MP Board Class 12th Biology Solutions Chapter 12 Biotechnology And its Application
Biotechnology And its Application NCERT Text Book Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Crystals of Bt toxin produced by some bacteria do not kill the bacteria themselves because:
(a) Bacteria are resistant to the toxin,
(b) Toxin is immature
(c) Toxin is inactive
(d) Bacteria enclose toxin in a special sac
Answer:
(c) Toxin is inactive: In bacteria, the toxin is present in an inactive form called prototoxin. This gets converted into the active form when it enters the salivary gland of insects having alkaline medium.
Question 2.
What are transgenic bacteria? Illustrate using any one example.
Answer:
The becteria whose DNA is manipulated to carry and express a foreign DNA is called transgenic bacteria. These microbes are used for producing important bio-chemicals. They have been synthesizing alcohol, enzymes, steroids and antibiotics. Example: Bacillus thuringiensis for Bt cotton, hirudin from transgenic Brassica napus seed. Hirudin is a protein which prevents blood clotting. Its gene was chemically synthesized and introduced in Brassica napus, in which hirudin accumulates in the seed from where it is extracted, purified and used as a medicine.
Question 3.
Compare and contrast the advantages and disadvantages of production of genetically modified crops.
Answer:
Advantages of GM crops :
- Genetic modification has made crops more tolerant to abiotic stresses (cold, drought, heat, salt.)
- Viral resistance can be introduced.
- Over ripening losses can be reduced. Example: Flavr Savr Tomato.
- Enhanced nutritional value of food. Example: Golden Rice.
- Reduced reliance on chemical pesticides.
Disadvantages of GM crops :
- Transgenes in crop plants can endanger native species. Example: The gene for Bt toxin expressed in pollen may end natural pollinators such as honeybees.
- Weeds also become resistant.
- Products of transgenes may be allergic or toxic.
- They cause damage to the natural environment.
![]()
Question 4.
What are Cry proteins? Name an organism which produces it How has man exploited this protein to his benefit?
Answer:
Cry proteins are toxic proteins (insecticidal proteins) secreted by Bacillus thuringiensis in crystal form during a particular phase of their growth. The toxin is coded by a gene called cry.
The genes encoding cry proteins called Bt toxin genes were isolated from B. thuringiensis and incorporated into several crop plants such as Bt cotton, Bt com etc. to provide resistance against insect pests.
Question 5.
What is gene therapy? Illustrate using the example of adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency.
Answer:
It is a collection of methods which allows correction of a gene defect that has been diagnosed in a child or embryo. In gene therapy, normal genes are inserted into a person’s cells or tissues to treat a hereditary defect. Gene therapy is being tried for sickle cell anaemia and Severe Combined Immuno Deficiency (SCID).
In some children, ADA deficiency can be cured by bone marrow transplantation. In others, it can be treated by enzyme replacement therapy, in which functional ADA is given to the patient by injection. However, both of these approaches are not completely curative.
In gene therapy, lymphocytes from the blood of the patient are grown in culture outside the body. A functional ADA cDNA (using a retroviral vector) is then introduced into these lymphocytes, which are subsequently returned to the patient. Because these cells are not immortal, the patient requires periodic infusion of such genetically engineered lymphocytes. However, if the gene isolated from marrow cells producing ADA is introduced into cells at early embryonic stages, the disease could be cured permanently.
Question 6.
Diagrammatically represent the experimental steps in cloning and expressing a human gene (say the gene for growth hormone) into a bacterium like E. coli.
Answer:
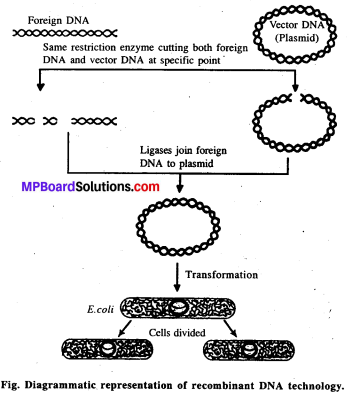
Question 7.
Can you suggest a method to remove oil (hydrocarbon) from seeds based on your understanding of rDNA technology and chemistry of oil?
Answer:
To remove oil from seeds using recombinat DNA technology would involve:
- Identifying the genes that code for oil production.
- Deleting these genes from the seed genome.
- Splicing back together the remaining DNA.
- Putting it back into the cell.
It will be not be very easy because the oils are made up of fatty acids and glycerol. Since, fatty acids are important components of cell membrane system, deleting or switching off of its genes might affect the cell structure itself.
Question 8.
Find out from internet what is golden rice.
Answer:
Golden rice is a variety of rice produced through genetic engineering to biosynthesize β -carotene, a precursor of vitamin ‘A’ in the edible parts of rice. It is intended to produce a fortified food to be grown and consumed in areas with a shortage of dietary vitamin ‘A’.
Question 9.
Does our blood have proteases and nucleases?
Answer:
No.
Question 10.
Consult internet and find out how to make orally active protein pharmaceutical. What is the major problem to be encountered?
Answer:
For making any oral drug or nutritional supplement, the action of digestive enzymes has to be taken into account. Most of the antibiotics and vitamin supplements are made in capsule form to prevent the action of HC1 in the stomach. For protein preparation, the major source is groundnut shells. The protein extracted from the source is predigested so, as to make it absorbable by the digestive system.
![]()
Biotechnology And its Application Other Important Questions and Answers
Biotechnology And its Application Objective Type Questions
1. Choose the Correct Answer:
Question 1.
Triticum aestivum wheat is:
(a) Haploid
(b) Diploid
(c) Tetraploid
(d) Hexaploid.
Answer:
(c) Tetraploid
Question 2.
Man-made cereal is:
(a) Potato
(b) Triticale
(c) Triticum
(d) Sugarcane.
Answer:
(b) Triticale
Question 3.
Wheat grain is a:
(a) Fruit
(b) Seed
(c) Embryo
(d) Glume.
Answer:
(b) Seed
Question 4.
Removal of stamens from the flower during hybridization is called:
(a) Cutting
(b) Self-fertilization
(c) Emusculation
(d) Topnin.
Answer:
(c) Emusculation
Question 5.
New crop is:
(a) Triticale
(b) Rye
(c) Winged bean
(d) Wheat.
Answer:
(a) Triticale
Question 6.
Wheat used in bread is:
(a) Triticum aestivum
(b) Triticale
(c) All species of triticum
(d) Secale.
Answer:
(a) Triticum aestivum
Question 7.
Sonera-64 and Lerma roja-64 A are the varieties of:
(a) Wheat
(b) Rice
(c) Pea
(d) Maize.
Answer:
(a) Wheat
Question 8.
Haploid male plants can be produced by the culturing of:
(a) Filament
(b) Pollen grains
(c) Stamens
(d) Androecium.
Answer:
(b) Pollen grains
Question 9.
Ti plasmid which is used in genetic engineering, is found in:
(a) Escherichia coli
(b) Bacillus thuringiensis
(c) Agrobacterium rhizogenes
(d) Agrobacterium tumefaciens.
Answer:
(d) Agrobacterium tumefaciens.
Question10.
Bt-Toxin is:
(a) Intercellutar lipid
(b) Intercellular crystal protein
(c) Extracellular crystal protein
(d) Lipid.
Answer:
(c) Extracellular crystal protein
Question 11.
The function of Bacillus thuringiensis is:
(a) Bio-metallurgy technique
(b) Bio-insecticides plant
(c) Bio-fertilizers
(d) Bio-mineralization process.
Answer:
(b) Bio-insecticides plant
Question 12.
Non-toxic crystal of Bt are made by bacteria but bacterias are not killed by own because:
(a) Non-toxic is immature
(b) Bacteria is immune resistant
(c) Non-toxic is inactive
(d) Bacteria has non-toxic sac.
Answer:
(c) Non-toxic is inactive
![]()
Question 13.
Genetic transfer through viruses is called:
(a) Sexduction
(b) Transduction
(c) Conjugation
(d) Transformation.
Answer:
(b) Transduction
Question 14.
Biopiracy is realated with:
(a) Discovery of biomolecules and genes
(b) Cultural knowledge
(c) Bio-research
(d) All of these.
Answer:
(d) All of these.
Question 15.
Golden rice is rich in which vitamin:
(a) Vitamin A
(b) Vitamin B
(c) Vitamin C
(d) Vitamin D.
Answer:
(a) Vitamin A
2. Fill in the Blanks:
- …………………………. is the appropriation of another’s knowledge of use of biological resources.
- A ……………………………. is a patent granted by the government to the inventor for biological entities.
- ………………………………….. is a loosely used term for molecules that are present in organisms.
- …………………………………… is a group of standards which is used in control of relations between our work and bio-diversity.
- The production of product, its extraction and process is called ……………………………….
Answer:
- Biopiracy
- Biopatent
- Bio-molecules
- Bio-code of conduct
- Downstream.
3. Match the Following:

Answer:
- (b)
- (d)
- (a)
- (c).
4. Answer in One Word/Sentence:
- Give the name of first transgenic crop.
- What is the name of insect resistant protein which is transferred in Bt Cotton?
- What is the name of first man-made insulin?
- In which organism nif-genes are found?
- Give the name of an antiviral protein.
Answer:
- Tobacco
- Cry protein
- Humulin
- Rhizobium
- Interferon.
Biotechnology And its Application Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name the organism whose genetic material has been altered using genetic engineering techniques.
Answer:
Genetically Modified Organisms (GMO).
Question 2.
Name the crops which are prepaired with the help of biotechnology.
Answer:
Bt cotton, Bt maize, paddy, tomato, potato and soya been.
Question 3.
Through whom Bt toxin protein originates?
Answer:
By Bacillus thuringiensis.
Question 4.
By which Bt toxin is coded?
Answer:
By cry genes Bt toxin is coded.
Question 5.
Full form of RNAi.
Answer:
RNA interference (RNAi).
Question 6.
Name the therapy which is help of missing of defective ones in order to correct genetic disorders.
Answer:
Gene therapy.
Question 7.
Name the scientific name of bacteria in which be form organism toxin.
Answer:
Bacillus thuringiensis.
![]()
Biotechnology And its Application Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is genetically modified (GM) food ? Give two examples.
Answer:
Genetically modified food (GM food): The food substances produced from ge-netically modified crops or transgenic crops is called GM food. This food differ from conventionally developed varieties in the following aspects :
- GM food contains antibiotic resistance gene itself.
- It contains protein produced by transgene, e.g. Cry protein in insect resistance varieties.
- These GM foods contain enzyme produced by the antibiotic resistance gene that was used during gene transfer by recombinant DNA technology.
Examples of GM Crops, Food and Fruits:
1. Flavr Savr Tomato : It is the first food containing genetically engineered DNA. . These tomatoes contain genes for antibiotic resistance for kanamycin.
2. Maize : GM maize has a bacterial gene which increases its resistance to pests and
diseases. It also has a gene for ampicillin resistance which is harmful for us, therefore introduction of GM maize is opposed by many European countries. ,
3. Rape oil seed : It is a new type of plant that contain genes for resistance to the herbicide Basta. It has for more potential, dangers and can become a weed and would be impossible to control with Basta. It could cross fertilize with relatives such as wild mustard, thus, spreading the resistance to wild plants. Such type of environmental risks could occur with genetically modified rapeseed crop. They might also effect food chains in unpredictable ways.
Question 2.
Write down the advantage of GM Crops.
Answer:
Advantages of GM crops :
- Genetic modification has made crops more tolerant to abiotic stresses (cold, drought, heat, salt.)
- Viral resistance can be introduced.
- Over ripening losses can be reduced. Example: Flavr Savr Tomato.
- Enhanced nutritional value of food. Example: Golden Rice.
- Reduced reliance on chemical pesticides.
Disadvantages of GM crops :
- Transgenes in crop plants can endanger native species. Example: The gene for Bt toxin expressed in pollen may end natural pollinators such as honeybees.
- Weeds also become resistant.
- Products of transgenes may be allergic or toxic.
- They cause damage to the natural environment.
![]()
Question 3.
What is perfect agriculture? How is this method better than traditional method? Explain.
Answer:
Perfect agriculture is a method of agriculture which is sustainable, perfect and harmless. Green revolution and there after the production of agricultural crops has definitely increased due to use of new and high yielding varieties, development of irrigation facilities, increased irrigated area, use of fertilizers etc. but it results many problems such as loss of soil fertility, pollution of food and water and diseases. The resistance power of plants and human heings falls slowly. Food and water borne diseases affecting the health of human beings and animals.
All of these conditions and events taking place due to the modem commercial agriculture. Therefore, it would become necessary to develop a method of agriculture which would be free from above mentioned demerits. This kind of agriculture is called to be as perfect or sustainable agriculture. Organic agriculture is the best example of perfect agriculture.
Question 4.
What is organic cropping? What are its basis?
Answer:
Organic agriculture: Organic agriculture is a method of agriculture which does not allow the use of synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, insecticides, weedicides, plant growth regulators, substances of animal origin and genetically modified bacteria. In this method biofertilizers, crop rotation methods are used to increase crop production and biopesticides are used to control insects and weeds.
Thus, organic farming is a holistic way of agriculture which tries to bridge the widening gap between man and nature. If has the commitment of meeting production needs on one hand and sustaining resources tand ecosystem function on the other hand. Thus, organic farming is an alternative agriculture production system which avoid or largely excludes the use of synthetic chemicals, fertilizers, pesticides and growth regulating hormones and live stock additives.
Basics of Organic agriculture :
- Organic agriculture is based on improvement of soil, plants, animals, man and global scinery and make it sustainable.
- Organic agriculture is based on those ecosystems and biocycles which utilize that organisms which would be promoted.
- It is based on the principle which are related with making pollution free environment and possibilities of life.
- It is also based on saving environment and health of present and future generations.
Question 5.
What is gene library?
Answer:
Gene library: Several clones of cells, each clone containing one or a few foreign genes representing almost all the genes of an organism is referred to as genes library. From this gene library it is possible to identify a clone containing gene of interest. In order to obtain gene library of an organism, its genome is first cut into smaller DNA fragments containing one or a few genes such as fragments can be cloned into a cell which may brfthat of bacteria, yeast, insects, plant or animal cell.
When such a cell multiplies to form a group of cells, all cells will contain the same foreign DNA fragment which was introduced initially. These cells which have similar foreign DNA fragment are referred to as a clone of cells. Several clones of cells each clone containing one or a few foreign genes are finally obtained and is called gene library.
![]()
Biotechnology And its Application Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is eugenics? Write importance of eugenics.
Answer:
Eugenics: The branch of biology which deals with the study of improvements of human race is called eugenics.
Importance:
- Development of selective reproduction in similar species.
- Transfer of genetic materials in various organisms.
- Development of GM food and GM crops.
- Gene cloning
- Gene therapy, etc.
Question 2.
Explain the following in brief:
- Biopiracy,
- Biopatent.
Answer:
1. Biopiracy : Some organisations and multinational companies exploid biological resources and genetical resources indegenous to a country without proper authorisation. This is called biopiracy. In fact it is illegal removal of biological material. The process of biopyracy involves collection of samples of biological sources, which can be done unnoticed. This biological material is then subjected to product development for use on a commercial scale.
Today a range of biological resources are facing biopiracy. It includes plants and animals, micro-organisms genetic materials etc. Western companies are getting great benefits from using the knowledge and biological resources of the third world communities.While the companies stand to make huge revenue from this process, the local communities are unrewarded and infact, may have to buy the products of these companies at high prices.
To check illegal exploitation of biological resources Government of India has signed the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), which opens country natural resources for foreign exploitation.
2. Biopatent : The protection given by government to an inventor of biological material to secure him for a specific time the exclusive right of manufacturing, exploiting, using and selling of an invention is called biopotent.
Today manufacturing companies are being granted patents for products and technologies that make of biological resources, such as plants and animals, genetic materials which was identified developed and used by farmers and indegenous peoples.
There is growing worldwide opposition to the granting of patents on biological materials such as genes, plants, animals and human. Farmers and indegenous peoples are outaged that’ plants that they developed are being ‘hijacked’ by companies. Groups are diverse as religious leaders, parliamentarians and environment NGOs are intensifying campaign against corporate patenting of living things.
Question 3.
Describe the application of genetic engineering in the field of Agriculture and Medicine.
Answer:
(A) Application of Genetic engineering or Biotechnology in Agriculture : Genetic engineering is found to be very beneficial in agriculture. Its important use in agriculture are:
1. Increase in photosynthetic efficiency: An increase in photosynthetic efficiency of crop plants can be achieved by introducing suitable Carbon dioxide Fixation Gene (cfx) from any plant into the crop plants.
2. Transfer of nitrogen fixing ability: Number of symbiotic and non-symbiotic micro-organism have capacity of fixing atmospheric nitrogen. Nitrogen fixers are found to possess nitrogen fixing gene (nif genes) which are located on chromosomes or plasmids. Introduction of nif gene in crop plants results in ability in crop plants to fix atmospheric nitrogen and reduction in the use of chemical nitrogen fertilizers.
3. Disease resistance in crop plants : Plant breeders at present are developing high yield varieties by transferring gene for disease resistance through conventional breeding.
4. Plant tissue in crop improvement: Some of the areas of plant improvement where tissue culture has been applied with success are as follows :
- Rescuing hybrids through embryo culture.
- Multiplication of germplasm.
- Production of disease free plants.
- Production of haploid through another culture.
- Somaclonal variation.
- Somatic hybridization.
- Cryopreservation of germplasm.
5. VAM (Vesicular-Arbuscular Mycorrhiza) fungi with Rhizobium can boost the yields: Recently there has been a new dimension to this farm practice by the way of increasing Rhizobium inoculation effect by simultaneous inoculating seeds with VAM as well as Rhizobium culture.VAM are structural modification of hyphae helping in absorption and storage of phosphorus.
(B) Application of Genetic engineering in Medical field :
1. The hereditary diseases like colour-blindness, haemophilia which are caused by recessive genes and also many inborn metabolic disorders due to defective genes as alkaptonuria, phenylketonuria can be cured with the gene therapy.
2. Substances like vitamins, hormones, amino acids and antibodies can be synthesized in bacteria by introducing the genes which code these substances. In this way bacteria can be used as biofactories for the synthesis of these substances.
3. Production of insulin: Insulin is medicine used for the treatment of diabetes. Initially it is derived from animals (pig and cows) but today it is produced by gene splicing.
4. Hepatitis-B vaccine: Hepatitis-B is a viral disease of liver. Today this vaccine is prepared with the help of genetic engineering.