures of the following derivatives :
(i) The 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone of benzaldehyde
(ii) Cyclopropanone oxime
(iii) Acetaldehydedimethylacetal
(iv) The semicarbazone of cyclobutanone
(v) The ethylene ketal of hexan-3-one
(vi) The methyl hemiacetal of formaldehyde.
Answer:
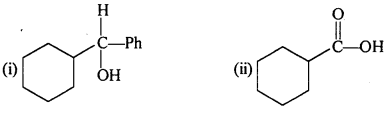
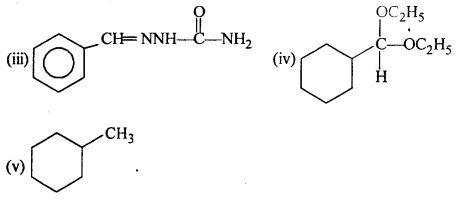
Question 6.
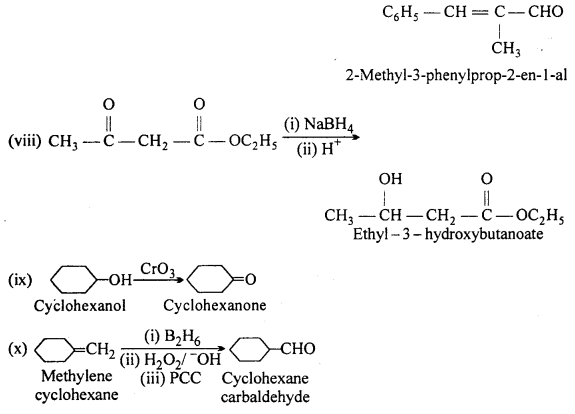
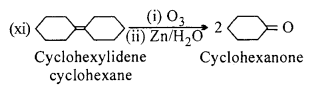
Predict the products formed when cyclohexanecarbaldehyde reacts with following reagents:
(i) PhMgBr and then H3O+
(ii)Toilens’ reagent
(iii) Semicarbazide and weak acid
(iv) Excess ethanol and acid
(v) Zinc amalgam and dilute hydrochloric acid.
Answer:
Question 7.
Which of the following compounds would undergo aldol condensation, which the Cannizzaro reaction and which neither ? Write the structures of the expected products of aldol condensation and Cannizzaro reaction :
(i) Methanal
(ii) 2-MethyIpentanal
(iii) Benzaldehyde
(iv) Benzophenone
(v) Cyclohexanone
(vi) 1-Phenylpropanone
(vii) Phenylacetaldehyde
(viii) Butan-l-ol
(ix) 2,2-DimethylbutanaI.
Answer:
(A) (ii) 2-methylpentanal, (v) Cyclohexanone, (vi) 1-phenylpropanone and (vii) Phenylacetaldehyde have one or more a-hydrogen atoms and hence undergo aldol condensation.
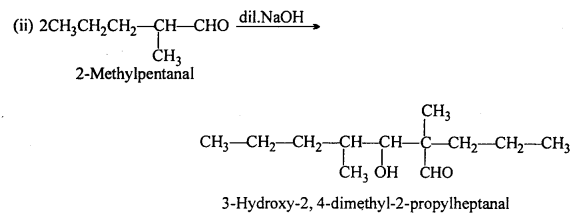
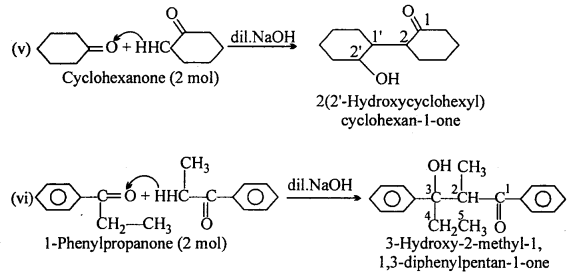
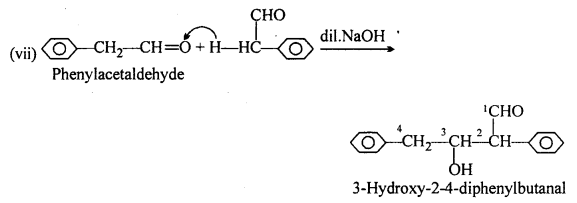
(B) (i) Methanal, (iii) Benzaldehyde and (ix) 2,2-Dimethylbutanal do not contain a- hydrogen and hence undergo Cannizzaro’s reaction.
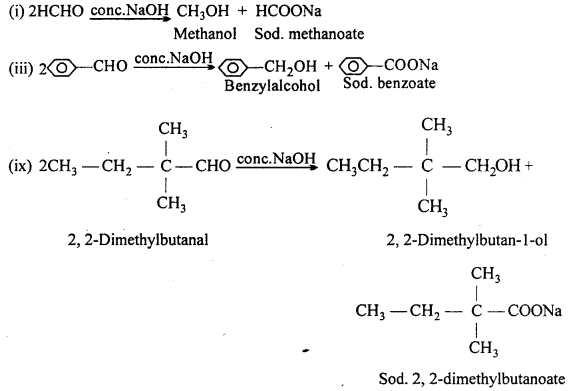
(C) (iv) Benzophenone is a ketone having no a-H.
(viii) Butan-l-ol is an alcohol.
Both of these neither undergo aldol Condensation nor Cannizzaro reaction.
Question 8.
How will you convert ethanal into the following compounds :
(i) Butane-1,3-diol
(ii) But-2-enal
(iii) But-2-enoic acid.
Answer:
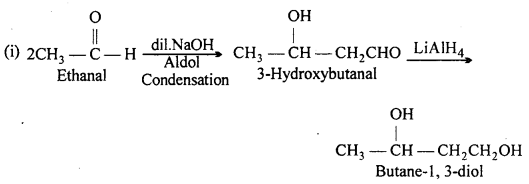
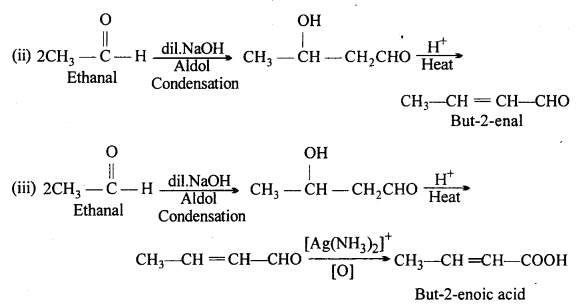
Question 9.
Write structural formulae and names of four possible aldol condensation products from propanal and butanal. In each case, indicate which aldehyde acts as nucleophile and which as electrophile.
Answer:
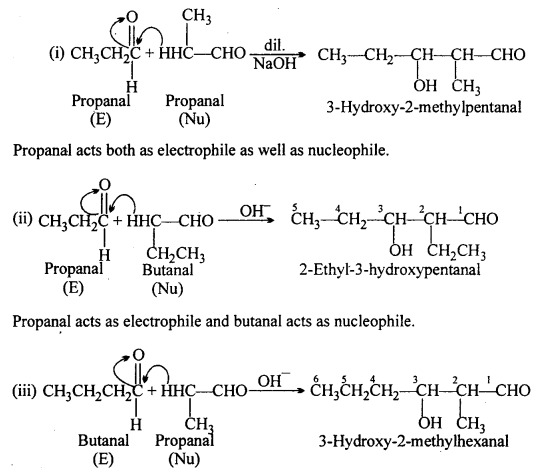
Butanal acts both as electrophile as well as nucleophile.
Question 10.
An organic compound with the molecular formula C9H10O forms 2, 4- DNP derivative, reduces Tollens’ reagent and undergoes Cannizzaro reaction. On vig-orous oxidation, it gives 1,2-benzene-dicarboxylic acid. Identify the compound.
Answer:
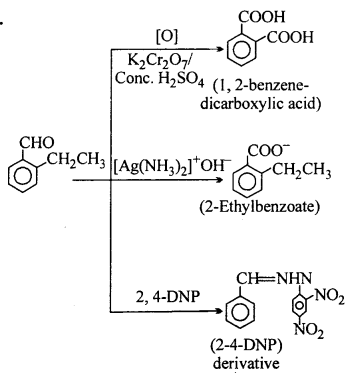
![]()
Question 11.
An organic compound (A) (molecular formula C8H16O2) was hydrolysed with dilute sulphuric acid to give a carboxylic acid (B) and an alcohol (C). Oxidation of (C) with chromic acid produced (B). (C) on dehydration gives but-1- ene. Write equations for the reactions involved.
Answer:
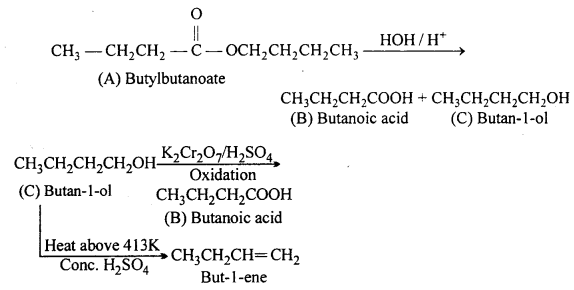
Question 12.
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their property as indicated :
(i) Acetaldehyde, Acetone, Di-tert-butyl ketone, Methyl terf-butyl ketone (reactivity towards HCN)
(ii) CH3CH2CH(Br)COOH, CH3CH(Br) CH2COOH, (CH3)2CHCOOH, CH3CH2-CH2COOH (acid strength)
(iii) Benzoic acid,’4-Nitrobenzoic acid, 3,4 Dinitrobenzoic acid, 4-Methoxybenzoic acid (acid strength).
Answer:
(i) The reactivity towards HCN addition decreases as the +1 effect of the alkyl groups increases.
Di-tert-butyl ketone < MethyL tert-butyl ketone < Acetone < Acetaldehyde.
(ii) +I effect decreases whereas —I effect increases the acidic strength of -COOH group. Further -I effect decreases with distance.
(CH3)2CHCOOH < CH3CH2CH2COOH < CH3-CH(Br)CH2COOH < CH3CH2CH(Br)COOH.
(iii) Electron donating group decreases the acidic strength whereas electron withdrawing effect increases the acidic strength.
4-Methoxybenzoic acid < Benzoic acid < 4 Nitrobenzoic acid < 3,4-Dinitrobenzoic acid.
Question 13.
Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds :
(i) Propanal and Propanone
(ii) Acetophenone and Benzophenone
(iii) Phenol and Benzoic acid
(iv) Benzoic acid and Ethyl benzoate
(v) Pentan-2-one and Pentan-3-one
(vi) Benzaldehyde and Acetophenone
(vii) Ethanal and Propanal.
Answer:
(i) Add Tollens’ reagent. Propanal will form silver mirror on heating, propanone will not react.
Alternative method : Add I2 and NaOH propanone will give yellow ppt. due to iodoform whereas propanal will not react.
(ii) Add I2 and NaOH. Acetophenone will give yellow ppt. of CHI3 whereas benzophenone will not give.
(iii) Add neutral FeCl3 to each of them separately. Phenol will give violet colour whereas benzoic acid will not react.
Alternative method : Add NaHCO3 to each of them in aqueous solution. Benzoic acid will give brisk effervescence of CO2 while phenol will not react.
(iv) Add NaHCO3 solution to each of them. Benzoic acid will give brisk effervescence due to CO2 whereas ethylbenzoate does not react.
(v) Add I2 and NaOH each of them separately. Pentan-2-one will give yellow ppt. of CHI3. Pen-tan-3-one will not.
(vi) Add Tollens’ reagent. Benzaldehyde will give silver mirror on heating, Acetophenone will not react.
(vii) Add I2 and NaOH. Ethanal will give yellow precipitate of iodoform, whereas propanal does not.
Question 14.
How will you prepare the following compounds from benzene ? You may use any inorganic reagent and any organic reagent having not more than one carbon atom:
(i) Methyl benzoate
(ii) m-Nitrobenzoic acid
(iii) p-Nitrobenzoic acid
(iv) Phenylacetic acid
(v) p-Nitrobenzaldehyde.
Answer:
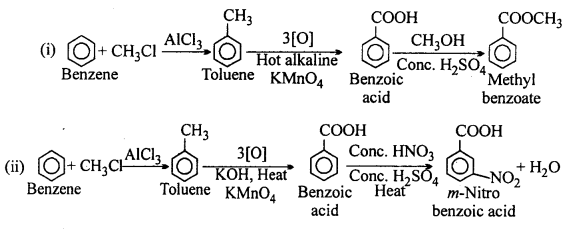
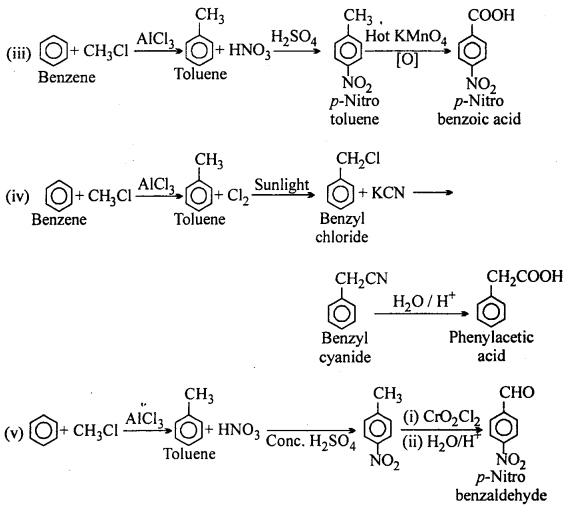
Question 15.
How will you bring about the following conversions in not more than two steps :
(i) Propanone to Propene
(ii) Benzoic acid to Benzaldehyde
(iii) Ethanol to 3-HydroxybutanaI
(iv) Benzene to m-Nitroacetophenone
(v) Benzaldehyde to Benzophenone
(vi) Bromobenzene to l-Phenylethanol
(vii) Benzaldehyde to 3-Phenylpropan-l-ol
(viii) Benazaldehyde to a-Hydroxy-phenylacetic acid
(ix) Benzoic acid to m-Nitrobenzyl alcohol.
Answer:
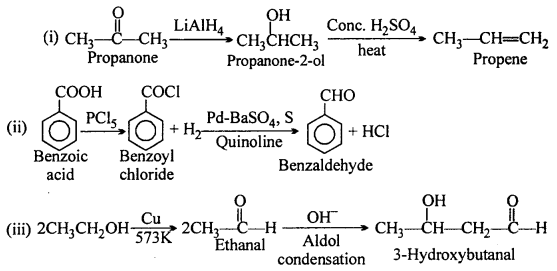
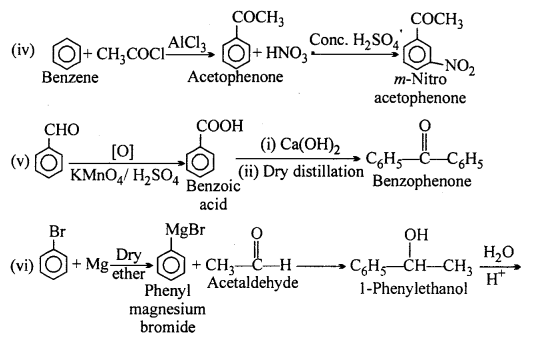
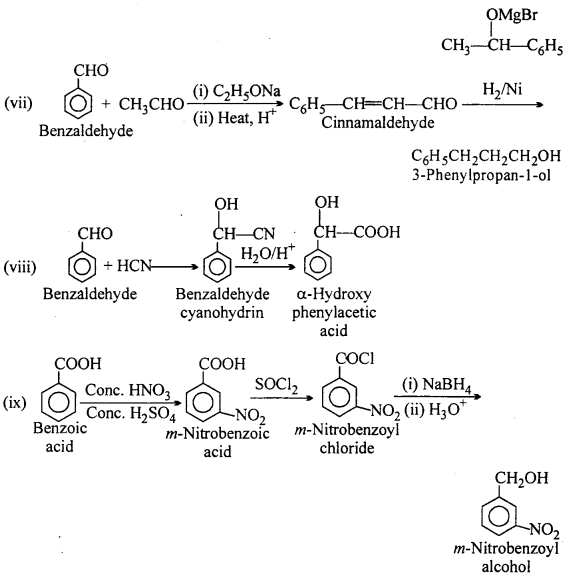
Question 16.
Describe the following :
(i) Acetylation
(ii) Cannizzaro
(iii) Cross-aldol condensation
(iv) Decarboxylation
Answer:
(i) Acetylation: The introduction of an acetyl functional group into an organic r compound is known as acetylation. It is usually carried out in the presence of a base such as pyridine, dimethylaniline, etc. This process involves the substitution of an acetyl group for an active hydrogen atom. Ecetyl chloride and acetic anhydride are commonly used as acetylating agents.
For example, acetylation of ethanol produces ethyl acetate.
CH3CH2OH + CH3COCI → CH3COOC2H5 + HCl
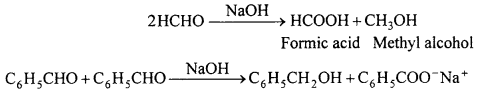
(ii) Cannizzaro reaction: Aldehydes which do not contain a-hydrogen like HCHO, C6H5CHO react with cone. NaOH solution to form methyl alcohol and formic acid. This reaction is called Cannizzaro reaction.
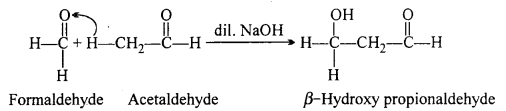
(iii) Cross-aldol condensation: When aldol condensation is carried out between different aldehydes or two different ketones or an aldehyde and a ketone, then the reaction is called a cross-aldol condensation. If both the reactants contain cr-hydrogens, four compounds are obtained as products.
(iv) Decarboxylation : Decarboxylation refers to the reaction in which carboxylic acids lose carbon dioxide to form hydrocarbons when their sodium salts are heated with soda-lime.
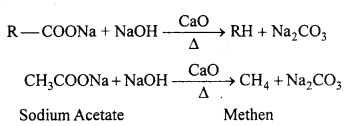
Decarboxylation also takes place when aqueous solutions of alkali metal salts of carboxylic acids are electrolysed. This electrolytic process is known as Kolbe’s electrolysis.
Question 17.
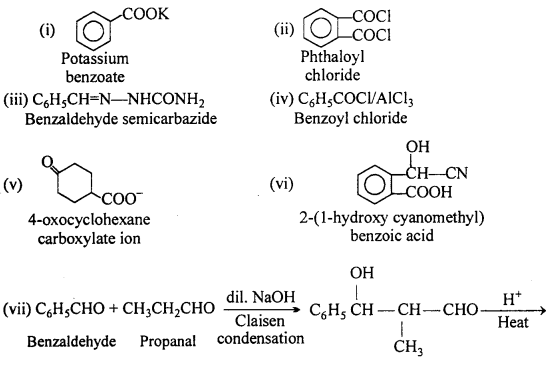
Complete each synthesis by giving missing starting material, reagent or products:
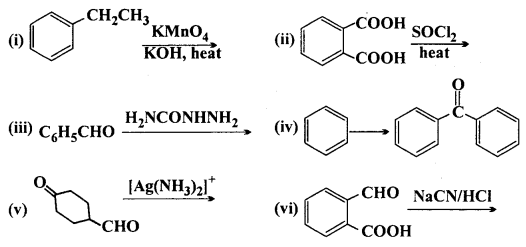
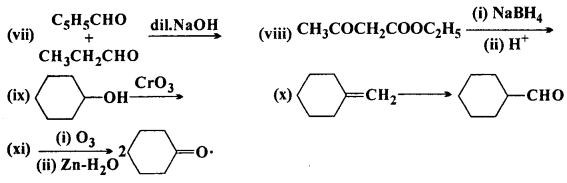
Answer:
Question 18.
Give plausible explanation for each of the following :
(i) Cyclohexanone forms cyanohydrin in good yield but 2,2,6-trimethyIcycIohexa- none does not.
(ii) There are two-NH2 groups in semicarbazide. However, only one is involved in the formation of semicarbazones.
(iii) During the preparation of esters from a carboxylic acid and an alcohol in the presence of an acid catalyst, the water or the ester should be removed as soon as it is formed.
Answer:
(i) In 2, 2, 6- trimethylcyclohexanone, there is steric hindrance of three methyl groups, therefore, it does not form cyanohydrin in good yield as compared to cyclohexanone which does not have steric hindrance.
(ii) The lone pair of electron on NH2 attached to carbonyl group is involved in resonance and hence not available for donation.
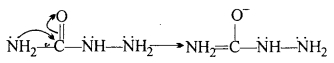
(iii) It is done so that ester formed does not get hydrolysed.
Question 19.
An organic compound contains 69-77% carbon, 11-63% hydrogen and rest oxygen. The molecular mass of the compound is 86. It does not reduce Tollens’ reagent but forms an addition compound with sodium hydrogensulphite and give positive iodoform test. On vigorous oxidation it gives ethanoic and propanoic acid. Write the possible structure of the compound.
Answer:
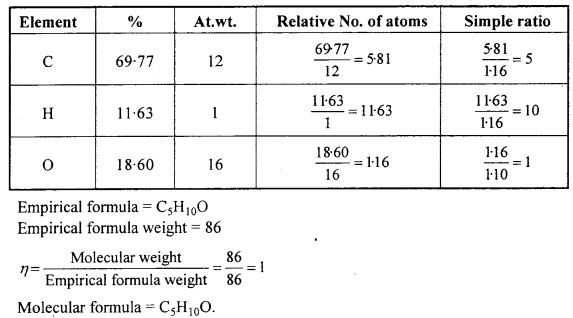
It does not react with Tollens’ reagent, therefore it is not an aldehyde.
It forms addition compound with NaHSO3, therefore it is a Ketone.
It gives Iodoform test therefore it is a methyl ketone.
On the basis of above the possible structure of compound is :
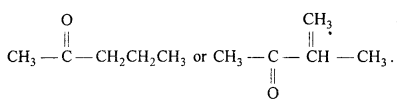
On vigrous oxidation it gives ethanoic acid and propanoic acid, therefore the com¬pound is pen-tan-2-one and not 3-methylbutan-2-one.
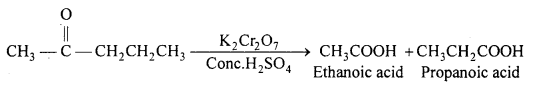
Question 20.
Although phenoxide ion has more number of resonating structures than carboxylate ion, carboxylic acid is a stronger acid than phenol. Why ?
Answer:
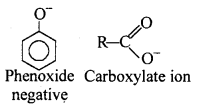
In carboxylate ion negative charge is delocalised over two oxygen atoms which are highly electronegative whereas in phenoxide ion negative charge is delocalised over only one oxygen atom. Carboxylate ion is more stable than phenoxide ion that is why carboxylic acid is more acidic than phenols.
![]()
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Other Important Questions And Answers
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Choose the correct answer :
Question 1.
Formation of cyanohydrin by Ketone is an example of:
(a) Electrophilic addition
(b) Nucleophilic addition
(c) Nucleophilic substitution
(d) Electrophilic substitution.
Answer:
(b) Nucleophilic addition
Question 2.
Which of the following reaction gives Cannizzaro reaction with cone, alkali solution :
(a) Benzaldehyde
(b) Acetaldehyde
(c) Propanaldehyde
(d) All the above.
Answer:
(a) Benzaldehyde
Question 3.
Aldehydes and Ketones react with which of the following to form oxime :
(a) NH3
(b) NH2-NH2
(c) NH2OH
(d) NH2CONH.NH2.
Answer:
(c) NH2OH
Question 4.
Aromatic aldehyde react with primary amines to give :
(a) Urea
(b) Amide
(c) SchifFs base
(d) Oxime.
Answer:
(c) SchifFs base
Question 5.
The reaction of acetaldehyde in basic medium is :
(a) Benzoin condensation
(b) Aldol condensation
(c) Polymerisation
(d) Cannizzaro reaction.
Answer:
(b) Aldol condensation
Question 6.
Which of the following does not give a yellow precipitate with I2 and NaOH :
(a) C2H5OH
(b) CH3CHO
(c) CH3—CO—CH3
(d) HCHO.
Answer:
(d) HCHO.
Question 7.
IUPAC name of the compound of formula Cl3—C—CH2—CHO is :
(a) 3,3,3 trichloropropanol
(b) 1,1,1 trichloropropanol
(c) 2,2,2 trichloropropanol
(d) Chloral.
Answer:
(a) 3,3,3 trichloropropanol
Question 8.
The following precipitate is obtained by the reaction of Fehling solution with ethanol:
(a) Cu
(b) CHO
(c) Cu2O
(d) Cu2O + Cu2O3.
Answer:
(c) Cu2O
Question 9.
Reduction of Aldehydes and Ketones to hydrocarbon occur in the presence of:
(a) Zn/Hg and HCl
(b) Pd/BaSO4
(c) Anhydrous AlCl3
(d) Ni/Pt.
Answer:
(a) Zn/Hg and HCl
Question 10.
Which of the following compound produce white precipitate with HgCl2 :
(a) HCOOH
(b) CH3COOH
(c) C2H5COOH
(d) C3H7COOH.
Answer:
(a) HCOOH
Question 11.
Formic acid :
(a) Is immiscible with water
(b) Reduces ammoniacal silver nitrate
(c) Is three and half times weaker acid than acetic acid
(d) Is obtained on heating KOH.
Answer:
(b) Reduces ammoniacal silver nitrate
Question 12.
Correct order of Acidic strength is :
(a) CH3COOH > CH2ClCOOH > CHCl2—COOH
(b) CHCl2—COOH > CH2ClCOOH > CH3—COOH
(c) CHCl2—COOH > CH3—COOH >CH2ClCOOH
(d) CH2—ClCOOH > CH3 — COOH > CHCl2—COOH.
Answer:
(b) CHCl2—COOH > CH2ClCOOH > CH3—COOH
Question 13.
Benzaldehyde on heating with alcoholic KCN gives :
(a) Benzoin
(b) Benzyl alcohol
(c) Sodium Benzoate
(d) Cinnamic acid.
Answer:
(a) Benzoin
Question 14.
Which of the following does not give silver mirror with ammoniacal AgNO3 :
(a) HCHO
(b) CH3—CHO
(c) CH3—COOH
(d) HCOOH.
Answer:
(c) CH3—COOH
Question 15.
The reagent compound which easily reacts with both acetaldehyde and ace-tone is: ,
(a) Fehling solution
(b) Grignard reagent
(c) Schiff’s reagent
(d) Tollen’s reagent.
Answer:
(b) Grignard reagent
Question 16.
Methyl Ketone is identified by :
(a) Tollen’s reagent
(b) Iodoform test
(c) SchifFs test
(d) Benedict solution.
Answer:
(b) Iodoform test
Question 17.
By Which reagent can Aldehyde and Ketone be differentiated :
(a) Fehling solution
(b) H2SO4 solution
(c) NaHSO3 solution
(d) NH3.
Answer:
(a) Fehling solution
Question 18.
Which compound will give Cannizzaro reaction :
(a) Propionaldehyde
(b) Benzaldehyde
(c) Bromobenzene
(d) Acetaldehyde.
Answer:
(b) Benzaldehyde
Question 19.
Tollen’s reagent is :
(a) Ammonical cuprous chloride
(b) Ammonical cuprous oxide
(c) Ammonical silver bromide
(d) Ammonical silver nitrate.
Answer:
(d) Ammonical silver nitrate.
Question 20.
By the reaction of Formaldehyde with KOH methanol and Potassium formate is formed. This reaction is known as :
(a) Perkin reaction
(b) Claisen reaction
(c) Cannizzaro reaction
(d) Knovengel reaction.
Answer:
(c) Cannizzaro reaction
![]()
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks :
- By the electrolysis of Potassium acetate …………………. is obtained.
- Mixture of Zinc-amalgam and cone, hydrochloric acid is called ………………….
- Bakelite is a polymer of phenol and ………………….
- Benzaldehyde is also known as ………………….
- Ketones do not …………………. Tollen’s reagent.
- 40% aqueous solution of formic acid is called ………………….
- Aldehyde give …………………. precipitate with Fehling solution.
- On heating acetic acid with phosphorous pentaoxide …………………. is formed.
- Paraldehyde is used as a …………………. medicine.
- In Rosenmund’s reduction BaSO4, acts as a …………………. for Pd and controls the reduction of aldehyde to ………………….
- Oxidation of Toluene to benzaldehyde by chromyl chloride is known as ………………….
- By the reduction of Acid chloride by Pd/BaSO4 …………………. compound is formed.
- By the reaction of aldehyde containing a-hydrogen with dilute NaOH …………………. is formed.
- …………………. is obtained by the dry distillation of calcium acetate.
Answer:
- Ethane
- Clemmensen reduction
- HCHO
- Oil of bitter almond
- Reduce
- Formalin
- Red
- Acetic anhydride
- Hypnotic
- Poison, alcohol
- Etard reaction
- Aldehyde
- Aldol
- Acetone.
Question 3.
Match the following :


Answer:
- (e)
- (a)
- (c)
- (b)
- (d)

Answer:
- (c)
- (d)
- (e)
- (b)
- (a)

Answer:
- (e)
- (c)
- (a)
- (b)
- (d).
Question 4.
Write answer in one word/sentence :
- SchifFs reagent gives which colour with Benzaldehyde.
- Write IUPAC name of glacial acetic acid.
- Sodium potassium tartarate associated with alkaline copper sulphate solution is known as.
- Why do carboxylic acids occur as cyclic dimer ?
- Which compound is obtained on heating aromatic aldehyde with acid anhydride in the presence sodium carboxylate ?
- Write the name of the condensation reaction of KCN in benzaldehyde.
- Which gas is obtained by the dehydration of formic acid ?
- Name the reagent which can convert an acid to ester without the use of alcohol.
Answer:
- Pink
- Ethanoic acid
- Fehling solution
- Due to intermolecular hydrogen bonding
- Un-saturated aromatic carboxylic acid (Cinnamic acid)
- Benzoin condensation
- Carbon monoxide
- CH2N2.
![]()
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
(i) Arrange the following acids in the order of increasing acidic strength :
HCOOH, CH3—COOH,C6H5COOH

(iii) Arrange in the increasing order of reactivity :
HCHO,CH3CHO and CH3COCH3
Answer:
(i) Increasing order of acidic strength :
CH3COOH < C6H5COOH < HCOOH
(ii) IUPAC name — 2 methyl propanal
Common name — Iso propyl aldehyde
(iii) Increasing order of reactivity :
CH3COCH3 < CH3CHO < HCHO.
Question 2.
(i) What is Hell- Volhard- Zelinsky (HVZ) reaction ?
(ii) What happens when formic acid is heated ?
Answer:
(i) Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction: When carboxylic acid is treated with Cl2 or Br2 in presence of phosphorus, α- halogenated carboxylic acid is formed. This reaction is known as Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction (HVZ).
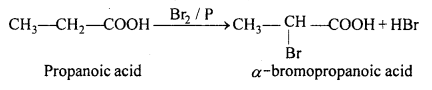
(ii) When formic acid is heated to 160°C it dissociates into CO and H2O.
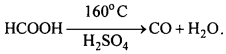
Question 3.
(i) Why ketones are less reactive than aldehydes ?
(ii) Benzaldehyde is less reactive than Acetaldehyde. Why ?
Answer:
(i) Ketones are less reactive than aldehydes because in ketones there are two alky group attached with carbonyl group, due to the positive inductive effect (+ I) of both the alkyl group the positive charge on carbon atom decreases.
Hence, the sensitivity of ketones to the nucleophilic reagents decreases.
In aldehydes, they have only one alkyl group so they are more reactive than ketones.
(ii) —CHO group of benzaldehyde becomes stable due to resonance with benzene ring whereas resonance is not found in acetaldehyde. Benzaldehyde is aromatic and aldehyde is aliphatic.
Question 4.
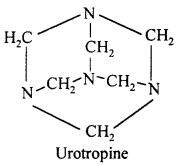
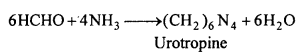
How is urotropine obtained from formaldehyde ? Write its chemical name and structural formula.
Answer:
When formaldehyde is treated with ammonia, urotropine is formed. Its chemical name is hexamethylene tetra ammine or Hexa ammine.
Question 5.
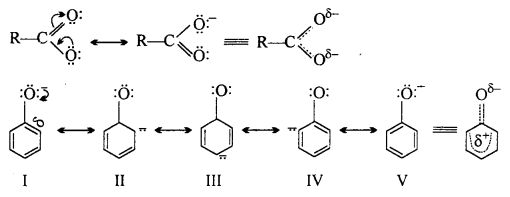
Although phenoxide ion has more number of resonating structures than carboxylate ion. Carboxylic acid is a stronger acid than phenol. Why ?
Answer:
Carboxylate ion and phenoxide ion both achieve stability due to resonance. But carboxylate ion is more stable than phenoxide ion because in it negative charge is delocalised over two highly electronegative oxygen atom whereas in structures II, III and IV of phenoxide ion the negative charge is delocalized on less electronegative carbon. That is why, carboxylic acid is more acidic than phenol.
Question 6.
Write a note on Tollen’s reagent.
Or,
What is Tollen’s reagent ? Write its reaction with Acetaldehyde.
Answer:
Tollen’s Reagent : Ammoniacal silver nitrate solution is known as Tollen’s reagent. When Tollen’s reagent is heated with aldehyde, aldehyde reduces Ag+ to Ag and forms a bright silver mirror on the wall.
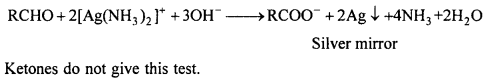
Question 7.
Why boiling point of carboxylic acid is higher than alcohols having same molecular mass ?
Answer:
Carboxylic acid exist as dimer due to hydrogen bond. These bonds are more stronger in acids com¬pared to alcohols, therefore boiling point of carboxylic acid is higher than alcohol.
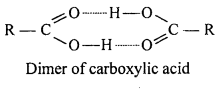
Question 8.
Explain Fehling reaction with equation.
Answer:
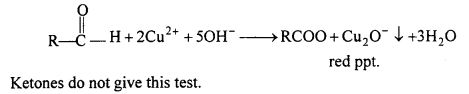
Fehling Reaction : Sodium Potassium tartarate associated with alkaline CuSO4 is known as Fehling solution. When aldehyde is heated with Fehling solution, then aldehyde is oxidized and red precipitate of cuprous oxide is obtained. This is known as Fehling test.
Question 9.
Why is the boiling point of ketone little higher than its corresponding isomeric aldehyde ?
Answer:
Ketones are comparatively more polar than their corresponding isomeric aldehyde because the >C=0 group in Ketone is linked with two electron releasing alkyl group. Thus, the dipole attractive force of ketone is comparatively higher. This is the reason that the boiling point of ketone is comparatively higher than its corresponding isomeric aldehyde.
Question 10.
Among formaldehyde, acetaldehyde and acetone which is more reactive and why ? Explain.
Answer:
Among HCHO, CH3CHO and CH3COCH3, HCHO is more reactive. This can be explained on the basis of:
1. Electron releasing effect : Alkyl groups are electron releasing in nature due to which magnitude of positive charge on carbonyl carbon decreases and hence it becomes less susceptible to nucleophilic attack.
2. Steric effect: The bulkier groups in ketones hinders approach of the nucleophile to the carbonyl carbon. This is known as steric effect.
Thus, HCHO with negligible electron releasing effect as well as steric effect is more reactive.
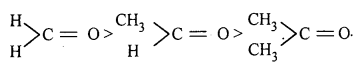
Question 11.
Compare acidic strength of acetic acid, formic acid and chloroacetic acid.
Answer:
Chlorine atom present in chloroacetic acid has strong negative inductive effect (-I). Due to this, electrons of O—H bond easily displaced towards oxygen and it releases H+ easily. CH3 group present in CH3COOH which produces (+ I) effect causes decrease in acidic nature.
In formic acid there is no such group which produces (+ I) or (- I) effect. Hence, formic acid is stronger than acetic acid and chloroacetic acid is stronger than acetic acid. In short chloroacetic acid is stronger than formic acid and formic acid is stronger than acetic acid.
Question 12.
Identify the compounds A, B and C in the following reactions :
![]()
Answer:
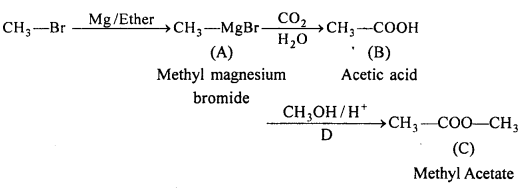
Question 13.
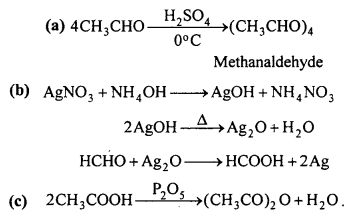
Write down the chemical equation for the following reaction :
(a) Reaction of acetaldehyde with H2SO4 at 0°C
(b) Reaction of formaldehyde with ammonical AgNO3
(c) Heating acetic acid with P2O5.
Answer:
Question 14.
Describe briefly polymerization of acetaldehyde.
Answer:
(i) At normal temperature acetaldehyde in presence of cone. H2SO4, polymerises into para-aldehyde.
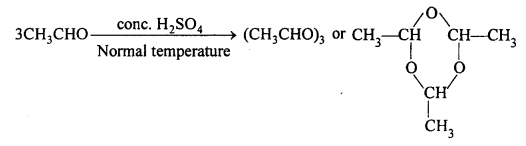
(ii) At 0°C, on passing HCl gas, acetaldehyde changes into meta-aldehyde.
![]()
Question 15.
Write down the difference between formic acid and acetic acid on the basis of following points :
1. Effect of heat.
2. Reaction with acidified KMnO4.
3. Distillation of Ca salt.
4. Reaction with ammoniacal silver nitrate solution.
5. Reaction with PCl5.
Answer:
Differences between Formic Acid and Acetic Acid
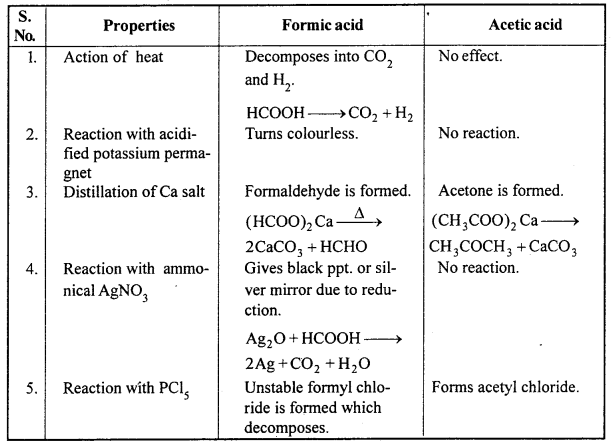
Question 16.
Explain Stephen’s reaction and Benzoin condensation with example.
Answer:
Stephen’s reaction : Alkyl cyanide on reduction with acidified stannous chloride (i.e., SnCl2 + HCl) at room temperature forms aldimine hydrochloride, which on hydrolysis with boiling water gives aldehyde. This specific type of reduction of cyanide is known as Stephen’s reduction.
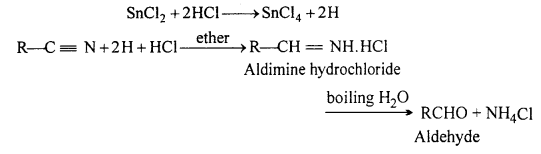
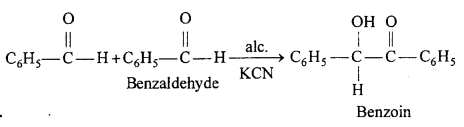
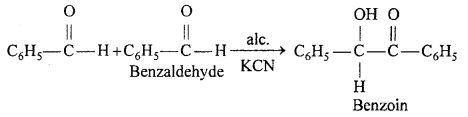
Benzoin condensation : Two molecules of benzaldehyde in presence of alcoholic KCN or NaCN condenses to form benzoin.
![]()
Question 17.
(i) Write short note on Perkin’s reaction.
(ii) What happens when acetone is heated with H2SO4 ?
Answer:
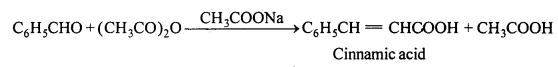
(i) Perkin’s reaction : When aromatic aldehyde is heated in presence of sodium salt of aliphatic acid with anhydride of aliphatic acid, then α,β unsaturated acid is obtained.
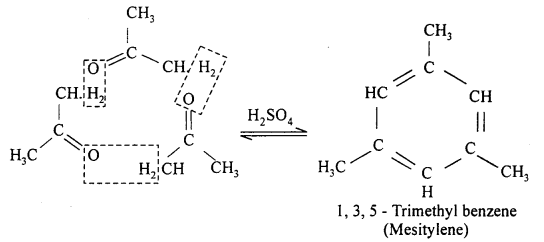
(ii) In presence of H2SO4 three molecules of acetone get condensed and form mesitylene.
Question 18.
What is Vinegar ? Write its two use.
Answer:
6 to 10% aqueous solution of acetic acid is known as vinegar.
Use : 1. In the preservation of pickle, chutney and Jam.
2. In the preparation of basic copper acetate.
Question 19.
What is Formalin ? Write its two use.
Answer:
40% aqueous solution of formaldehyde (H—CHO) is known as Formalin.
Uses : 1. In cleaning the rooms of patients.
2. In the preservation of dead bodies.
Question 20.
What happens when (Give only equations):
(i) Calcium formate is heated alone.
(ii) Calcium benzoate is heated alone.
(iii) Calcium formate is heated with calcium acetate.
(iv) Dry distillation of calcium benzoate and calcium formate takes place.
Answer:
(i) Formaldehyde is formed :
![]()
(ii) Benzophenone is formed :
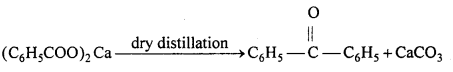
(iii) Acetaldehyde is formed :
![]()
(iv) Benzaldehyde is formed :
![]()
Question 21.
What happens when (Give only equations) :
(i) Formaldehyde reacts with ammonia.
(ii) Calcium formate is heated with calcium acetate.
(iii) Acetone reacts with Grignard’s reagent.
(iv) Acetylene reacts with water in the presence of HgSO4 and H2SO4.
(v) Acetyl chloride to Acetaldehyde.
Answer:
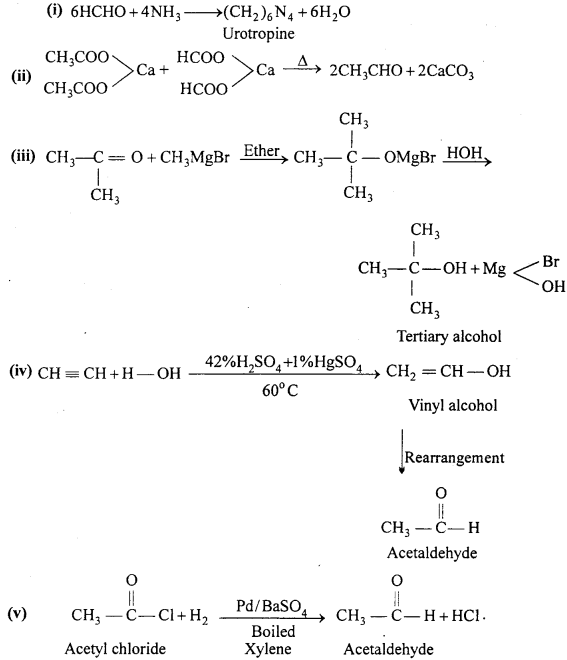
Question 22.
Write down the difference between compounds containing aldehydic group and ketonic group.
Answer:
Differences between Aldehydic and Ketonic group :


Question 23.
An organic compound A (molecular formula C8H8O) gives positive 2,4 DNP test. On treating with iodine and sodium hydroxide it gives yellow precipitate of compound B. Compound A does not give Tollen and Fehling test. On drastic oxidation with potassium permanganate it forms a carboxylic acid C (molecular formula C7H6O2) which is also formed with yellow compound in the above reaction. Identify A, B and C and write the related reactions.
Answer:
Compound A does not give Tollen and Fehling test. Thus, it is a Ketone not aldehyde.
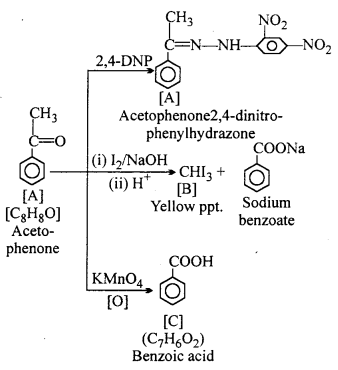
Question 24.
Why trichloroacetic acid is strong like inorganic acid ? Explain, benzoic acid is solid while primary aliphatic acids are liquids. Give reason.
Answer:
Chlorine atom present in trichloroacetic acid is electron withdrawing group. Due to this, release of H+ ion becomes easier as trichloroacetate ion is more stable than its molecule because of dispersal of negative charge on its oxygen. Thus, it behaves as a strong acid like inorganic acid.
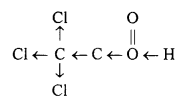
Benzoic acid is solid due to its poiar nature dye to the presence of O-δ – H+δ group and high molecular mass while lower aliphatic acids dimerises due to H-bonding hence they are liquid.
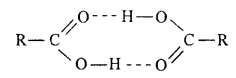
Question 25.
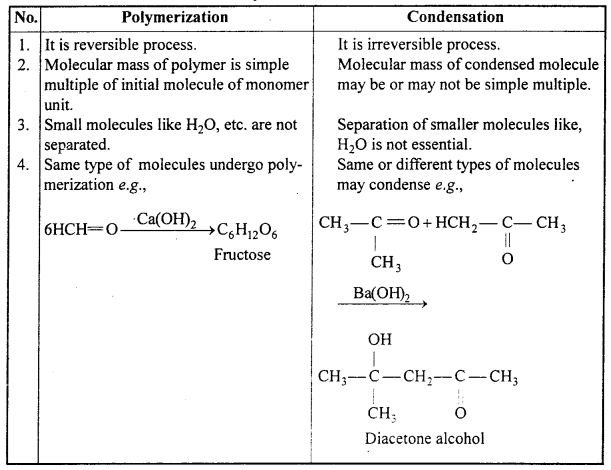
Differentiate Polymerization and Condensation.
Answer:
Differences between Polymerization and Condensation :
![]()
Question 26.
Write down the reactions showing conversion of
(i) Acetic acid into formic acid
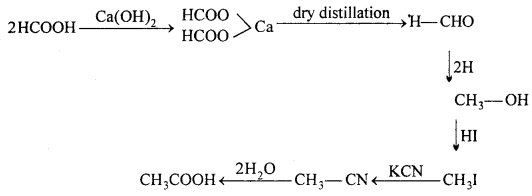
(ii) Formic acid into acetic acid.
Answer:
(i) Conversion of CH3—COOH into H—COOH :
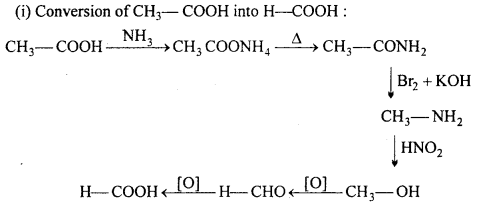
(ii) Conversion of formic acid into acetic acid:
Question 27.
How will you obtain the following :
(i) Acetaldehyde from acetyle chloride
(ii) Acetone from calcium acetate
(iii) Acetic acid from ethyl acetate
(iv) Ethane from acetic acid.
Answer:
(i) Aldehyde can be prepared by the reduction of acetyl chloride with H`2 in the presence of palladium deposited over barium sulphate.
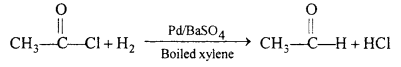
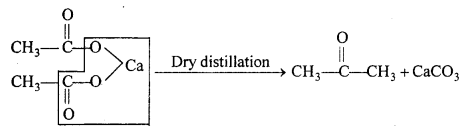
(ii) Calcium acetate on dry distillation gives a acetone.
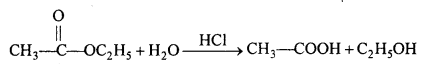
(iii) Ethyl acetate are hydrolysed by mineral acids or alkalies to give acetic acid and ethyl alcohol.
(iv) Acetic acid on reduction with HI in presence of red phosphorus at 500 K to give ethene.
![]()
Question 28.
When liquid A is treated with freshly prepared ammoniacal silver nitrate solution, it give bright silver mirror. When the liquid is reacted with sodium hydrogen sulphite a white crystalline solid is formed. Liquid B also forms white crystalline solid with sodium hydrogen sulphite but it does not give test with ammoniacal silver nitrate. Which among the two liquids is an aldehyde ? Write chemical equations of these reactions.
Answer:
Since, liquid A reduces ammoniacal silver nitrate (Tollen’s reagent). Thus, A is an aldehyde.
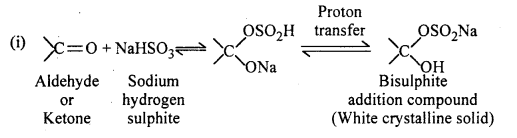
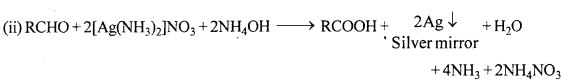
Question 29.
How formic acid is prepared in laboratory ? Write two uses of it.
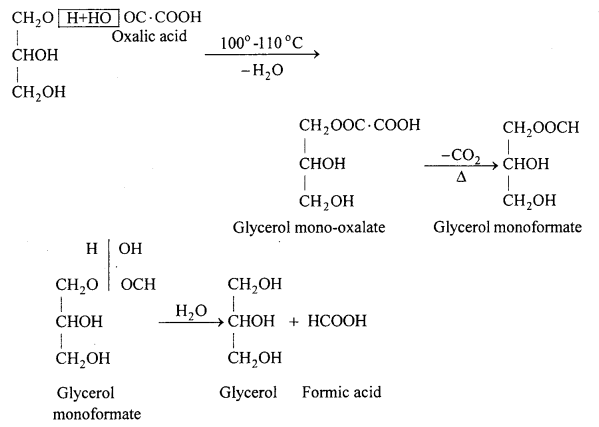
Answer:
Formic acid is prepared in the laboratory by heating glycerol with oxalic acid at 100-110°C in a distillation flask fitted with the thermometer and condenser.
Uses : (i) For dyeing of cotton and woollen cloth.
(ii) In leather industry.
(iii) Preservation of fruits.
(iv) In rubber industry.
(v) In electroplating.
![]()
Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
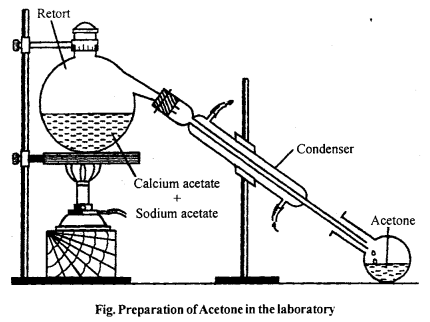
Describe the laboratory method of preparation of acetone. Draw labelled diagram and write down chemical equations.
Answer:
In laboratory, acetone is prepared by dry distillation of anhydrous calcium acetate.
![]()
Method : 30-40 gm of calcium acetate mixed with equal amount of sodium acetate is heated in a glass retort fitted with a condenser and receiver. Acetone is collected in the receiver. The acetone so obtained is not pure. To purify this, it is shaken with saturated solution of sodium bisulphite then crystals of acetone sodium bisulphite salt separate out. The crystal is washed and heated with sodium carbonate and then dried over anhydrous CaCl2 and then distilled at 56°C to get pure acetone.
(CH3)2C = O + NaHSO3 → (CH3)2C(OH)SO3Na
2(CH3)2C(OH)SO3Na + Na2CO3 → (CH3)2C = 0 + 2Na2SO3 + H2O + CO2.
Question 2.
Write down the following reaction giving example and equation :
(a) Iodoform reaction
(b) Tischenko reaction
(c) Gattermann-Koch synthesis
(d) Rosenmund’s reaction.
Answer:
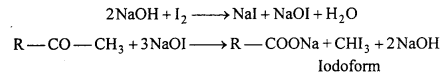
(a) Iodoform (Haloform) reaction : Acetaldehyde or methyl ketone reacts with iodine in presence of alkali to form yellow coloured iodoform. This reaction is known as iodoform test.
(b) Tischenko reaction: Two molecules of benzaldehyde is coupled together in presence of aluminium ethoxide or isopropoxide then benzylbenzoate (ester) is formed.
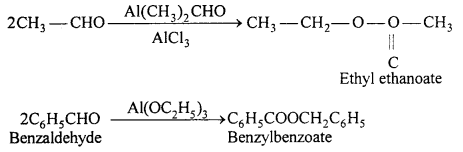
(c) Gattermann-Koch synthesis : Mixture of CO and HCl bubbled through a solution of aromatic hydrocarbon in ether solution in the presence of anhydrous AlCl3, then benzaldehyde is formed.
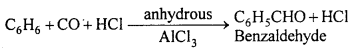
(d) Rosenmund’s reaction : Aldehydes are obtained by the reduction of acid chloride with hydrogen in boiling xylene in presence of a catalyst Pd suspended in BaSO4.
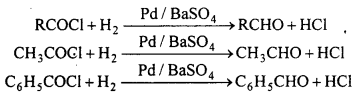
This reaction is called Rosenmund reaction.
Question 3.
Give quick vinegar method of preparation of acetic acid. Give its reaction with phosphorus pentaoxide and phosphorus pentachloride and write its two uses.
Answer:
In this process, a dilute aqueous solution of ethyl alcohol is oxidized in presence of enzyme Mycoderma aceti.
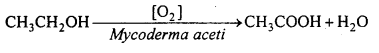
In this process, a wooden vat is fitted with two wooden plates having holes. Between these plates is filled by beech wood savings, moistened with old vinegar solution which is the chief source of Mycoderma aceti. A 10% aqueous solution of ethyl alcohol is dropped slowly from the top of the vat and air is passed at a controlled rate through the holes near the bottom of the vat. Ethyl alcohol is oxidized to acetic acid. This process is called quick vinegar process because vinegar is formed very quickly.
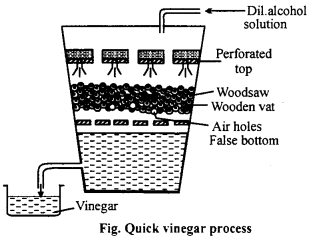
(a) Reaction with P2O5:
![]()
(b) Reaction with PCl5:
![]()
Uses : (i) As a reagent and solvent in the lab.
(ii) As vinegar in the preparation of pickel, chutney etc.
(iii) In the preparation of methyl acetate, ethyl acetate and other esters.
Question 4.
Write a brief note on :
(i) Claisen condensation
(ii) Benzoin condensation.
Answer:
(i) Claisen condensation : When aromatic aldehyde reacts with aliphatic aldehyde or ketone with α-hydrogen, in presence of weak base, α,β unsaturated aldehyde or ketone is formed. This type of condensation is called claisen condensation.
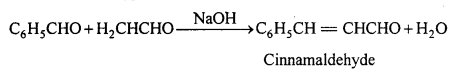
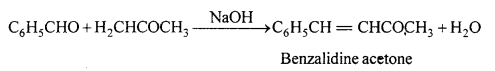
(ii) Benzoin condensation : Two molecules of benzaldehyde in presence of alcoholic KCN orNaCN condenses to form benzoin.
Question 5.
How will you obtain the following from acetic acid (Give only equations):
(i) Acetamide
(ii) Ethyl acetate
(iii) Acetic Anhydride
(iv) TVichloro acetic acid.
Answer:
(i) Acetamide:
![]()
(ii) Ethyl acetate:
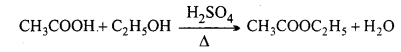
(iii) Acetic anhydride:
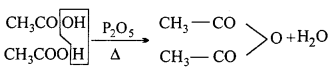
(iv) Trichloro acetic acid:
![]()
Question 6.
What happens when (Write only equations):
(i) Acetone reacts with chloroform,
(ii) Benzaldehyde reacts with acetic anhydride.
Answer:
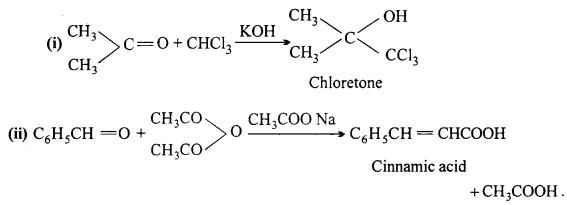
Question 7.
Write notes on the following reactions:
(i) Stephen reaction
(ii) Etard reaction
(iii) Knoevenagel reaction.
Answer:
(i) Stephen reaction : In this reaction, phenyl cyanide is reduced in etheral solution by stannous chloride and hydrogen chloride followed by hydrolysis to form benzaldehyde.
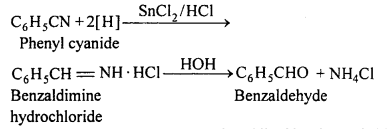
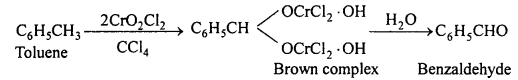
(ii) Etard reaction: In this reaction toluene is oxidised by chromyl chloride dissolved in CS2 or CCl4, a brown complex initially formed is separated. This is then decomposed by water to form benzaldehyde.
(iii) Knoevenagel condensation: Benzaldehyde reacts with compounds having active methylene group (e.g., malonic ester and acetoacetic ester) in the presence of pyridine or glacial acetic acid in acetamide thereby forming α,β unsaturated carbonyl compounds.
For example, with malonic ester, cinnamic acid is formed.
![]()
Question 8.
What happens when (only equation)
(a) On reacting acetone with grignard reagent.
(b) Reaction of acetone with chloroform in presence of KOH.
(c) Benzaldehyde reacts with aniline.
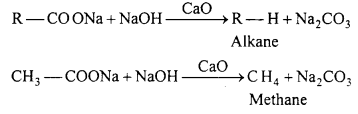
(d) On heating sodium salt of carboxylic acid with soda lime.
(e) Benzyl chloride reacts with acetyl chloride in presence of anhydrous AlCl3.
Answer:
(a) Reaction of acetone with Grignard reagent.
(b) Reaction of acetone with chloroform.
(c) Reaction of benzaldehyde with aniline.
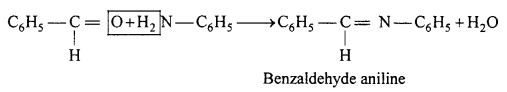
(d) Reaction of sodium salt of carboxylic acid with soda lime.
(e) Reaction of benzene with CH3COCl.

Question 9.
How will you obtain :
(a) Acetaldehyde from acetylene
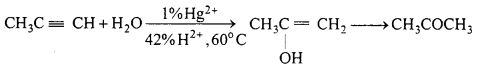
(b) Propanone from propyne.
Answer:
(a) Acetaldehyde from acetylene :
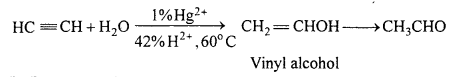
(b) Propanone from propyne :
Question 10.
Starting from acetic acid how will you get the following :
(1) Ethyl alcohol
(2) Ethyl acetate
(3) Methyl bromide
(4) Acetone
(5) Acetic anhydride
(6) Acetamide
(7) Trichloroacetic acid.
Answer:
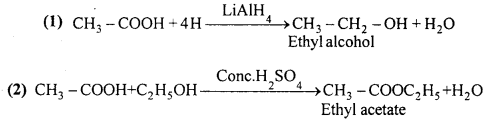
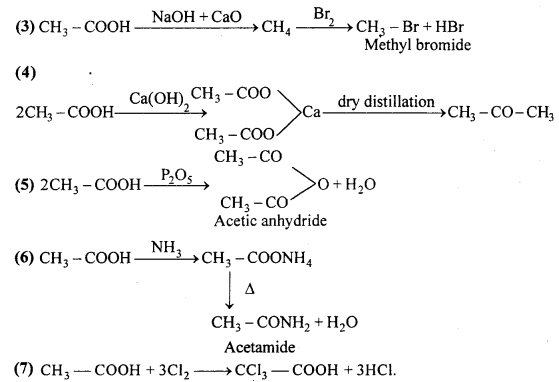
Question 11.
How will you obtain (Give equation):
(i) Benzoic acid from toluene
(ii) Acetic acid from propanoic acid
(iii) Propanol from propanoic acid
(iv) Formic acid from acetic acid.
Answer:
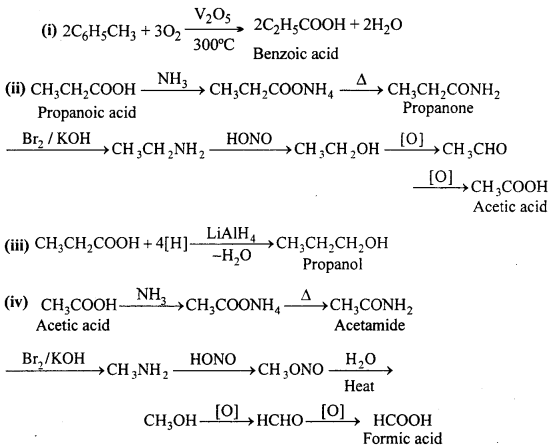
Question 12.
Give chemical equation of the following :
(i) Acetaldehyde from formaldehyde
(ii) Formaldehyde from acetaldehyde
(iii) Acetic acid from formic acid.
Answer:
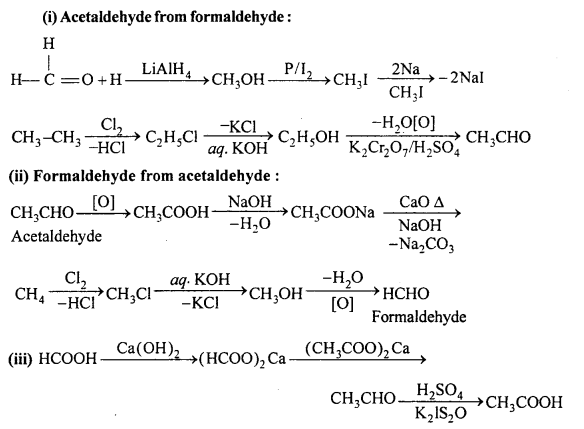
Question 13.
Give equation for reactions of Grignard reagent with following :
(a) CO
(b) HCN
(c) HCOOC2H5
(d) CH3CN.
Answer:
(a) With CO : Aldehyde is obtained.
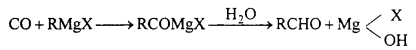
(b) With HCN : Aldehyde is formed.
![]()
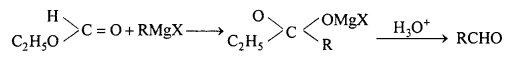
(c) With HCOOC2H5 : Aldehyde is formed.
(d) With CH3CN : Propanone is formed.
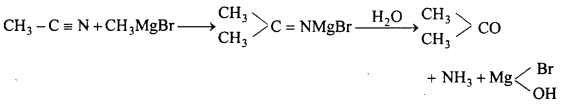
![]()
Question 14.
What happens when (Write only equations):
(i) Acetic acid reacts with ethyl alcohol
(ii) Acetic acid reacts with ammonia
(iii) Acetone reacts with chloroform
(iv) Benzaldehyde reacts with acetic anhydride.
Answer:
![]()
Question 15.
Explain:
(a) Boiling points of aldehydes and ketones are less than corresponding alcohols and acids.
(b) Boiling points of carboxylic acids are higher than carboxylic acid of similar molecular masses.
Answer:
(a) Aldehydes and ketones are polar compounds so their b.p. are higher than non-polar hydrocarbons but less than that of corresponding alcohols and carboxylic acids. Alcohol and carboxylic acids form associated molecules due to intermolecular hydrogen bonding while hydrogen bonding is not possible in aldehydes and ketones because hydrogen atom is not bonded with oxygen atom. Thus, due to presence of intermolecular hydrogen bonding b.p. of alcohol and acids are higher.
(b) Boiling points of carboxylic acids are higher than alcohols of similar molecular mass because acids have stronger hydrogen bonding than alcohols. Thus, molecules of carboxylic acids linked with hydrogen bonds have more attractive force and thus they possess higher boiling points.