Students get through the MP Board Class 9th Social Science Important Questions Chapter 17 State of Industries in India which are most likely to be asked in the exam.
MP Board Class 9th Social Science Important Questions Chapter 17 State of Industries in India
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Why are industry and agriculture growing side by side? Explain.
Answer:
Agriculture and industiy both arc interrelated. Agricuiture supplies raw materials industries, but industry supplies all the modern machines. fertilizers, improved seeds and medicines for the development of the agriculture, e.g., cotton, silk, jute, etc. Raw materials are supplied by agriculture, e.g., cotton for cotton textile industry, for sugar industry sugarcane is supplied by agriculture.
In the same way tractor, thresher, urea, insecticides and pesticides, medicines are supplied by industries to the agriculture. Therefore, for the development of the country agriculture and industry both should be developed side by side.
Question 2.
Why are iron and steel industries regarded important today?
Or
why are iron and steel industries called basic industries?
Or
Iron is the mother of development. Explain the statement.
Answer:
Iron and steel industry is called a basic industry or key industry. On it depend several light, medium, small and cottage industries. The production of iron and steel is an index of modernization and industrialization of a country. It precedes heavy machines and tools industries. The iron and steel industry helps most of the large and small industries. The industry calls for huge investment, basic infrastructure, particularly efficient means of modern transport and communication and abundant fuel or power supply.
Question 3.
What is the contribution of industry in the National economy of the country?
Answer:
Industrialization is very essential for the development of any country Industries are helpful in adding the values to the natural resources of any country. After independence many big industries were set up. Self sufficiency was given more importance. Today India is not only the exporter of raw material but also the exporter of finished products.
A big portion of our national income is contributed by industries of our country. Many people are getting jobs in these industries. Because of industrialisation, agricultural development has taken place. So we are able to satisfy our own wants without depending on foreign countries. Today India is in such position that it can give technical assistance to other countries she can provide management knowledge and efficient labours to foreign countries setting up of industries in foreign countries is done by India.
![]()
Question 4.
Describe the state of cottage industry in India. (MP 2011)
Answer:
State of cottage industry in India is as follows:
Glass industry: Glass industry is an old industry of India but modernised development of the glass industry started after the second world only. At present in this industry glass is being produced by modem and latest technology. At present out of 56 big factories of glass 15 are modem factories which manufacture high quality of glass goods completely with the help of machines.
As a cottage industry it is localised mainly at Ferozabao and Beigaon. There are more than 225 small and big factories of glass in Ferozabad, which manufacture bangles. In Atta Shikohabad, Fatehabad and Hathra also it is running as cottage industry whereas in Uttar Pradesh. Maharashtra, West Bengal, Punjab, Madhya Pradesh, Bihar, Tamil Nadu and Orissa it is centralised as a modem industry. Maximum factories in the country are situated in West Bengal.
India exports manufactured glass goods to Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Nepal, Afghanistan, Kuwait, Iran, Greece, Saudi Arabia, Burma, Malaysia etc.
Silk industry: From the very beginning silk industry has been one of the major industry of India. At present of the total production of silk in the world 17 per cent is produced in India.
There are four major areas of pure silk production in India:
- Kashmir Valley
- Eastern Karnataka (Plateau) and mountainous regions of Tamil Nadu
- Areas of Hugh in West Bengal
- Mountainous region of Assam
This industry provides employment to 58 lakh people. For encouraging this industry “The Central Silk Board” has been established in the year 1949.
Lac industry: India is a major producer of lac. Before 1950 India was the only country where Lac was cleaned but today his work is also done in Thailand. It has influenced the Indian Lac industry. Earlier 15 per cent of the total world production of lac was produced by India which at present has reduced to 50 per cent.
In India maximum lac is produced in the plateau of Chhota Nagpur. Out of the total production of lac in the country 50 per cent of lac is produced in India. Apart from his Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, West Bengal, Maharashtra, Orissa, Gujarat and Mirzapur district of Uttar Pradesh are major centres of production.
Major buyers of Indian lac are China, America, Russia and Britain. Apart from these Germany, Brazil, Italy, France and Japan are also important buyers. This industry provides employment to about 10,000 people of the country. 60 – 70 per cent of schedule tribe people do the work of bringing lac worms and extracting juice from them.
Question 5.
Write short notes on leather industry.
Answer:
It is one of the oldest industry in India. This is a traditional industry. There are several things which are made of leather as coat, jersey, purse, playing material, toys, monkey cap, belt, hand gloves, shoes, foot wear etc. Majority of the leather goods in the country are produced in Tamil Nadu, Kolkata, Kanpur, Mumbai, Aurangabad, Kolhapur, Dewas, Jalandhar and Agra. Out of the total production of leather goods 75 per cent is produced by small scale and cottage industries.
In India, leather and leather goods are included in the top ten list of the products having maximum export. During the year 2003 – 04, the leather industry earned 2.1 million American dollars as income from export.
Mostly people from minority and poor section are employed in the field of leather production. Out of total employed people 30 per cent are women. It is estimated that 10 per cent of total supply of leather of the world is from India.
Question 6.
Explain the paper industry in India.
Answer:
In India the art of paper making by hands is developed from the ancient time. The first modem mill was set up at Bali near Kolkata in 1870.
At present there are several paper mills in India among which the chief are National New Print and Paper Mill Limited. (Nepanagar, Madhya Pradesh and Security Paper Mill (Hoshangabad, Madhya Pradesh). At present there are 515 paper mills in the country.
The paper is produced by (all types of production units) small, medium and large. The contribution of small and medium units is 50 per cent of the total product. At present in India, around 15 lakh people are employed in this industry.
It ranks twentieth in the world in the production of paper. The chief paper producing states in India are Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra, West Bengal, Orissa, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar and Kerala.
![]()
Question 7.
“Information and technology industry is rapidly growing industry of India.” Explain.
Answer:
Information and Technology: The information technology industry is an industry based on technology with the help of computers and its applications, computers, communication, technology and concerning software. The knowledge reaches through means of communication and equipment. It is a knowledge based industry.
In India, the development of information technology is recent, but it is growing rapidly. However, enormous efforts are required for making it competitive with developed countries.
In India this industry developed after the International Treaty of 1994. In 1944 – 95, this industry earned Rs. 6345 crore rupees which increased to 79337 crore in the year 2002 – 03. It shows that this is the fastest growing industry of India.
Question 8.
Explain the difference between the public sector industry and private sector industry.
Answer:
1. Private Sector Industries: The industries which are owned by private individual and the management and control of these industries are in the hands of private persons are called private sector industries. The responsibility of running such industries and gaining the profit or loss is in the hands of owner only in private sector “Iron and steel Industry” of Jamshed Jee Tata is the example of it.
2. Public Sector Industries: In such industries the whole capital in invested by the government and ownership is also of the government. These industries are controlled and managed by the government only. The profit and loss is also beared by the state or local administration. “Coal India Limited” Hindustan Zinc Limited are the example of it.
Question 9.
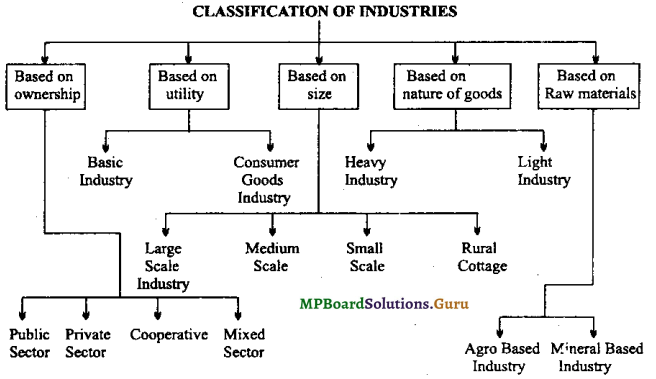
Explain the basis on which the different industries are classified in India?
Answer:
We can classify industries on the basis of their ownership, utility size and nature.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What efforts have been undertaken by the government to promote the small scale industry?
Answer:
Following efforts are made:
1. Establishment of boards and corporations: Government has from time to time established different boards and corporations like All India Board of Cottage Industries. All India Handicrafts Boards, Khadi Gram Udyog Mandal, Board of Small Scale Industry, Coir Board, National Small Scale Corporation, Indian Handicrafts Development Corporation.
2. Establishment of the council of small scale industry: Small scale industry development corporation. Nationalised Banks, State Finance Corporation are the members of this council.
3. Financial assistance: The financial assistance is provided to small scale industries through Reserve Bank, State Bank of India, The National Small Scale Corporation, State Finance Corporation, Cooperative Banks. Loan facilities are provided by the National Small scale Development Banks. State government also provides long term loan in their area under Government Assistance to Industries Act.
4. Technical Assistance: The organisation for development of small scale industries is established to provide technical assistance to the small scale industries. Under these services, Indians are sent to foreign countries for training and experts are invited to India to provide training in India.
5. Exemption from taxes: Concession in taxes are provided to small scale industries. Taxes like production tax are not imposed on the goods produced by these industries, if imposition of tax becomes essential then only a nominal tax is imposed. Apart from the exemption in taxes concessions are provided in the transportation expenditure.
6. facilities for Selling of products: Immense facilities are provided for the marketing of products of the small-scale industries. Showrooms or emporiums are being opened at various places by Central and State Government and by specific corporations for the selling of products of small-scale industries. Along with this big societies and board for the sale of the products of small scale goods are set up with help of state governments.
7. Exemption from licensing: Some goods are reserved under this area to promote small-scale industries.
8. Preference given by government in purchasing: The government gives preference to the products of small scale industries in purchasing goods for the use of its own departments and some goods are purchased completely from these industries.
9. Organising exhibitions: The government from time to time organises exhibitions at different places to make people aware about the products of small scale industries. Apart from this it provides assistance to those representatives of people who organise these exhibitions.
10. Establishment of Indian development bank for small scale industry: This bank is established as a co-organisation of Indian Industrial Development Bank. Its capital is rupees 450 crore rupees and its main function is to provide financial assistance to the small-scale industries. Its offices are opened in different states.
11. Interest on delayed payment: The government has made arrangement that if a buyer delays the payment of the goods purchased from a small industrial unit then he will have to pay interest on the delayed period.
12. Credit card scheme for small entrepreneurs: This scheme was implemented with the aim to make credit easily available to small businessman, artisans and entrepreneurs in 2002 – 03.
![]()
Question 2.
Write the importance of small scale and cottage industries.
Answer:
Small scale and cottage industries play an important role in Indian economy. These industries are suited to the Indian economy. These industries can be established with less capital and require more human labour. In India due to large population there is more human labour and also due to poverty there is less capital. For these reasons these are considered important part of Indian economy. This can be made clear by the following facts:
1. Suitable for rural economy: Around 50.4 per cent working population of India depends on agriculture, but the farmers do not get work for the whole year. Therefore small scale industries are important for them and suitable for Indian economy.
2. Reduces unemployment: The small scale industries reduce unemployment as they have potential of employing large number of workers with less capital investment for the same.
3. Help in reducing inequalities of incomes: The ownership of small scale industries is distributed among lakhs of people and families as a result of this economic power cannot be centralised hence it helps in equal distribution of income.
4. Development of individual art: Small scale industries are helpful in developing individual art.
5. Decrease pressure of population on agriculture: Major part of population is already dependent on agriculture in India and increasing population increases pressure on agriculture. If small scale industries are set up in rural areas it will reduce pressure on agriculture which will be beneficial for the country.
6. Help in industrial decentralisation: Small scale industries help in decentralisation of industries in the country. Large scale industries get centralised in a particular place due to some specific reasons but small scale industries are developed in villages and small towns.
7. Less requirement of technical knowledge: Small scale industries require less technical knowledge and less capital for its establishment. They can run with less trained worker. Thus they are best suited for Indian economy.
8. Fast producing industry: Produced goods can be obtained within a short time after the establishment of these industries. Therefore these are called fast producing industry. There is always a shortage of goods in India and these industry can contribute significantly in removing of this shortage.
9. Earning of foreign currency: The export of the goods manufactured by small scale industries is increasing day by day which helps the country in obtaining the valuable foreign currency. At present out of total export of the country the share of the goods produced by small scale industry is 35 per cent.
10. Less dependency on imports: We have to depend on imports from foreign countries to establish large scale industries either for technology or for machine or raw material. With small scale industries there is no such requirement, we do not have to import machines or techniques or raw material. Thus it decreases dependency on imports.
11. Supplementary to large scale industries: The small scale industries can work as supplementary industries to large scale industries for example, small scale industries can manufacture intermediate goods which can be used by large scale industries to produce final goods.
12. Use of local resources: Small scale industries utilise local resource. These industries help the rural people and common man to be an entrepreneur and give opportunities of investment of rural savings.
Question 3.
Explain the effects of industrial pollution.
Answer:
The effects of industrial pollution is as follows:
- Air pollution: Due to heavy industries air pollution has caused, smoke of mills and industries, waste material heat pollute the air. It disturbs the balance of air.
- Water pollution: Water gets polluted due to industrialization. The wastage and filth coming out of big industrial thrown in the river cause water pollution on. It causes may water diseases.
- Increase in the temperature of the earth: Because of excessive heat of industries the amount of carbon dioxide increases in the atmosphere due to their the temperature of the earth is increasing continuously. If it goes on increasing in the same way the polar region will melt and sea cost areas will submerge.
- Noise pollution: Heavy noise is caused due to machines of industries. It causes deafness, mental sickness, tension etc.
- Loss of ozone layer: Due to industrial pollution ozone layers are becoming then. Due to this skin cancer is causing.
![]()
I. Choose the correct alternatives:
Question 1.
The maximum investment limit of small scale industrial unit is:
(a) Rupees 1 crore
(b) Rupees 5 crore
(c) Rupees 3 crore
(d) Rupees 7 crore
Answer:
(b) Rupees 5 crore
Question 2.
Which of the following is not a crop of lac:
(a) Baisakhi
(b) Jaithavi
(c) Sawari
(d) Aghoni
Answer:
(c) Sawari
Question 3.
Out of total production of jute in the world India produces:
(a) 25%
(b) 10%
(c) 50%
(d) 35%
Answer:
(c) 50%
Question 4.
Which of these is concerned with the information technology:
(a) Motor car
(b) Beautiful clothes
(c) Computer
(d) Gold and silver
Answer:
(c) Computer
II. Fill in the blanks:
Question 1.
India is a major producer of ……………
Answer:
lac
Question 2.
Cottages industries which are run in villages are called ……………
Answer:
village industry
Question 3.
Maximum glass industries are situated in ……………
Answer:
W. Bengal
Question 4.
In the production of sugar our country stands …………… in the world.
Answer:
second
Question 5.
On the basis of capital investment the industries can be divided into …………. parts.
Answer:
three.
![]()
III. Match the following:
| A | B |
| 1. Cement industry | (a) Kashmir valley |
| 2. Sugar industry | (b) W. Bengal |
| 3. Jute industry | (c) Gujarat |
| 4. Cotton textile industry | (d) Chhota Nagpur plaeau |
| 5. Lac industry | (e) Uttar Pradesh |
| 6. Silk industry | (f) Maharashtra |
Answers:
1. (c)
2. (e)
3. (b)
4. (f)
5. (d)
6. (a)
IV. Write ‘true’ or ‘false’:
Question 1.
Concession in taxes are provided to small scale industries.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
Cottage and small scale industries are fast producting industries.
Answer:
True
Question 3.
In India Jute industry was started in India in 1955.
Answer:
False
Question 4.
India stands 5th in the production of cement.
Answer:
True
Question 5.
Glass industry is a new industry of India.
Answer:
False
![]()
V. Give answer in one word:
Question 1.
The oldest industry of India is.
Answer:
Cotton textile industry
Question 2.
Silk industry stands second in the world.
Answer:
India
Question 3.
Paper production comes under the industry.
Answer:
Cottage industry
Question 4.
By information and technology we mean.
Answer:
Computer, communication
Question 5.
All India handloom board was established in.
Answer:
1952
Question 6.
The resource on economic system is called private ownership.
Answer:
Private sector (ownership) or capitalist.