MP Board Class 12th Biology Solutions Chapter 3 Human Reproduction
Human Reproduction NCERT Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Fill in die Blanks:
- Humans reproduce …………………….. (asexually/ sexually)
- Humans are …………………….. (oviparous, viviparous, ovoviviparous)
- Fertilization is …………………….. in humans, (external / internal)
- Male and female gametes are …………………….. (diploid / haploid)
- Zygote is …………………….. (diploid / haploid)
- The process of release of ovum from a mature follicle is called ……………………..
- Ovulation is induced by a hormone called ……………………..
- The fusion of male and female gametes is called ……………………..
- Fertilisation takes place in ……………………..
- Zygote divides to form …………………….. which is implanted in uterus.
- The structure which provides vascular connection between fetus and uterus is called ……………………..
Answer:
- Sexually
- Viviparous
- Internal
- Haploid
- Diploid
- Ovulation
- LH and FSH
- Fertilisation
- Follopian tube
- Embryo
- Placenta.
Question 2.
Draw a labelled diagram of male reproductive system.
Answer:
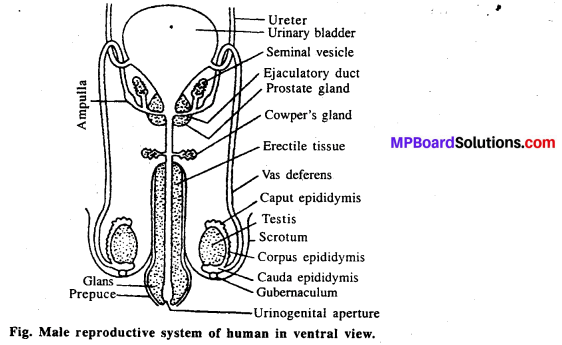
![]()
Question 3.
Draw a labelled diagram of female reproductive system.
Answer:
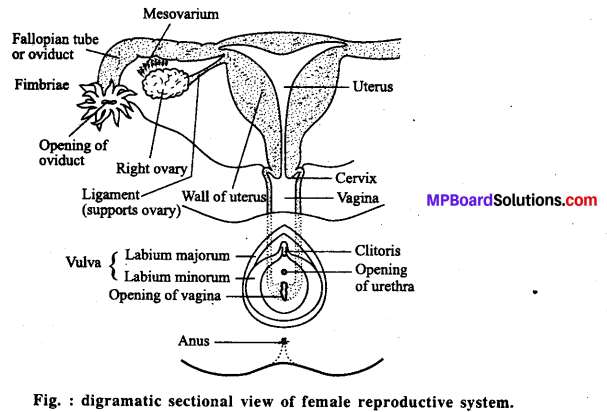
Question 4.
Write two major functions each of testis and ovary
Answer:
Functions of testis functions:
- Production of sperms by seminiferous tubules.
- Production of male sex hormone, testosterone by leydig cells.
Functions of Ovary
- Production of ova (eggs).
- Production of female sex harmones, estrogen and progesterone.
Question 5.
Describe the structure of a seminiferous tubuls.
Answer:
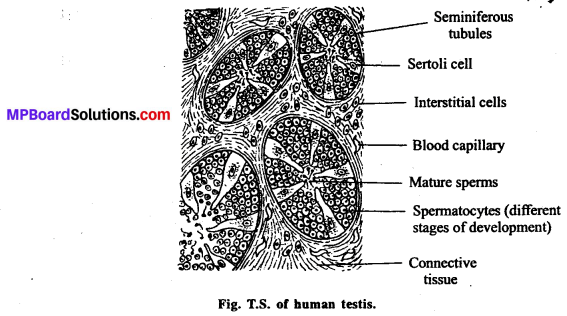
Seminiferous tubules are highly coiled tubes, which are lined on the inside by :
- Male germ cells called spematogonia that undergo meiotic division to form sperm celts.
- Sertoli cells provides nutrition and molecular signals to the germ cells.
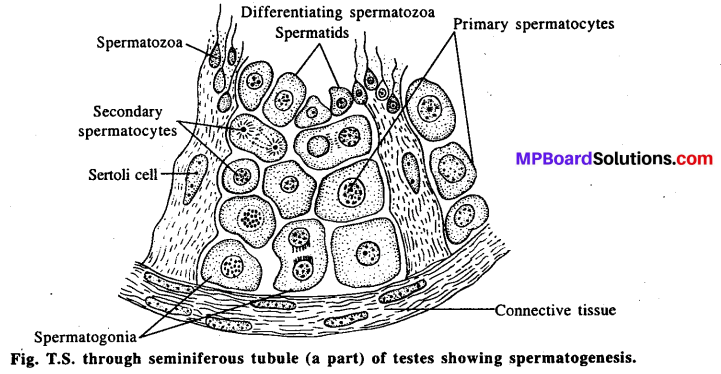
Question 6.
What is spermatogenesis? Briefly describe the process of spermatogenesis.
Answer:
Spermatogenesis : Formation of sperms in the testis is called as spermatogenesis. It involves in the following steps :
1. Multiplication phase : In this phase, sperm cells are formed in testes.
The inner layer of seminiferous tubules of testes is formed of germinal epithelium.
Some of these cells called primary germ cells divide mitotically into spermatogo¬nia which become separated in the germi¬nal layer. Other cells of this layer serve as nutrition for the dividing cells.
2. Growth phase : In this phase, spermatogonia starts growing, absorbing nutrient substances. These large cells are called primary spermatocytes.
3. Maturation phase : It is a very important phase. Primary spermatocytes divide twice. The first division is meiotic due to which the number of chromosomes is reduced to half. In this process, primary spermatocyte divides into two halves which are known as secondary spermatocytes. The second division is mitotic and no change takes place in the number of chromosomes. Thus, from two secondary spermatocytes four spermatids are formed. In this manner from one primary spermatocyte four spermatids are formed. These spermatids change into sperm cells of spermatozoa by a process called metamorphosis.
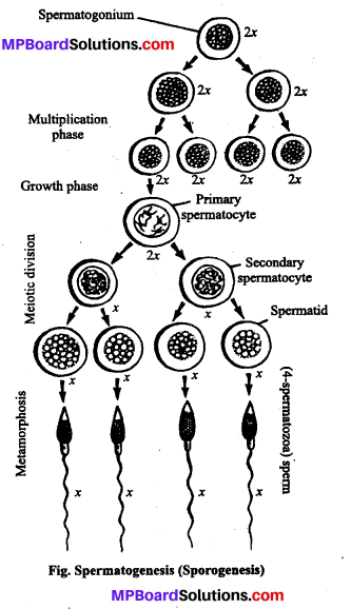
Question 7.
Name the hormones involved in regulation of spermatogenesis.
Answer:
The hormones involved in regulation of spermatogenesis are:
- Gonadotropin releasing hormone
- Luteinizing hormone (LH)
- Follicle stimulating hormone
- Testosteron.
Question 8.
Define spcrmiogenesis and spermiation.
Answer:
Spermiogenesis : The process involving transformation of spermatid into spermatozoa is called spermiogenesis.
Spermiation: After spermiogenesis sperm heads became embedded in the sertoli cells and are finally released from the seminiferous tubules by the process called spermiation.
Question 9.
Draw a labelled diagram of human sperm and explain its defferent parts.
Answer:
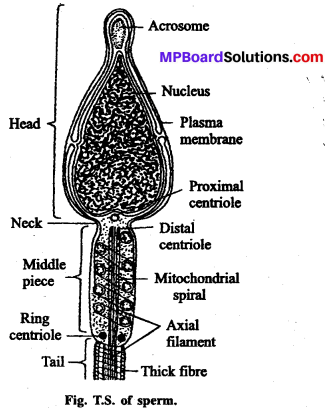
Structure of sperm: A mature sperm is a delicate microscopic, motile structure. A typi¬cal mammalian sperm consists of the following three parts:
- Head,
- Middle piece and
- Tail.
(1) Head: Head is knob like terminal part of the sperm. It is composed of a large nucleus and an acrosome. At die time of entry of the sperm into egg acrosome Secretes spermlysin which dis¬solve the egg membrane and thus facilitates entry of sperm into the egg or ovum.
(2) Middle Piece : It is short and lies be¬tween head and tail. It contains two granules called the proximal and distal centrioles in front side and towards posterior side cylindrical middle part of sperm. It is considered as the power house of sperm as it contains compact mass of mitochondria, which provides energy for metabolism and movement of sperm.
(3) Tail: It is situated on posterior part of sperm. It moves with the help of axial filament. The posterior part of the tail is called as end piece and it is not covered by membrane.
Question 10.
What are the major components of seminal plasma?
Answer:
The main components of the seminal plasma are fructose, calcium ion, some enzymes and prostagladines.
Question 11.
What are the major functions of male accessory ducts and glands?
Answer:
The main functions of male accessory ducts and glands are as follows :
1. Functions of accessory ducts:
(a) Rete Testis : They transport sperms from seminiferour tubule to Vas efferentia.
(b) Vas efferentia : Transports sperms to epdidymis.
(c) Epididymis : Sperms are stored here. Maturation of sperms occur.
(d) Vas deference : Transports sperms from epididymis to the urethra.
(2) Functions of glands:
(a) Prostate gland : It produces milky secretion which forms considerable part of the semen. It makes sperm motile.
(b) Bulbourethral gland : Its secretion make the penis lubricated.
(c) Seminal vesicle: It secrete mucus and watery alkaline fluid which provide energy to the sperm.
![]()
Question 12.
What is oogenesis ? Give a brief account of oogenesis. .
Answer:
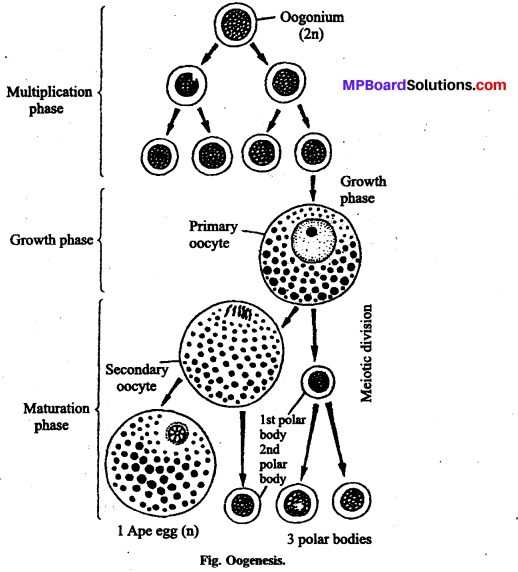
Oogenesis is the process of formation of mature female gametes from primordial germ cells.
- This process is initiated during embryonic developmental stage when about two million gamete mother cells (oogonia) are formed in each foetal ovary.
- Oogonia start meiotic division which gets arrested at prophases-I stage. They are referred to as primary oocytes.
- Each of these gets covered with layers of granulose cells and are then called primary follicle.
- Many of the primary follicles degenerate from birth to puberty, leaving about 60000-80000 in each ovary at puberty.
- More layers of granulose cells and another theca layer surround it and now it is called secondary follicle. Theca layer is arranged as inner theca-intema and outer theca- extema.
- Secondary follicle transforms into tertiary follicle that has a fluid filled cavity called antrum.
- The primary oocyte within the tertiary follicle grows in size and completes its first meiotic division now.
- This is an unequal division resulting in the formation of:
(a) A large haploid cell (that keeps the majority of nutrient rich cytoplasm) called secondary oocyte.
(b) A tiny cell, with haploid nucleus and almost no cytoplasm called first polar
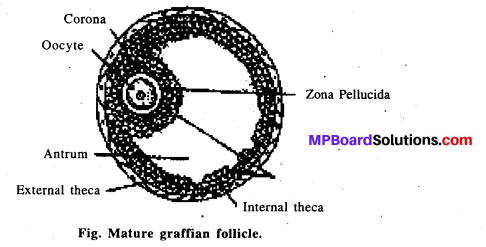
body. - The tertiary follicle undergoes certain changes to mature into graafian follicle.
Secondary oocyte forms a new membrane around it, called zona pellucida. - Under the influence of LH, the Graaffian follicle now ruptures to release secondary oocyte from the ovary by a process called ovulation.
Summary of oogenesis:
Oogonia Meiosis-I initiated -4 Primary oocyte (arrested at prophase-I) → Granu¬losa layer builds → Primary follicle → More granulose and theca layer added → Secondary follicle → Fluid filled cavity develops → Tertiary follicle → Primary oocyte completes meio- sis-I → Secondary oocyte (haploid)+ polar body → Tertiary follicle transforms to Graafian follicle → Zona pellucida builds around secondary oocyte Graafian follicle ruptures → Secondary oocyte (ovum) released.
Meiosis-II will occur only at the time of penetration of sperm into the ovum.
Question 13.
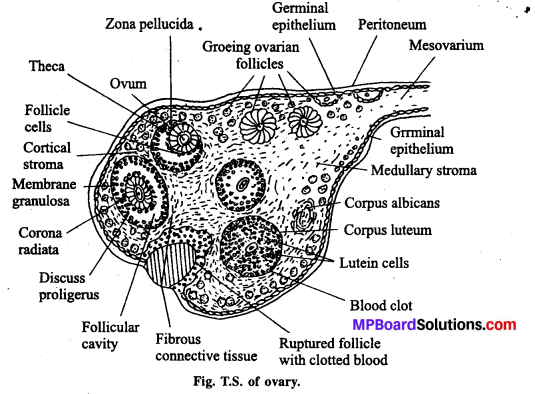
Draw a labelled diagram of a section through ovary.
Answer:
Question 14.
Draw a labelled diagram of a graafian follice.
Answer:
Question 15.
Name the function of the following:
(a) Corpus luteum
(b) Endometrium
(c) Acrosome
(d) Sperm tail
(e) Fimbriae.
Answer:
The functions of the following :
(a) Corpus luteum Secretes large amount of progesterone which is essential for the maintenance of endometrium of the uterus.
(b) Endometrium is necessary for the implantation of the fertillised ovum, for contrib¬uting towards making of placenta and other events of pregnancy.
(c) Acrosome is filled with enzymes that help in dissolving the outer cover of the ovum and entry of sperm nucleus.
(d) Sperm tail facilitates motility of the sperm essential for reaching the ovum to fertilise it.
(e) Fimbriae are fmgers-like projections at the mouth of fallopian tubules that help in
collection of the ovum after ovulation.
Question 16.
Identify true/ false statement to make it true.
- Androgens are produced by sertoli cells. (True / False)
- Spermatozoa get nutrition from sertoli cells. (True / False)
- Leydig cells are found in ovaiy. (True / False)
- Leydig cells synthesise androgens. (True / False)
- Oogenesis takes place in corpus luteum. (True / False)
- Menstrual cycle ceases during pregnancy. (True / False)
- Presence or absence of hymen is not a reliable indicator of virginity or sexual experience. (True /False)
Answer:
- Flase
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
- True.
Question 17.
What is mentrual cycle? Which hormones regulate menstrual cycle?
Answer:
The reproductive cycle in the female primates is called menstrual cycle. The uterus linings becomes thick and spongy to receive fertilised egg. If the egg is not fertilised, this lining is not needed any longer so, it slowly breaks and comes out through vagina along with blood and mucous. This is called menstruation. It is repeated at an average interval of about 28/29 days.
Following hormones are regulate this cycle:
- Gonadotropin
- strogen
- Luteinizing hormone
- Follicular stimulating hormone
- Progesteron.
Question 18.
What is parturition? Which hormones are involved in induction of parturition?
Answer:
The process of delivery of the foetus (Child birth) at the end of the pregnancy is called parturition. The signals for parturition originate from the fully developed foetus and the placenta, which trigger the release of oxytocin from the maternal pitutary. Oxytocin acts on the uterine muscles and induces stronger uterine contractions leading to expulsion of the baby. Relaxin hormone released by the ovary widens the vagina to facilitate birth.
Following hormones are involved in induction of parturition:
- Cartisol
- Estrogen
- oxytocin.
![]()
Question 19.
In our society the women are often blamed for giving bird) to daughters. Can you explain why this is not correct?
Answer:
Women are blamed for giving birth to daughters. This is wrong because sex of the baby is determined by the sperm that can have either X or Y-chromosome. Women have only one type of chromosome (X) in all the ova.
If the sperm having X-chromosome fertillises the ovum (X), the resulting zygote (XX) will become a female.
If the sperm having Y-chromosome fertillises the ovum (X), the resulting zygote (XY) will become a male.
Question 20.
How many eggs are released by a human ovary in a month? How many eggs do you think would have been released if the mother gave birth to identical twins? Would your answer change if the twins born were fraternal?
Answer:
Only one egg is released by a human (female) ovary in a month. Only one egg is released if the mother gave birth to identical twins. Yes two or more eggs are released in case fraternal twins are born.
Question 21.
How many eggs do you think were released by the ovay of the female dog which gave birth to 6 puppies?
Answer:
Six eggs are released by the ovary of a female dog if it gave birth to six puppies.
Human Reproduction Other Important Questions and Answers
Human Reproduction Objective Type Questions
1. Choose the Correct Answers:
Question 1.
Fertilization is related by: (CBSE PMT 2007)
(a) Realizing & gamete cells from gonad
(b) Transfer of male gametophy te to female gamete
(c) Fusion of male and female sex organs
(d) Fusion of nucleus of male gametes and nucleus of female gamete.
Answer:
(d) Fusion of nucleus of male gametes and nucleus of female gamete.
Question 2.
Cleavage is a process of fertilized egg, in which egg.
(a) Does not divide, but grows in sizes
(b) Divides continuously but does not grow in size
(c) Divided continuously and grows in size
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Divides continuously but does not grow in size
Question 3.
Foetal membranes provide:
(a) Protection of embryo
(b) Nutrition to embryo
(c) Protection and nutrition to embryo
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Protection and nutrition to embryo
Question 4.
Science of ageing is called:
(a) Chronology
(b) Odontology
(c) Gynecology
(d) Gerontology.
Answer:
(d) Gerontology.
![]()
Question 5.
The female counterpart of prostate gland in male (man) is:
(a) Bertholin’s gland
(b) Uterus
(c) Clitoris
(d) None of these
Answer:
(d) None of these
Question 6.
Humanis:
(a) Oviparous
(b) Viviparous
(c) Ovoviviparous
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Viviparous
Question 7.
Periodic cycle is:
(a) Of menstrual phase
(b) Of estrogen secretion
(c) Of fertilization
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Of menstrual phase
Question 8.
Ageing in mammals including man is due to:
(a) Adverse changes in environment
(b) Interaction between hereditary factors (genes) and the environment
(c) Malnutrition and stress
(d) All of these.
Answer:
(b) Interaction between hereditary factors (genes) and the environment
Question 9.
The part of the human body shows regeneration is:
(a) Spleen
(b) Kidney
(c) Brain
(d) Liver
Answer:
(d) Liver
Question 10.
Fertilization in mammals occurs in:
(a) Oviduct funnel
(b) Fallopian tubule
(c) Uterus
(d) Vagina.
Answer:
(b) Fallopian tubule
Question 11.
The capsule enclosing testes of mammal is called:
(a) Tunica albugenia
(b) Tunica membrana
(c) Tunica vaginalis
(d) Tunica vesculosa
Answer:
(a) Tunica albugenia
![]()
Question 12.
Sertoli cells are found in:
(a) Testes of Earthworm
(b) Testes of Frog
(c) Testes of Mammals
(d) Testes of Cockroach
Answer:
(a) Testes of Earthworm
Question 13.
The cavity of gastrula is known as:
(a) Blastocoel
(b) Coelome
(c) Archenteron
(d) Haemocoel
Answer:
(c) Archenteron
Question 14.
Implantation is the process in which
(a) Fertilization of egg
(b) Movemènt of egg
(c) Disappear of egg
(d) Blastosyst is formed by uterus.
Answer:
(a) Fertilization of egg
Question 15.
Seminiferous tubule is found in: ‘
(a) In testes
(b) In ovary
(c) In kidney
(d) In lungs.
Answer:
(a) In testes
![]()
2. Match the Following:

Answer:
1. (e)
2. (d)
3.(a)
4. (c)
5.(b).

Answer:
- (b)
- (c)
- (d)
- (e)
- (a).
3. Answer in One Word/Sentence:
- How many sperms will be produced from 24 spermatocytes during spermatogenesis ?
- Where does fertilization takes place in mammals ? (SSCE1993, CBSE 95)
- Write the name of various phases of embryogenesis.
- How many polar bodies are formed during the formation of one gamete?
- Write die name of three layers of gastrula.
- How many polar bodies are formed during the formation of ovum during oogenesis? (CBSE 1993)
- Name the substance formed in sperms and which helps the sperms to enter into ovum. (AISB1991)
- How many sperms and ova are formed from 100 primary spermatocytes and primary oocyte respectively ? (SSCE 1992)
- Name the part of sperm secreting enzyme for the entrance of sperms into ovum. (SSCE 1992)
- Name the organ where corpus luteum is formed. (SSCE 1995)
- Write the duration of gestation period in human cases.
- How many autosomes are found in human sperm ?
- Where is corpus luteum formed ?
- Name the developmental stage of man in which it is transplanted of uterus wall.(SSCE 1993)
- Name the process of release of ovum from graafian follicle.
Answer:
- 96,
- Fallopian tube
- Cleavage
- Blastula and Gastrula Infant, 4.3
- Ectoderm, mesoderm and endodenn
- 2
- Spermlysin
- 400,100
- Head
- Ovary
- 240 days
- 22
- Ovary
- Blastula
- Ovulation.
Human Reproduction Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
By which term, the process of the formation of morulla from zygote is referred?
Answer:
Cleavage.
Question 2.
What is called first menstrual stage or phase in the girls age 12-14 years?
Answer:
Menarche.
Question 3.
What is the example of spermatogenesis?
Answer:
Male gametogenesis.
Question 4.
What provides nourishment to foetus inside the uterus?
Answer:
Placenta.
Question 5.
How many germinal layers are there in gastrula stage?
Answer:
Three.
Question 6.
By which term, the middle germinal layer of gastrula is referred?
Answer:
Mesoderm.
Question 7.
After Fertilization, how many days are needed for the birth of human child?
Answer:
280 days (9 months and 10 days).
Question 8.
To produce the new organisms of their own kind is called by a term, name it
Answer:
Reproduction.
Question 9.
By which name, the reproduction happens by means of fusion of two different gametes?
Answer:
Sexual reproduction.
Question 10.
Which gametogenesis goes on till life span in human beings after attaining puberty?
Answer:
Spermatogenesis.
![]()
Question 11.
The stoppage of menstrual cycle in a 50 yrs old female is known as.
Answer:
Menopause.
Question 12.
What is pregnancy?
Answer:
The time period between fertilization to the birth of child is called pregnancy.
Question 13.
Where is carpora cavernosa found?
Answer:
Carpora cavernosa is found in penis.
Question 14.
What is the gestation period in elephant, dog and cat ?
Answer:
Elephant 641 days dog 58-68 days, cat 63 days.
Question 15.
Name the hormone that relaxes public symphysis during parturition.
Answer:
Relax in hormone.
Human Reproduction Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain menarchy or menopause.
Answer:
Menopause: In every human female, puberty period starts from 12-13 yrs of age to 45-50 yrs of the age. During this period except pregnancy at every interval of a month during 26th day to 28th day. If pregnancy does not occur then the internal wall of the uterus secretes out mucilaginous liquid along with blood. Secretion continues for 3-4 days called menses. As it comes at definite period so, it is called menstruation cycle. At the age of 40-50 yrs. menses stop and females reach to a stage called menopause. Ability pregnancy also stops after attaining menopause.
Question 2.
Draw a well labelled diagram of the T.S. of human testis.
Answer:
Question 3.
Draw a well labelled diagram of Oogenesis.
Answer:
Question 4.
What is the position of fallopian tubule in female reproductive organs? What are their significance ?
Answer:
Fallopian tubules are a pair of small muscular tubes, one each on either side ol*the uterus. These tubules extend from the vicinity of the ovary to the ovary. Each tubule is about 10 cm in length. The free end of each tube lies near the ovary of its side. This end is funnel shaped and fimbriated. It is called ostium and infundibulum. Infundibulum opens in the abdominal cavity by means of abdominal ostium. The fallopian tubule is kept in position by a mesentery which is attached to the uterus.
Significance of Function of Fallopian Tubes:
- By their lashing movement of the cilia present in the lining of infundibulum and nearby area help in pulling the released ovum into fallopian tube.
- Passage of ovum into uterus is aided by muscular movement of fallopian tube as well as beating of cilia present in the lining layer of tube.
- Fertilization of ovum mostly takes place in the ampulla part of fallopian tube.
![]()
Human Reproduction Long Answer Type Question
Question 1.
Write differences between spermatogenesis and oogenesis
Answer:
Differences between Spermatogenesis and Oogenesis:
| Spermatogenesis | Oogenesis |
| 1. Sperms are produced by this process. | 1. Ovums are produced by this process. |
| 2. In this process primary spermatocytes are formed by maturation of germinal epithelium cells. | 2. In this process primary oocytes are formed by maturation of germinal epithelium. |
| 3. Primary spermatocyte divides to form four spermatids. | 3. Primary oocytes divides to form one ovum and three polar bodies. |
| 4. There is equal division. | 4. There is unequal division. |
| 5. Large number of sperms are formed by this | 5. Less number of ovums are formed by this process. |
Question 2.
Describe the process of the formation and functions of corpus luteum.
Answer:
Corpus luteum is formed within ovary. It is a yellow body or structure which develops from ruptured Graafian follicle after the release of ovum. The cells become enlarged and conical. They are filled with a fluid called as luteum. It is developed under influence of L.H. of anterior pituitary. If fertilization do not occur it degenerates but if fertilization occurs, it remains for seven months during pregnancy and is responsible for the formation of some hormones which stimulates pregnancy and lactation.
Question 3.
Describe the structure and function of fallopian tubes.
Answer:
Fallopian tubules are a pair of small muscular tubes, one each on either side of the uterus. These tubules extend from the vicinity of the ovary to the ovary. Each tubule is about 10 cm in length. The free end of each tube lies near the ovary of its side. This end is funnel shaped and fimbriated. It is called ostium and infundibulum. Infundibulum opens in the abdominal cavity by means of abdominal ostium. The fallopian tubule is kept in position by a mesentery which is attached to the uterus.
Function of Fallopian Tubes:
By their lashing movement of the cilia present in the lining of infundi-bulum and nearby area help in pulling the released ovum into fallopian tube. ,
Passage of ovum into uterus is aided by muscular movement of fallopian tube as well as beating of cilia present in the lining layer of tube.
Fertilization of ovum mostly takes place in the ampulla part of fallopian tube.
Question 4.
In our society the women are often blamed for giving birth to daughters. Can you explain why this is not correct ?
Answer:
It is not correct to blame women for giving birth the daughters. The male sperm contains either X or Ychromosome whereas the female egg contains only x chromosomes. At the time of fertilisation when sperm carrying x chromosome combines with egg carring x chromosome of female Xygote z is formed which would be a female and when sperm with Y chromosome combines with egg containing X chromosome XY zygote is formed which would be a male. Thus scientifically sex of the baby is determined by the father and not by the mother as blamed in our society.
Question 5.
Describe the structure of ovary.
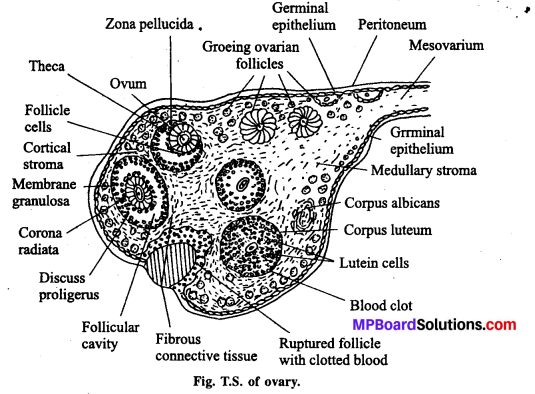
Answer:
These are a pair of female gonads or primary sex-organs lying one on each side of uterus. Ovary is attached to abdominal wall as well as uterus by means of ligaments. It is surrounded by a fold by peritoneum named mesovarium. Ovary is internally differentiated into four parts: germinal epithelium, tunica albuginea, cortex and medulla. Germinal epithelium is the outermost layer of cuboidal to flattened cells. Germinal epithelium is followed by a sheath of condensed connective tissues which is termed as tunica albuginea. It is followed by cortex. The central part of ovary contains medulla. A large number of groups of specialized cells are present in the cortex which are termed as ovarian follicles. These follicles are found in four development stages :
Incipient follicle : The central part of these follicles contain a large cell which is covered by smaller cells.
Primary follicle: These follicles are developed from incipient follicles.
Vascular follicle: It is formed from primary follicles. The oocyte of these follicle is covered by a many layered thick wall.
Graafian follicle: Mature ovarian follicle is termed as graafian follicle. It is covered by two sheaths derived from cortex. The follicle contains a single oocyte. A group of follicular cells surrounds the oocyte or ovum. It is called cumulus ovaricus. Another group produces membrane granulosa. Oocyte has two non-cellular membranes, inner vitelline membrane and outer zona peUucida.
Question 6.
Describe the process of fertilization and give its significance.
Answer:
Fertilization: Fertilization is the fusion of male and female gametes to produce a single diploid cell, called zygote. Fertilization in human female takes place in fallopian tube.
In a sexual mating or coitus the male ejaculates semen into the vaginal passage of the female using the copulatory organ, the penis. In a single coitus as many as 200 million sperms are introduced into the female genital tract but out of this huge number of sperms only one is destined to fuse with the ovum, provided the fallopian tube lodges of fully developed seqondary oocyte.Sperms travel through the vaginal passage and enter the uterus through the cervix.
They travel further through the uterus and finally enter the fallopian tube.The vaginal passage is highly acidic to prevent any bacterial infection but this acidic medium is not suitable for the survival of sperms. Many sperms die on the way. The liquid medium of the semen is alkaline which can neutralize the acidity of vagina to some extend and keep the. sperms alive and active. The sperms move with the speed of 1 -5 to 3 mm per minute.
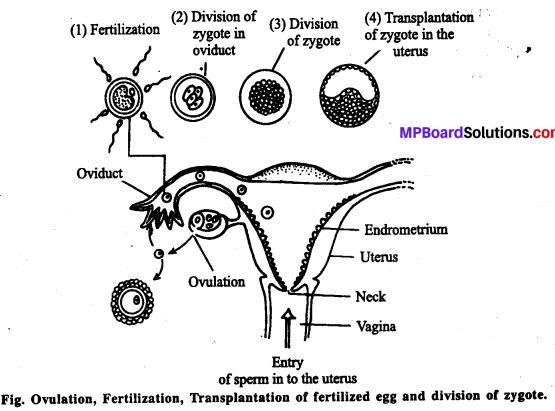
The ovum gets surrounded by a large number of sperms but usually only one fuses with the ovum. The sperm penetrates the ovum using certain chemical substances of enzymatic nature.These chemicals are called spermlysins which are present in the acrosome. Certain receptors on the cell surface of the ovum enable the sperms to penetrate the wall of ovum. The ovum is surrounded by follicle cells. These cells are joined together by a glue like substance known as mucopolysaccharide, an acid, called hyaluronic acid. The sperm pro¬duces spermlysin, known as hyaluronidase. The over all changes in a sperm before the fertilization is called capacitation.
The hyaluronidase enzyme facilitates the sperm to pen¬etrate through the corona radiata (follicle cells), zona pellucida and the plasma membrane of ovum. The nucleus and the cytoplasmic components get inside the ovum, leaving the tail outside. The entry of sperm stimulates the ovum and the signal is transmitted to the egg surface incapacitating all the other cells surrounding the ovum. Nucleus of sperm move towards the nucleus of ovum and they fuses with each other to form zygote. It takes 2 \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) hours to complete fertilization process. Once the ovum has been fertilized a barrier forms around it that normally prevents other sperms from entering.
Now fertilized egg reaches to the uterus and within seven days of fertilization it is transplanted to the wall of the uterus.
Significance of Fertilization
Egg become active after entry of sperm and completes its second maturation division.
Formation of fertilization membrane prevent entry of other sperms in the ovum. In human this membrane is not formed.
It restores the diploid number (2n) of chromosomes in the zygote.
It combines characters of male and female resulting in the introduction of variations. These variations make the offspring better equipped for struggle against environmental conditions to ensure the existence.
The ovum is stimulated to cleavage.
After fertilization ovum rotate inside the membrane.
Ovum do not contain centriole and obtain it from sperm during this process thus zygote continuously divides.
It is necessary for the egg to attain maturity.
![]()
Question 7.
Describe development of embryo up to the formation of three germ layer. Give the names of organs formed by three germ layer.
Or
Define cleavage. Describe the changes that occur in embryo till gastrulation.
Answer:
The term cleavage refers to a series of rapid mitotic divisions of the zygote following fertilization forming a many celled blastula. Following are the various steps of embryonic development in human up to the formation of three germ layer:
1. Formation of morula : The fertilized zygote divides. It undergoes successive quick mitotic cell divisions called cleavage. First cleavage is holoblastic, unequal and meridional. It divides the ovum completely into two unequal blastomeres. The plane of cleavage passes through animal vegetal axis, i.e., it is meridional. Large blastomere divides little earlier than the small one giving a transitional three cell stage. As a result of further cleavages, a solid mass of mulberry-shaped embryo is formed called morula.
Morula is of the size of zygote but consists of 32 cells. These cells are of two types : The outer layer of smaller cells around, inner larger cells. Within 72 hours of fertilization, morula reaches the uterus.
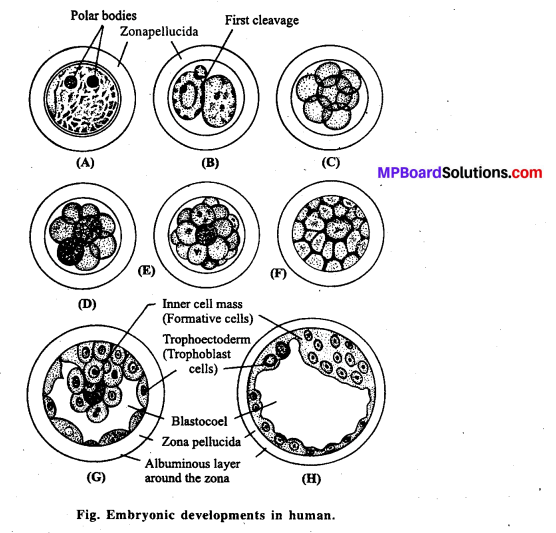
2. Formation of blastula : Transformation of morula into a blastula starts by the rearrangement of blastomeres. This leads to the formation of a central cavity inside the morula. The outer cells of morula absorb the nutritive fluid secreted by the uterine mjueous membrane and transform into trophoblast. The fluid absorbed by these cells collects in the central cavity called blastocoel. This cavity separates the trophoblast from the inner mass of larger cells except on one side and is termed blastocyst. The inner cell mass is pushed to one pole as a small knob. This knob gives rise to the embryo and is termed as embryonal knob.
3. Formation of gastrula : In this embryonic stage development of three germ layer occurs. In this stage morphogenic movement of cells of embryo occurs, as a result of this three germ layers are formed. A cavity develops at the centre called as archenteron which open outside through blastopore.
4. Formation of three germ layers :
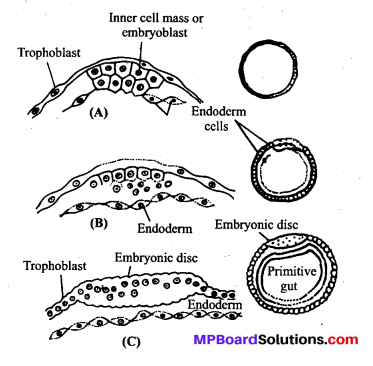
Formation of endoderm : The enlargement of blastodermic vesicle is followed by the separation of few cells from the inner cell mass. These cells push out from the blastocoel to become the initial cells of the innermost layer of gastrula, the pattern of a tube within a tube. The inner tube is called primitive gut. It is differentiated into gut tract which is within the body and a yolk sac that communicates with the gut of the embryo. The remaining cells of the inner Cell mass are organized to form the embryonic disc.
Formation of mesoderm : After the formation of endoderm an increased rate of cell proliferation takes place at the caudal end of the embryonic disc. This results in the localised increase in the thickness of the disc. These cells subsequently get detached from the embryonic disc and get organized to a well demarcated mesodermal layer.
Formation of ectoderm: After the formation of endoderm and mesoderm, the remain¬ing cells of the embryonic disc arrange themselves in a layer to form ectoderm.
Fate of three germinal layer : Three germ layers differentiated at the time of gastrula- tion give rise to all the tissues and organs of the body of adult by the process of differentia¬tion and organogenesis.
Germ layers
1. Germ layers : Ectoderm
Tissue or organs of adult :
- Epidermis and its derivatives.
- Cutaneous sensory organs.
- Olfactory organs.
- Lens of eye.
- Membranous labyrinth (internal ear).
- Anterior lobe of pituitary gland.
- Lining of buccal cavity.
- Enamel of teeth.
- Endoderm
- Lining of proctodaeum.
- Brain, spinal cord, spinal and cranial nerves.
2. Germ layer : Endoderm
Tissue or organs of adult :
- Lining of alimentary canal except buccal cavity and rectum.
- Lining of larynx, trachea and lungs.
- Urinary bladder.
- Parathyroid, thyroid and thymus.
- Liver and pancreas.
3. Germ layer : Mesoderm
Tissue or organs of adult :
- Dermis.
- Vertebral column.
- Muscles of the body.
- Excretory organs.
- Reproductive tracts.
- Peritoneum.
- Circulatory system, heart, blood vessels, blood, lymph and spleen.