MP Board Class 11th Accountancy Important Questions Chapter 12 Provision and Reserves
Provision and Reserves Important Questions
Provision and Reserves Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Choose the correct answers:
Question 1.
Which reserve is not shown in balance sheet –
(a) General reserve
(b) Specific reserve
(c) Secret reserve
(d) Capital reserve.
Answer:
(c) Secret reserve
Provision and Reserves Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is General Reserve? What are its objectives?
Answer:
Reserve mean amounts set aside out of profits and other surpluses to meet future uncertainties. In other words, a reserve is meant for meeting any unknown liability or loss in the future. General Reserves are not meant for any purpose but can be utilised for any exigencies. General reserves are created for the following purposes:
- To compensate the unknown loss arising in future.
- To strengthen the financial position of the business.
- For reinvesting the profits in the business so as to expand the Current business.
- In case of companies, to maintain the rate of dividends for the shareholders.
Question 2.
Define secret Reserve. Explain the objects of secret Reserve.
Answer:
The main objects of secret reserve are:
- To strengthen the internal situation of the business.
- To compensate uncommon losses.
- To show reduced profit of the company.
- To hide the errors committed by Managers.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the methods of creating secret Reserve.
Answer:
Secret reserve is mainly created by showing Assets at a value less than its actual value or by way of showing Exaggerated liabilities. Some main methods adopted are:
- To provide more than required depreciation on Fixed Assets.
- Not to show Goodwill in the books.
- Not disclosing Accrued Incomes in the balance sheet.
- Not adjusting prepaid expenses.
- To show liabilities at a higher value than its actual value.
Question 4.
Mention three characteristics of Reserve.
Answer:
The characteristics or features of ‘Reserves’ are:
- It is created out of net profits or divisible profits. As such the reserves are also termed as ‘Retained Earnings’ or ‘Undistributed Profits.’
- Creation of Reserves is not a legal necessity. It is created voluntarily for strengthening the financial position of the business and for meeting an unforeseen Exigencies in the future.
- It is not created to meet any known liability or depreciation in the value of assets but for meeting an unknown liability or loss in the future.
Question 5.
What do you mean by bad debt reserve?
Answer:
Bad debt is a business loss for adjusting this loss, a reserve is maintained each year from the debtors. This reserve is known as bad debt reserve, it is the amount of provision to write off bad debt in future.
![]()
Question 6.
What do you mean by bad and doubtful debt?
Answer:
Provisions for Bad and Doubtful Debts: At the end of the year there are certains debtors from whom it is expected that some amount may be received and some amount may not be received and there may be debtors from whom it is expected that no amount will be received. Hence, provision made for such losses or doubtful amount is known as “Provision or Reserve for Bad and Doubtful Debts.” Its amount and time is not known exactly. Hence provision is made for an expected amount.
This provision is deducted from the amount of debtors in balance sheet. If provision made is more than the amount of doubtful debts then such excess will be termed as Reserve and will be shown in the liability side of balance sheet. Accounting Treatment: The amount of provision or reserve for bad and doubtful debts is shown in the debit side of Profit and Loss Account and is deducted from the amount of debtors in Balance Sheet in the asset side.
Provision and Reserves Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Distinguish between Reserves and provisions.
Answer:
Difference between Reserves and Provisions:
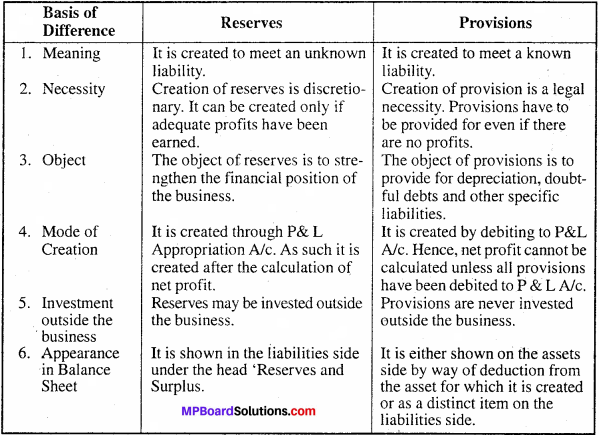
Question 2.
Why a provision for discount on debtors and creditors are maintained in the business?
Answer:
Discount provision on sundry debtors:
When the sundry debtors make their payment before the prescribed time, they are allowed some concession. This concession is called cash discount. It is a loss to the business. In certain condition, the trader keeps a reserve to allow discount on debtors for future, in anticipation.
This reserve or provision is known as discount provision on sundry debtors. It is calculated after the deduction of further bad debt and new reserve from debtors at a percentage. This amount is shown in the debit side of profit and loss account and is also deducted from debtors in the balance sheet.
Discount provision on sundry creditors:
When the trader makes the payment before the stipulated time, he is allow’ed some discount. It is an income of the business. In certain condition, the trader keeps a reserve in anticipation that some discount may receive in future. This reserve on provision is called, ‘Discount provision on sundry creditors’. It is shown in the credit side of P&L A/c and is deducted from the sundry creditors in the balance sheet.
Question 3.
Distinguish between revenue reserve and capital reserve.
Answer:
Difference between Revenue and Capital reserve
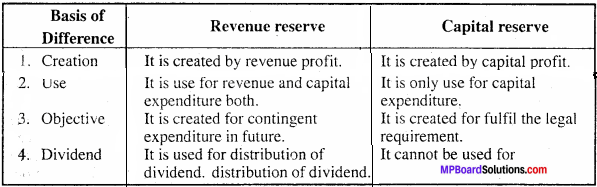
Question 4.
Explain the various types of Reserve.
Answer:
Reserve can be classified as follows:
1. Revenue reserve – Revenue reserves are those reserve which are created out of profit (revenue) earned through the business activities. Any reserve which is not capital reserve is called capital reserve.
2. Capital reserve – Capital reserve is created by capital profit or capital receipt. The profit which has not been earned from general business activities of the firm are termed as capital profit.
3. Specific reserve – When any part of profit the of business is kept for any specific purpose and it is utilised for that specific purpose then such reserve are called as specific reserve.
4. General reserve – A part of reserve which is created out of revenue reserve to meet out future contingencies and risk is called as general reserve.
5. Secret reserve – It is not shown in liabilities. If any reserve which is not shown in balance sheet which is called secret reserve.