MP Board Class 7th Science Solutions Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants
Nutrition in Plants Intext Questions
Question 1.
Boojho wants to know how plants prepare their own food?
Answer:
Plants are the only that can prepare food for themselves by using water, carbon dioxide and minerals.
Question 2.
Paheli wants to know why our body cannot make food from carbon dioxde, water and minerals like plants do?
Answer:
Our body do not have chlorophyll.
Question 3.
Boojho wants to know how water and minerals absorbed by roots reach the leaves?
Answer:
Water and minerals are transported to the leaves by the vessels which run like pipes throughout the roots, stems and leaves of the plant. They form a continuous path or passage for the nutrients to reach the leaves.
Question 4.
Paheli wants to know what is so special about the leaves that they can synthesize food but other parts of the plant cannot?
Answer:
Because the leaves have a green pigment called chlorophyll.
![]()
Question 5.
Boojho has observed some plants with deep red, violet or brown leaves. He wants to know whether these leaves also carry out photosynthesis?
Answer:
No.
Question 6.
Paheli wants to know whether mosquitoes, bed bugs, lice and leeches that suck our blood are also parasites?
Answer:
Lice are parasites. Mosquitoes are not parasites because they suck blood to incubit their eggs and not for nutrition.
Question 7.
Boojho is confused. If the pitcher plant is green and carries out photosynthesis, then why does it feed on insects?
Answer:
Because these plants do not get enough nutrition from the soil as required.
Question 8.
Boojho wants to know how these organisms acquire nutrients. They do not have mouths like animals do. They are not like green plants as they lack chlorophyll and cannot make food by photosynthesis?
Answer:
These organisms acquire food from dead organisms.
Question 9.
Paheli is keen to know whether her beautiful shoes, which she wore on special occasions, were spoiled by fungi during the rainy season. She wants to know how fungi appear suddenly during the rainy season?
Answer:
The fungal spores are generally present in the air. When they land on wet and warm things they germinate and grow During rainy season, there are more chances of things getting wet So, fungi spoil more things in rainy season.
Question 10.
Boojho says once his grandfather told him that his wheat fields were spoiled by a fungus. He wants to know if fungi cause diseases also?
Answer:
Yes, fungi causes diseases in plants, animals and humans. However, some fungi are also used is medicines.
Nutrition in Plants Text book Exercises
Question 1.
Why do organisms need to take food?
Answer:
Food is needed by all living organisms for the following purposes:
- Get energy to do work.
- Build up body.
- Improve resistance power against diseases and protects us from infections.
- Replacement and repairing damaged part in the body.
- Maintain the functions of the body.
![]()
Question 2.
Distinguish between a parasite and a saprotroph?
Answer:
Distinguish Parasite and Saprotroph:
Parasite:
- They derives nutrients from the body of some other living organisms.
- They use the heterotrophic mode of nutrition.
- They mostly live on or in the host.
- Examples: Tapeworm, Round warm, Cuscutta, Puccinia, etc.
Saprotroph:
- They derives nutrients from dead and decaying organisms.
- They use saprotrophic mode of nutrition.
- They live on dead and decaying stuff.
- Examples: Mushrooms, Bacteria, Yeast, etc.
Question 3.
How would you test the presence of starch in leaves?
Answer:
Starch Test:
Take the green leaf to be tested. Boil it in water for 5 minutes (approximately). Keep it in the 60% angle amyle alcohol at 60°C till it becomes colourless. Now take the colourless leaf out from alcohol and wash it with cold water. Also pour few drops of dilute iodine solution on the leaf. The leaf becomes very blue with the solution which proves the presence of starch is the leaf.
![]()
Question 4.
Give a brief description of the process of synthesis of food in green plants?
Answer:
The leaves have a green pigment called chlorophyll. It helps leaves to capture the energy of the sunlight. This energy is used to synthesize (prepare) food from carbon dioxide and water. Since the synthesis of food occurs in the presence of sunlight, it is called photosynthesis (Photo: light: synthesis: to combine).
So we find that chlorophyll, sunlight, carbon dioxide and water are necessary to carry out the process of photosynthesis. It is a unique process on the earth. The solar energy is captured by the leaves and stored in the plant in the form of food. Thus, sun is the ultimate source of energy for all living organisms.
During photosynthesis, chlorophyll containing cells of leaves, in the presence of sunlight, use carbon dioxide and water to synthesise carbohydrates. The process can be represented as an equation.
![]()
During the process oxygen is released. The carbohydrates ultimately get converted into starch. The presence of starch in leaves indicates the occurrence of photosynthesis. The starch is also a carbohydrate.
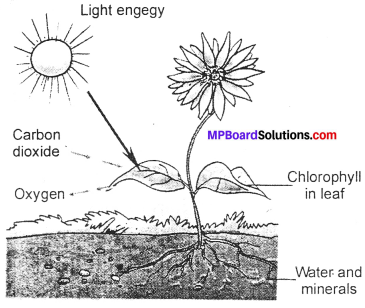
Question 5.
Show with the help of a sketch that the plants are the ultimate source of food?
Answer:
Question 6.
Fill in the blanks:
- Green plants are called …………….. since they synthesise their own food.
- The food synthesised by the plants is stored as ……………..
- In photosynthesis solar energy is captured by the pigment called ……………..
- During photosynthesis plants take in …………….. and release
Answer:
- Autotrophs
- Starch
- Chlorophyll
- Carbon dioxide, oxygen.
![]()
Question 7.
Name the following:
- A parasitic plants with yellow, slender and tubular stem.
- A plant that has both autotrophic and heterotrophic mode of nutrition.
- The pores through which leaves exchange gases.
Answer:
- Cuscuta (Amarbel)
- Pitcher plant
- Stomata.
Question 8.
Tick the correct answer:
(a) Amarbel is an example of –
(i) Autotroph
(ii) Parasite
(iii) Saprotroph
(iv) Host.
Answer:
(ii) Parasite
(b) The plant which trape and feeds on insects is –
(i) Cuscuta
(ii) China rose
(iii) Pitcher plant
(iv) Rose.
Answer:
(iii) Pitcher plant.
Question 9.
Match the items given in Column I with those in Column II:

Answer:
(i) (d)
(ii) (a)
(iii) (e)
(iv) (b)
(v) (c)
![]()
Question 10.
Mark “T” if the statement is true and “F” if it is false:
- Carbon dioxide is released during photosynthesis. (T/F)
- Plants which synthesise their food themselves are called saprotrophs. (T/F)
- The product of photosynthesis is not a protein (T/F)
- Solar energy is converted into chemical energy during photosynthesis. (T/F)
Answer:
- False (F)
- False (F)
- True (T)
- True (T)
Question 11.
Choose the correct option from the following:
Which part of the plant gets carbon dioxide from the air for photosynthesis –
(i) Root hair
(ii) Stomata
(iii) Leaf veins
(iv) Sepals.
Answer:
(ii) Stomata.
Question 12.
Chose the correct option from the following:
Plants take carbon dioxide form the atmosphere mainly through their –
(i) Roots
(ii) Stem
(iii) Flowers
(iv) Leaves.
Answer:
(iv) Leaves.
Nutrition in Plants Additional Important Questions
Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Choose the correct alternative:
Question (i)
The green coloured pigment present in plants is ………….
(a) Xanthophyll
(b) Haemoglobin
(c) Chlorophyll
(d) None of these.
(c) Chlorophyll
Question (ii)
The life processes that provide energy are ……………
(a) Respiration
(b) Nutrition
(c) Both respiration and nutrition
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Both respiration and nutrition
Question (iii)
Which of these are autotrophs …………..
(a) Green plants
(b) All plants
(c) All animals
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Green plants
![]()
Question (iv)
………….. changes solar energy into chemical energy.
(a) Oxygen
(b) Carbon – di – oxide
(c) Water
(d) Chlorophyll.
Answer:
(d) Chlorophyll.
Question (v)
………….. is saprophyte.
(a) Fungus
(b) Cuscuta
(c) Money plant
(d) Mosquito.
Answer:
(a) Fungus
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks:
- Resin, gum, latex are ……………. substances of plants.
- …………….. is the mode of taking food by an organism and its utilisation by the body.
- The plant on which it climbs is called a ……………
- Plants which use saprotrophic mode of nutrition are called …………..
- Oxygen is produced during ……………..
Answer:
- Excretory
- Nutrition
- Host
- Saprotrophs
- Photosynthesis.
Question 3.
Which of the fallowing statements are true (T) or false (F):
- All organisms take food and utilise it to get energy for the growth and maintenance of their bodies.
- Chlorophyll and sunlight are not the essential requirements for photosynthesis.
- Solar energy is stored by the leaves with the help of chlorophyll.
- Oxygen is not produced during photosynthesis.
- Only a few plants adopt other modes of nutrition like parasitic and saprotraphic.
Answer:
- True (T)
- False (F)
- True (T)
- False (F)
- True (T).
![]()
Question 4.
Match the items is Column A with Column B:

Answer:
(i) (b)
(ii) (d)
(iii) (a)
(iv) (b).
Question 5.
Name the following :
- A plants food factory.
- Living on another organisms and derive food from them.
- A chlorophyll containing partner, which is an alga, and a fungus live together.
Answer:
- Leaf
- Parasitic
- Lichens
Nutrition in Plants Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
How many types of nutritions are there?
Answer:
There are two types of nutritions. These are holophytic nutrition and holozoic nutrition.
Question 2.
How do symbiotic live?
Answer:
Symbiotic live with host and parasite which depend on host benefit.
![]()
Question 3.
What are autotrophs? Give examples.
Answer:
The organism who can prepare their own food utilising sunlight, carbon dioxde and water, are known as autotrophs.
Examples: All green plants are autotrophs.
Question 4.
Define photosynthesis?
Answer:
The process by which the green plants prepare their food using carbon dioxide and water in the presence of chlorophyll and light is called photosynthesis.
Question 5.
What is the function of chlorophyll?
Answer:
Chlorophyll helps leaves to capture the energy of the Sun.
Question 6.
What are algae?
Answer:
The slimy green patches in ponds or in other stagnant water bodies are called algae.
Question 7.
What is the purpose of starch test?
Answer:
To confirm the presence of starch in the green plants.
Question 8.
Name two herbivorous animals?
Answer:
Deer, cow.
Question 9.
Name two omnivorous animals?
Answer:
Dog, cat.
![]()
Question 10.
Name two carnivorous animals?
Answer:
Tiger, lion.
Question 11.
Name two leguminous plants?
Answer:
Gram, pea.
Question 12.
Name two insectivorous plants?
Answer:
Sundew, Aldrovenda.
Question 13.
Which bacteria can convert nitrogen into soluble term?
Answer:
Rhizobium.
Question 14.
Define autotrophs?
Answer:
Green plants synthesise their food themselves by the process of photosynthesis. They are autotrophs.
Nutrition in Plants Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
How do the exchange of gases occur in plants?
Answer:
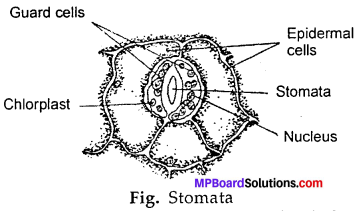
In case of plants the lower surface of leaves have small pores called stomata. These are provided by two guard cells which control the opening or closing of the stomata. When the concentration of O2 gas increases during photosynthesis the guard cells open and O2 gas is given out and if concentration of CO2 gas increases during respiration, the guard cells cause CO2 gas to go out of the cells. This is how the exchange of gases occur in plants.
Question 2.
How many types of heterotrophs are there? Give examples.
Answer:
Organisms which depend upon plants and other organisms for their food are called heterotrophs. Heterotrophs can further be classified as:
1. Herbivorous Animals:
The organisms or animals who eat plants and plant products.
Examples: cow, horse, goat, etc.
2. Carnivorous Animals:
The animals who eat flesh of other animals are called carnivorous.
Examples: lion, tiger, wolf, etc.
3. Omnivorous Animals:
The animals who eat both plant and animals are called ominivorous animals.
Examples: man, cat, dog, crow, etc.
![]()
Question 3.
W’hat is the difference between ‘heterotrophs and autotrophs’?
Answer:
The differences between two are:
Heterotroph:
- These are organism which can not make their own food.
- They do not have chloroplast.
Autotroph:
- They can make their own food.
- They have chloroplast.
Question 4.
Give two examples of insectivorous plants?
Answer:
The plants which have the special system to trap the insects and kill them are called insectivorous plants. The pitcher plant and venus faly trap plants. In the pitcher plant, the leaf is modified in form of a pitcher. When any insect visits this pitcher it is trapped and killed in it.
Question 5.
What is the difference between holophytic and holozoic type of nutrition?
Answer:
Those living beings such as plants who prepare their own food are called autotrophic and this type of nutrition is called as holophytic type of nutrition.
Those living beings who cannot prepare their own food but depend on food prepared by some other living beings are called heterotopic. This type of nutrition is called holozoic nutrition.
![]()
Question 6.
How is Sun the ultimate source of energy for all the living beings?
Answer:
Green plants prepare food utilising sunlight. All other organisms depend on green plants directly or indirectly for their nutrition. Thus, Sun is the ultimate source of energy.
Question 7.
How is holophytic nutrition different from holozoic nutrition?
Answer:
1. Holophytic nutrition is found in plants and lower forms of animals they consume liquid food as they lack digestive systems.
2. Holozoic nutrition is found in man and other higher forms of animals. There is a well developed digestive system in all of them. Hence, they can consume solid food.
Nutrition in Plants Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Draw a diagram of stomata?
Answer:
Question 2.
Give an experiment to demonstrate that light is necessary for photosynthesis?
Answer:
Take a broad leaved potted plant and keep it under dark for 24 – 48 hours. The plant is kept in dark to make the plant free from starch. After this fix a leaf still attached to the plant with a paper clip having paper black as shown in figure. Now keep the plant in light for few hours and test the leaf for starch. To test the leaf for starch, pluck the lgaf and kill its cells in boiling water. Remove the chlorophyll by boiling in alcohol. Wash the boiled leaf in water and treat with iodine solution.
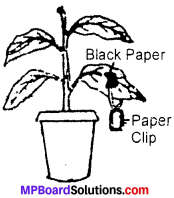
It is believed that the portion of the leaf, exposed to sunlight turned blue in colour while the covered portion did not undergo any change. You know that starch give blue colour with iodine solution. This was because the covered portion did not receive any sunlight. This shows that sunlight is necessary for photosynthesis.
![]()
Question 3.
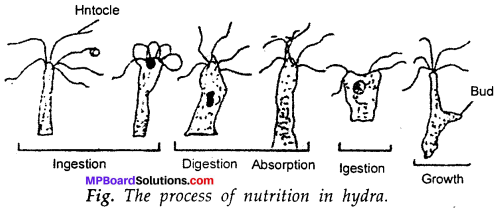
Describe the process of nutrition in hydra?
Answer:
In hydra, the tentacles help in ingesting the food (taking the food inside). The cells inside the body cavity wall secrete certain chemicals and enzymes to digest the food. The digested food is absorbed by the cells of the wall in the body cavity by diffusion. On eating food the hydra grows and reproduces by forming buds.
Question 4.
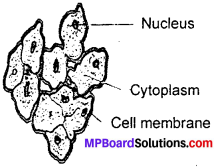
Define cell with their structure
Answer:
The bodies of living organisms are made of tiny units called cells. Cells can be seen only under the microscope. Some organisms are made of only one cell. The cell is enclosed by a thin outer boundary, called the cell membrane. Most cells have a distinct, centrally located spherical structure called the nucleus (Fig.). The nucleus is surrounded by a jelly – like substance called cytoplasm.