MP Board Class 12th Biology Solutions Chapter 7 Evolution
Evolution NCERT Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Explain antibiotic resistance observed in bacteria in light of Darwinism selection theory.
Answer:
Darwinism theory of natural selection states that environment selects organisms with favourable variations and these organisms thus, survive and reproduce. It is observed when bacterial populations are exposed to certain antibiotic, the sensitive bacteria could not tolerate and hence, died due to the adverse environment. Whereas some bacteria that developed mutation became resistant to the particular antibiotic and survived. As a result such resistant bacteria survive and multiply quickly as compared to other sensitive bacteria. So, the whole population is regained by multiplication of resistant variety and antibiotic resis¬tant gene becomes widespread in the bacterial population.
Question 2.
Find out from newspapers and popular science articles any new fossil dis-coveries or controversies about evolution.
Answer:
Fossils of dinosaurs have revealed the evolution of reptiles in Jurassic period. As a result of this evolution of other animals such as birds and mammals has also been discovered. However, two unusual fossils recently unearthed in China have ignited a controversy over the evolution of birds confiiciusomis is one such genus of primitive birds that were crow sized and lived during the Cretaceous period in China.
Question 3.
Attempt giving a clear definition of the term species.
Answer:
A species generally includes similar organism. Members of this group can show interbreeding. Similar group of genes are found in the members of same species and this group has capacity to produce new species. Every species has some cause of isolation which intruped the interbreeding with nearest reactional species which is refer as reproductively isolated.
![]()
Question 4.
Try to trace the various components of human evolution (Hint: Brain size and function, skeletal structure, dietary preference, etc.)
Answer:
The various components of human evolution are as follows:
- Brain capacity.
- Posture
- Food/Dietary preference and their important features.
Name brain capacity, posture and food features :
- Dryopithecus Africans : Knuckle walker, walked similar to Gorillas and Chim-panzees (was more apelike) soft fruit and leaves; canines large, arm and legs are of equal size.
- Ramapithecus: Semi-erect (more manlike) seeds, nuts canines were small while molars were large.
- Australopithecus africanus: Australopithecus africanus 450 cm3 full erect prosture, height (1 -05m) Herbivorous (ats fruits). Hunted with stone weapons, lived as trees, canines and incisors were small.
- Homo habilus: Homo habilus 735 cm3 fully erect posture, height (1 -5m) carnivo¬rous canines were small. They were first tool makers.
- Homo erectus: Homo erectus 800-1100 cm3 fully erect posture, height (1-5- l-8m) omnivorous. They used stone and bone tools for hunting games.
- Homo neanderihalensis : Homo neanderthalensis 1300 – 1600 cm3 fully erect posture, height (1-5 – l-6m) omnivorous cave dwellers, used hiles to protect their bodies and buried their dead.
- Homo sapiens fossils : Homo sapiens fossils 1650 cm3 fully erect posture with height (l -8m) omnivorous. They had strong jaw with teeth close together. They were cave dwellers, made painting and carvings in the caves. They developed a culture and were called first modem man.
- Homo sapiens sapiens : Homo sapiens sapiens 1200 – 1600 cm3 fully erect pos¬ture, height (1-5 – l-8m) omnivorous. They are the living modem men with high intelligence. They developed art, culture, language, speech, etc. They cultivated crops and domes¬ticated animals.
Question 5.
Find out through internet and popular science articles whether animals other than man has self-consciousness.
Answer:
There are many animals other than humans, which have self-consciousness. An example of an animal being self-conscious is dolphins. They are highly intelligent. They have a sense of self and, they also recognize others among themselves and others. They communicate with each other by whistles, tail-slapping, and other body movements, not dolphins, there are certain other animals such as Crow, Parrot, Chimpanzee, Gorilla, Orangutan, etc., which exhibit self-consciousness.
Question 6.
List 10 modern day animals and using the internet resources link it to a corresponding ancient fossil. Name both.
Answer:
Modern and Ancient corresponding animals :
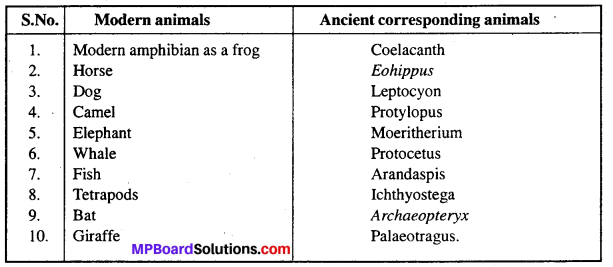
Question 7.
Practise drawing various animals and plants.
Answer:
Question 8.
Describe one example of adaptive radiation.
Answer:
Darwin’s finches in the Galapagos Island once had a common ancestor but with evolution, they modified into different types according to their food habitat.
Question 9.
Can we call human evolution as adaptive evolution ?
Answer:
No, we can not be called human evolution as adaptive evolution.
Question 10.
Using various resources such as your school Library or the internet and discussions with your teacher, trace the evolutionary stages of any one animal, say horse.
Answer:
The evolution of horse started with Eohippus during Eocene period. It involved the following evolutionary stages :
- Gradual increase in body size
- Elongation of head and neck region
- Increase in the length of limbs and feet
- Gradual reduction of lateral digits
- Enlargement of third functional toe
- Strengthening of the back
- Development of brain and sensory organs
- Increase in the complexity of teeth for feeding on gras
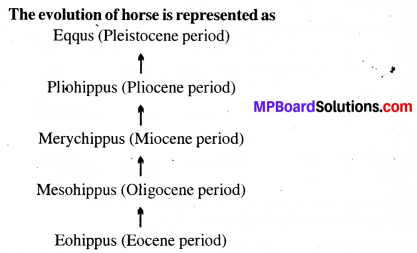
- Eohippus : It had a short head and neck. It had four functional toes and a splint of 1 and 5 on each hind limb and a splint of 1 and 3 in each forelimb. The molars were short crowned that were adapted for grinding the plant diet.
- Mesohippus : It was slightly taller than Eohippus. It had three toes in each foot.
- Merychippus : It had the size of approximately 100 cm. Although it still had three toes in each foot, but it could run on one toe. The side toe did not touch the ground. The molars were adapted for chewing the grass.
- Pliohippus : It resembled the modern horse and was around 108 cm tall. It had a single functional toe with splint of 2nd and 4th in each limb.
Equus : Pliohippus gave rise to Equus or the modern horse with one toe in each foot. They have incisors for cutting grass and molars for grinding food.
![]()
Evolution Other Important Questions and Answers
Evolution Objective Type Questions
1. Choose the Correct Answer.
Question 1.
These are found at the atmosphere of earth before evolution:
(a) Water vapour, CH4, NH3 and Oxygen
(b) CO2, NH3, H2 and Water vapour
(c) CH4, NH3, H2 and Water vapour
(d) CH4, O3, O2 and Water vapour.
Answer:
(c) CH4, NH3, H2 and Water vapour
Question 2.
Which gas is absent at the atmosphere of earth at the time of origin of earth:
(a) NH3
(b) H2
(c) O3
(d) CH4
Answer:
(c) O3
Question 3.
Which gaseous mixture are used and found the amino acid by Miller:
(a) Methane, Ammonia, Hydrogen and Water vapour
(b) Methane, Ammonia, Nitrogen and Water vapour
(c) Methane, Nitrogen, Hydrogen and Water vapour
(d) Ammonia, Carbon dioxide, Nitrogen and Water vapour.
Answer:
(a) Methane, Ammonia, Hydrogen and Water vapour
Question 4.
Who gave the theory “Survival of the fittest” :
(a) Charles Darwin
(b) Herbert Spencer
(c) Lamarck
(d) Hugo de Vries.
Answer:
(b) Herbert Spencer
Question 5.
Who gave the theory of inheritance of acquired, characters :
(a) Charles Darwin
(b) Lamarck
(c) Valles
(d) de Vries.
Answer:
(b) Lamarck
![]()
Question 6.
Who wrote origin of species :
(a) Oparin
(b) Beajman
(c) Lamarck
(d) Darwin.
Answer:
(d) Darwin.
Question 7.
What is the name of Darwin’s ship:
(a) Gangotri
(b) Beagle
(c) Atlantic
(d) Seagull.
Answer:
(b) Beagle
Question 8.
‘Atmosphere is a factor of variation’ who gave this theory :
(a) Mendel
(b) Darwin
(c) Lamarck
(d) Laplace.
Answer:
(c) Lamarck
Question 9.
Darwinism explain it:
(a) Characters are grown by heredity
(b) Species are changed into structural form with time .
(c) Nature selected the animals which are adapted
(d) Origin of evolution due to effect of environment.
Answer:
(c) Nature selected the animals which are adapted
Question 10.
Which antibiotic is used to Replica planting experiment of Ladderberg:
(a) Penicillin
(b) Streptomycin
(c) Erythromycin
(d) Neomycin.
Answer:
(a) Penicillin
Question 11.
Which is the basic unit of natural selection:
(a) Species
(b) Community
(c) Genous
(d) Solitary organism.
Answer:
(c) Genous
Question 12.
Who gave the theory of natural selection :
(a) Lamarck
(b) de Vries
(c) Darwin
(d) Mendel.
Answer:
(d) Mendel.
Question 13.
Darwinism is based on:
(a) Segregation
(b) Independent assortment
(c) Quantitative heredity
(d) Natural selection.
Answer:
(b) Independent assortment
![]()
Question 14.
Who discover the uses and experiment of organs:
(a) Valles
(b) Lamarck
(c) Darwin
(d) de Vries
Answer:
(a) Valles
Question 15.
The unit of natural selection :
(a) Solitary animal
(b) Family
(c) Community
(d) Species.
Answer:
(d) Species.
Question 16.
Mule is a product of:
(a) Mutation
(b) Reproduction
(c) Inter-species hybridization
(d) Intra-species hybridization
Answer:
(b) Reproduction
Question 17.
Who use first the word ‘species’:
(a) Linnaeus
(b) John
(c) Aristotle
(d) Darwin
Answer:
(b) John
Question 18.
Homologus organs are :
(a) Similar in origin
(b) Similar in function
(c) Similar in evolution
(d) Similar in behaviour.
Answer:
(a) Similar in origin
Question 19.
Which era are called as golden period of Reptilia or Dinosaurs :
(a) Mesozoic
(b) Cenozoic
(c) Palaeozoic
(d) Cenozoic.
Answer:
(a) Mesozoic
Question 20.
Dinosaurs are distinct in this era:
(a) Jurassic
(b) Triassic
(c) Cretaceous
(d) Permian.
Answer:
(c) Cretaceous
Question 21.
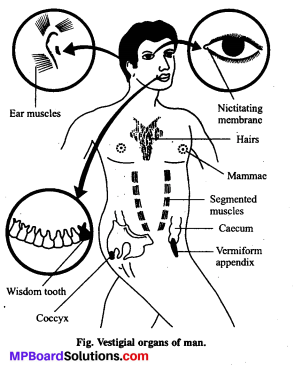
Vestigial organs of human’ are:
(a) Wisdom teeth, Coccyx, Nail, Eyelids, Vermiform appendix
(b) Wisdom teeth, Coccyx, Vermiform appendix, Pancreas
(c) Wisdom teeth, Coccyx, Vermiform appendix, Nictating membrane
(d) Coccyx, Wisdom teeth, Nail, Auricular muscle.
Answer:
(c) Wisdom teeth, Coccyx, Vermiform appendix, Nictating membrane
Question 22.
How made fossils :
(a) Animals are naturally buried in land after death
(b) Animals are decomposed by decomposers
(c) Animals are eaten by their hunter species
(d) Animals are destroyed due to environmental conditions.
Answer:
(d) Animals are destroyed due to environmental conditions.
Question 23.
Species which are similar in shape and different in reproduction are called :
(a) Sub-species
(b) Sibling
(c) Isotopic
(d) Allopetric species.
Answer:
(c) Isotopic
Question 24.
Name the ship which had been used by Darwin for journey :
(a) Ciloge
(b) Beagle
(c) Seagull
(d) Atlantic.
Answer:
(b) Beagle
Question 25.
Life is not in this era :
(a) Mesozoic
(b) Palaeozoic
(c) Cenozoic
(d) Azoic.
Answer:
(d) Azoic.
![]()
Question 26.
Which factor is responsible for evolution due to New-darwinism theory :
(a) Mutation
(b) Usefull variation
(c) Hybridization
(d) Mutation and Natural selection.
Answer:
(d) Mutation and Natural selection.
Question 27.
Found the age of fossils by which :
(a) By quantity of calcium ions
(b) By quantity of organic radioactive components
(c) By struggle from other mammals
(d) By structure of bones.
Answer:
(d) By structure of bones.
Question 28.
Darwin finches are related to which of the following evidences :
(a) Fossils
(b) Embryology
(c) Anatomy
(d) Geographical distribution.
Answer:
(d) Geographical distribution.
Question 29.
Who gave Recapitulation theory :
(a)Weizmann
(b) Haeckel
(c) Darwin
(d) Malthus.
Answer:
(b) Haeckel
Question 30.
Which definition of organic evolution is correct:
(a) Evolutionary history of a species
(b) History of species with the variations is the species
(c) Embryonal history of species
(d) Development of species.
Answer:
(a) Evolutionary history of a species
Question 31.
What is the perfect sequence of development of human:
(a) Peking man, Heidelberg man, Neanderthal Cro-Magnon
(b) Peking man, Homo sapiens, Cro-Magnon, Neanderthal
(c) Peking man, Neanderthal,.Homo sapiens, Heidelberg
(d) Peking man, Cro-Magnon, Homo sapiens, Neanderthal.
Answer:
(a) Peking man, Heidelberg man, Neanderthal Cro-Magnon
Question 32.
Which of the following is the most primitive ancestor of man :
(a.) Australopithecus
(b) Ramapithecus
(c) Homo habilis
(d) Homo neanderthalensis.
Answer:
(b) Ramapithecus
Question 33.
Ancestral amphibians were tetrapods that evolved during :
(a) Jurassic period
(b) Cretaceous period
(c) Devonian period
(d) Carboniferous period.
Answer:
(c) Devonian period
2. Fill in the Blanks :
- Earth is a member of …………….
- ……………. wrote ‘Origin of life’.
- Oxygen is find the earth because photo-synthetic organisms are present on the earth, this phenomenon is called …………….
- ………….. is the connecting link between Reptiles and Aves.
- …………………. is the ancesters of horse.
- The evolution of ……………. molecule set the stage for evolution of autotrophs.
- Evolution of birds and mammals were ……………. era.
- Golden era of Dinosaurs is ……………. period.
- ……………. fossil man has been known from Shivalik hills in India.
- Book of Charles Darwin “Origin of life” has been explained of …………….
- ……………. be change of hareditary characters.
Answer:
- Solar system
- Oparin
- Oxygen revolution
- Archaeopteryx
- Eohippus
- Chlorophyll
- Jurassic
- Mesozoic
- Ramapithecus
- Natural selection
- Mutation.
![]()
Question 3.
Match the Following :

Answer:
- (d)
- (a)
- (e)
- (c)
- (b)

Answer:
- (d)
- (c)
- (e)
- (a)
- (b)
- (f).
4. Answer in One Word / Sentence:
- The matter which gave rise to the universe 15 billion years ago.
- The matter which is a link between acellular and cellular system.
- The island at which Darwjn studies the organisms for his theory of evolution.
- Origin of two or more unlike species from a common ancestor.
- The whole process of development at changes from embryo to adult organism.
- The process of changes in the course of origin of a new species.
- The theory of organic evolution proposed by Darwin.
- The permanent, heritable and spontaneous changes in organisms.
- The remains of ancient organisms.
- The organs which are different in their origin but have similar function.
Answer:
- Ylem
- Coacervates
- Galopegos
- Adaptive radiation
- Ontogeny
- Phytogeny
- Natural selection
- Mutation
- Fossils
- Homologous organs.
Evolution Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name the non-cellular organism.
Answer:
Virus.
Question 2.
Name the theory which tell about the milky way and formation of star.
Answer:
Big Bang.
Question 3.
Releasing of 02 by the evolution of photosynthesis an ancient time is called?
Answer:
Oxygen revolution.
![]()
Question 4.
Which planet has the possibility of origin of life other than earth?
Answer:
ars.
Question 5.
Where did life originate ?
Answer:
In water.
Question 6.
What is the art of limitation, which is practiced the world over from annoying siblings or plant resembles another creature to gain other advantages?
Answer:
Mimicry.
Question 7.
Name the method of the changing of the structure of a gene resulting in a variant form that may be transmitted to.
Answer:
Mutation.
Question 8.
What is the collection of different genes within an inter breading population?
Answer:
Gene pool.
Question 9.
Who wrote origin of species?
Answer:
Charles Darwin.
Question 10.
Who proposed the theory of natural selection?
Answer:
Darwin.
Question 11.
Who proposed the Recapitulation theory or Biogenetic law?
Answer:
Haeckel.
Question 12.
Astronomical distance measured in?
Answer:
Astronomical distance measured in Light years.
Question 13.
Name the theory by which earth is said to originate.
Answer:
The big bang theory.
Question 14.
What is fossil ?
Answer:
Fossils are the remains or impressions of ancient organisms preserved in sedimentary rocks or other media.
Question 15.
What is mutation ?
Answer:
New species originate due to changes of hereditary characters are called mutation.
Question 16.
Name the scientist who tell the spontaneous theory is wrong.
Answer:
Louis Pasteur’s.
Question 17.
Which era is called golden period of Dinosaurs?
Answer:
Mesozoic period is called golden period of Dinosaurs.
Question 18.
In which ship Darwin studied the nature ?
Answer:
Beagle.
![]()
Question 19.
Name any two vertibrates body organ which are homologus organs of human forelimb.
Answer:
(1) Flipper of Whale,
(2) Wing of birds.
Question 20.
What is the scientific name of modern man ?
Answer:
Homo sapiens.
Question 21.
Who is the early man of the modern human?
Answer:
Cro-Magnon peoples are early human of modern human.
Question 22.
Who are the early human and sub-human.
Answer:
Ramapithecus is early human and Australopithecus is early human.
Question 23.
Which human form first started to walk on two legs?
Answer:
Australopithecus form first started to walk on two legs.
Question 24.
Which type of human was ‘Cro-Magnon’ on the basis of food in take?
Answer:
Cro-Magnon was carnivorous.
Question 25.
On the basis of evolution which human had brain size of 1400cc?
Answer:
Neanderthal.
Question 26.
Give the name of apelike ancestors of humans
Answer:
Apelike ancestors of human’s are Dryopithecus.
Question 27.
Differentiate between Dryopithecus and Ramapithecus.
Answer:
Dryopithecus were apelike but Ramapithecus were mostly human like.
Evolution Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is virus ? Why is it treated as a link between living and non-living ?
Answer:
Viruses are simplest organism of the earth, which consists of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) surrounded by protein cover. It shows characteristics of living as well as non-living organisms.
(A) Living characters of virus:
- Virus shows structural differentiations.
- They contain hereditary material.
- They exhibit mutation.
- They spread plant and animal diseases.
- Growth and development present.
- They exhibit adaptaion.
- They possess sensitivity.
(B) Non-living characters of virus:
- Lack protoplasm and cell organelles.
- Can be crystallized.
- No metabolic activities seen.
- Cannot reproduce outside living cells.
- They lack enzymes.
Due to above reason, viruses are considered as link between living and non-living organisms, thus, it is the first life originated in the earth.
![]()
Question 2.
What is oxygen revolution? Explain.
Answer:
Oxygen revolution : Evolution of 02 in photosynthesis during primitive environmental conditions is very important because, it is required in the evolution of organism and conversion of reducing environment into oxidizing environment hence, it is called oxygen revolutioa Oxygen evolution should cause the following changes in the environment:
- Oxygen evolution should cause the conversion of reducing environment into oxidizing environment
- Ozone layer is formed 15 miles above from the earth which absorbs the ultraviolet light of the sunlight and thus, prevents the entry of uv light in the atmosphere.
- O2 present in the environment dissociates methane (CH4) into CO2 and O2. This CO2 is used in photosynthesis.
- NH3 of the primitive environment is dissociated into H2O.and nitrogen.
CH4 + 2O22 → CO2 + 2H2O
4NH3 + 3O2 → 2N2 + 6H2O.
Question 3.
Explain the origin of the earth.
Answer:
Origin of the earth:
- Earth was formed 4-5 billion years back.
- Initially, die surface was covered with water vapOur, methane, C02 and NH3.
- The UV rays of the sun broke water into hydrogen and oxygen.
- Hydrogen escaped and oxygen combined with NH3 and CH4 to form water, C02 and other gases, also forming die ozone layer.
- Cooling of water vapour led to rain which filled the depressions on earth’s surface, forming water bodies.
Question 4.
Mention the names of discoveries and principles given by the following scientists:
- Louis Pasteur
- A. I. Oparin
- Urey and Miller
- Francesco Redi
- Faux.
Answer:
- Louis Pasteur : He proved that air contains spores of microorganism and Biogenesis theory was supported by him.
- A. I. Oparin: He presented the biochemical explanation of origin of life in his book “The Origin of Life on Earth”.
- Urey and Miller : They supported the evidence of Oparin-Haldane theory of Origin of life.
- Francesco Redi: He by conducting experiments proved that abiogenesis cannot exist but bioginesis theory can exist i.e., Life arises from pre-existing life.
- Faux: He has been experimentally supporting the organic substances as described by Oparin.
Question 5.
Write down the difference between :
- Ozone and Oxygen
- Micro-molecules and Macro-molecules.
Answer:
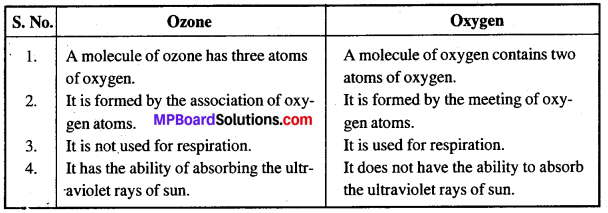
1. Differences between Ozone and Oxygen :
2. Differences between Micro-molecules and Macro-molecules :

Question 6.
What are homologous organs ?
Or
What is homology ?
Answer:
Organs which are similar in structure and origin but different in appearance and functions are called homologous organs and the phenomenon is called homology.
Examples : Forelimbs of bat, wings of bat, hands of man, forelimbs of horse. These are the examples of homologous organs because, they are made up of similar bones, hu¬merus, radius-ulna, carpals, metacarpals and fingers.
Question 7.
What do you mean by analogous ?
Answer:
Analogous organs: Organs which are different in origin and structure but per¬forming similar functions are known as analogous organs and the phenomenon is called as analogy. Analogous organs do not indicate phylogeny.
Examples : Wings of butterflies are made up of chitin, wings of birds made by production of feathers on forelimbs and skin present between the fingers of bat are the examples of analogous organs.
Question 8.
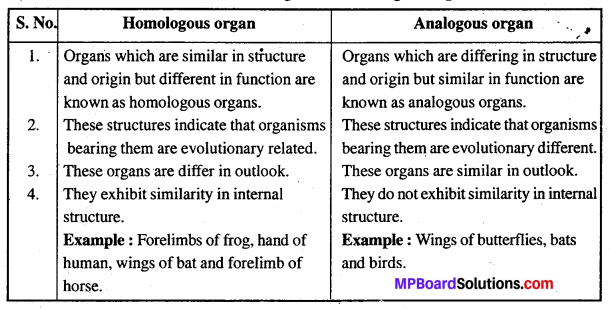
What is the difference between homologous and analogous organs ? Give two examples of each of them.
Answer:
Differences between Homologous and Analogous organs :
Question 9.
What do you mean by vestigial organs ?
Or
Write the two names of vestigial organs of man.
Or
What are vestigial organs ? Explain. Write four vestigial organs of the human body.
Answer:
Vestigial organs : Organs that are reduced and have become functionless in an organism but were functional in their ancestors are called as vestigial organs :
Examples :
- Vermiform appendix
- Coccygial vertebrae
- Nictitating membrane in the eyes of human
- Muscles of external ear (Pinna).
Question 10.
What is connecting link ? Also explain the significance of connecting links.
Answer:
Connecting link : Certain organisms which share characters with two different groups. Such organisms are called connecting links.
Examples : Some fossils present in nature like Archaeopteryx is known as fossils connecting link and it is the connecting link of birds and reptiles. Neopilina, Platyptus, Protopterus, etc. Neopilina is a mollusc and is the connecting link of mollusca and annelida.
Significance of Connecting links : It proves the process of organic evolution and helps in the identification of organism closely related.
![]()
Question 11.
Write down the demerits of Darwinism.
Answer:
Some of the demerits of Darwinism are :
- Darwinism stresses upon small fluctuating variations which has no role in evolution.
- Does not satisfactorily explain effect of use and disused and presence of vestigial organs:
- It did not differentiate somatic and germinal variations.
- It explains survival of the fittest but not arrival of the fittest. .
Question 12.
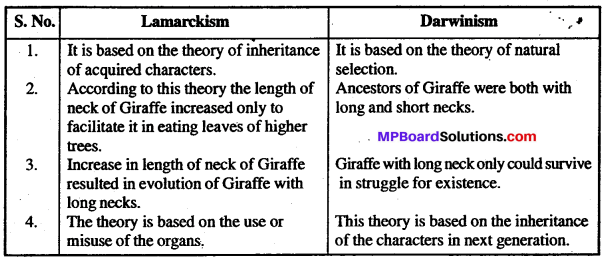
Differentiate between Lamarckism and Darwinism.
Answer:
Differences between Lamarckism and Darwinism:
Question 13.
Explain Lamarckism in short
Or
Explain Lamarckism of organic evolution in brief.
A ns. Lamarckism : In 1809, Lamarck has proposed a theory to explain organic evolution, which is known, as the “Theory of inheritance of acquired characters.” According to Lamarck, organisms acquire certain characters during their lifetime due to changes in environment and these acquired characters are heritable. According to this theory, new species are originated as follows :
- New requirements and wills are produced in the organisms due to the effect of changed environment
- New requirements and wills of organisms resulting in the production of new habits.
- Changes in the habit bringing about modifications of the organ.
- New habits resulting in the use or disuse of the organs:
- Use of organ resulting in the development of acquired characters.
- These acquired characters are heritable.
- Inheritance of acquired characters resulting in the development of new species.
Evolution Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Draw a well-labelled diagram of Miller and Urey’s experiment
Answer:
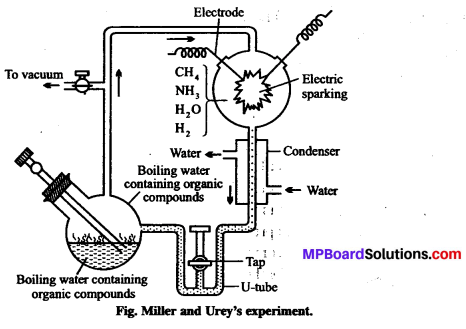
Experimental evidence of Chemical evolution or Miller’s experiment:
- Experiment was performed by S.L. Miller and H.C. Urey in 1953.
- Experimental set-up: In a closed flask containing CH4, H2, NH3 and water vapoiy at 800°C, electric discharge was create. The conditions were similar to those in primitfve atmosphere.
- Observations: After a week, they observed presence of amino acids and complex molecules like sugars, nitrogen bases, pigments and fats in the flask.
- Conclusions : (i) It provides experimental evidence for the theory of chemical origin.
(ii) It showed that the first non-cellular form of life was created about 3 billion years ago.
(iii) It showed that non-cellular biomolecules exist in the form of DNA, RNA, polysaccharides and protein.
Question 2.
Write an essay on modern concepts of origin of life.
Or
Explain the role of non-living in origin of life.
Answer:
Modern concept of origin of life : The modem concept of origin of life was postulated by a Russian biochemist A.I. Oparin in 1936. According to this theory, after the formation of earth various chemicals played important role in the formation of atmosphere. Life originated and first organism came into existence from certain molecules when atmospheric conditions became suitable. According to Oparin, life originated in the following steps:
1. Formation of earth and its atmosphere: Earth is believed to be originated some 4,500 million years ago by the condensation and cooling of the clouds of cosmic dust and gases called ylem. The heavier elements collected at the core and lighter elements around the core. Outermost layer contains H, C, O and N. Oxygen was found only in combination of other elements. These four elements reacted with each other forming H2, H2O, CH4, NH3, CO2 and HCN.
2. Formation of small organic molecules : The mixture of methane, ammonia, water and hydrogen comes in contact of solar energy. Cosmic rays and electric discharge could produce some simple organic compounds. These simple organic compounds formed in such a way and accumulated in primitive atmosphere and oceans were responsible for synthesis of complex micro molecules as follows :
3. Formation of polymers : It is clearly understood from the above description that a large number of micro molecules such as hydrocarbons, amino acids, fatty acids, purine and pyrimidines and simple sugars accumulated in the oceans. When atmospheric water condensed on further cooling, the inorganic precursors collided, reacted and aggregated to form new molecules of increasing size and complexity. Thus, by polymerization macromolecules were formed. The chemical reactions for the formation of macro-molecules can be summarized as follows:
(a) Sugar + Sugar → Polysaccharides
(b) Fatty acid + Glycerine → Lipids
(c) Amino acid + Amino acid → Protein
(d) Nitrogenous base (Adenine) + Sugar + Phosphate → Adenosine phosphate
(e) Nitrogenous base + Sugar → Nucleoside
(f) Nucleoside + Phosphate → Nucleotide
(g) Nucleotide + Nucleotide → Nucleic acid.
4. Formation of molecular aggregates and primitive cells : Over a vast of time, these molecules became associated with one temporary complex. Ultimately, it leads to the formation of a coacervate. A coacervate is a solution of high molecular weight of chemicals, i.e., proteins and carbohydrates, which become bounded by lipid membrane, which is selectively permeable. The coacervate grows by absorbing molecules from their environment. The substances which got accumulated in the coacervates underwent reactions and resulted in the molecular reorganization of some proteins into enzymes. A coacervate having nucleoprotein surrounded by various nutritive organic substances and covered by surface membrane is considered to be the precell, which got later transformed into first living cell. The coacervate can reproduce by budding.
5. Evolution of complex biochemical reactions : Primitive organism utilize chemi¬cal substances present in the environment as food hence, they are:
(a) Heterotrophic, chemosynthetic organisms appeared due to mutation and natural selection in heterotrophs.
(b) Blue-green algae evolved from chemosynthetic organisms by mutation and natural selection.
(c) The liberation of free oxygen into the atmosphere produced by the blue-green algae due to the process of photosynthesis. It finally changed the reducing atmosphere into an oxidizing one and therefore, all possibilities of further chemical evolution were finished.
Free living eukaryotes originated in the ocean from blue-green algae.
6. The origin of well-developed organisms : From the simple eukaryotes which were like unicellular organisms of today various forms of life evolved during passage of time.
![]()
Question 3.
Write the process of formation of organic molecules in sea water on earth with the help of Miller and Urey’s experiment
Answer:
The work of A.I. Oparin (1938-1965), HLUrey and Stanley Miller (1959) pro¬vided evidences in the favour of biochemical origin of life. They had prepared the atmos¬phere like that of primitive earth and as described by Oparin, they made the synthesis of organic compounds by the following methods:
(i) Four elements H, C, O (not free O2) and N react .with each other to form H2O, CH4, NH3, CO2 and HCN on primitive earth.
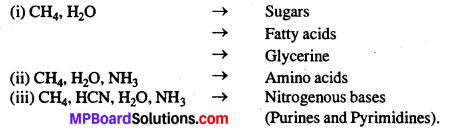
(ii) From these four elements following organic molecules were formed in sea water of earth:
(a)
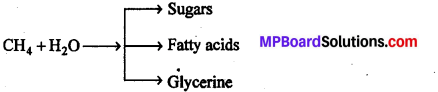
(b) CH4, H2O, NH3 → Amino acids.
(c) CH4, HCN, H2O, NH3 → Nitrogenous bases.
(iii) Macro-molecules of organic compounds were synthesized by these above pre¬pared organic compounds.
(a) Sugar + Sugar → Polysaccharides (Carbohydrate).
(b) Fatty acids + Glycerol → Fats.
(c) Amino acid + Amino acid → Protein.
(d) Nitrogenous base + Sugar → Nucleoside.
(e) Nucleoside + Phosphoric acid → Nucleotide.
(f) Nucleotide + nucleotide → Nucleic acid.
(g) Nitrogenous base (Adenine) + Sugar + Phosphate →Adenosine phosphate.
(iv) The above organic compounds and salts together constituted the first living being.
Question 4.
Name connecting link of reptiles and birds. Also write their characters.
Answer:
Archaeopteryx is the connecting link of birds and reptiles. Archaeopteryx was a bird. It is regarded as the connecting link between reptiles and birds, which suggests the path of evolution of the latter from the former. It is found as fossils. They are found during Jurassic period 140 million years. Archaeopteryx exhibits both reptiles and birds like characters.
1. Reptiles like characters:
- Bones were similar to that of reptiles in which air sacs were absent.
- Tail bearing vertebra.
- It had teeth in jaws, scales were present on the body.
- Metacarpals were free.
- Pelvic girdle recombines with the pelvic girdle of reptiles.
2. Birds like characters :
- Presence of feathers on body. .
- Forelimbs were modified in wings.
- Skull large and monocondylar.
- Jaws were modified into beak.
- Hallux was backwarded and pointed.
![]()
Question 5.
Give a detailed account of theory of natural selection.
Or
Describe the Darwin’s opinion about the origin of new species of organisms.
Answer:
Charles Darwin (1809-1882) explained the theory of evolution in his book “Origin of species by natural selection.” Darwin undertook a long voyage for five years in the capacity of a naturalist on a British warship ‘Beagle’. He travelled to islands of Galapagos and collected evidences to explain evolution.
To explain origin of species he gave theory of natural selection as a mechanism for evolution.
The main points of Darwinism are given below:
1. Over production of offsprings : Every living being has an inherent tendency to produce more offspring than that can survive.
2. Struggle for existence : Though the offsprings are produced in large number yet their production remain almost constant. This is because of struggle for existence. There is struggle for food, space, breeding, etc. Moreover death of individuals due to diseases an
3. Survival of the fittest: Darwin believed that any individual is successful in struggle for existence if it survives long enough to produces offsprings. Individuals who are fit in a particular environment can only survive.
4. Variation: Due to constant struggle, the organisms change themselves in accordance with the new needs.
5. Natural selection : In the struggle, for existence organisms having variations favourable to the environment would have more chance to survive and reproduce their own kind. Those which do not possess favourable variations would die or fail to reproduce.
6. Origin of species : Any changes in environmental conditions cause natural selection to act upon the population and select the well adapted individuals. It results in changes of characters of the populations. By the inheritance of these changes in successive generations, new species are formed.
Question 6.
Organic Evolution is a continued process, explain it in favour of it giving any three evidences.
Answer:
Evolution is a complex phenomenon accounting for the present day diversity among organisms. But it has clearly maintained the basic unity among them since it occurred over a period of millions of years, no one would have seen/recorded evolution and hence scientists have provided various evidences to prove evolution.
Some of the evidences of organic evolution are described below :
I. Evidences from Embryology :
- Important activities that occur various animals are:
- For the survival, all animals get energy and various substances from environment.
- In all organisms energy is produced from ATP.
- In all organisms, the duplication of DNA is similar.
- In all organisms, protein synthesis is same and it is produced from ribosomes.
- In all organisms respiration and steps of respiration is same.
- All organisms multiplicate and reproduce, due to which they have basic similarities.
- All organisms conduct hereditary characters on similar principles.
II. Evidence from Anatomy: Anatomy of living organisms will be explained with different examples:
- Homologous organs: Organs which are similar in structure and origin but diffeifent in function and appearance is known as homologous organs.
- Analogous organs : Organs which are different in origin and structure but performing similar functions are known as analogous organs.
- Vestigial organs : Organs that are reduced and have become functionless in an organism, but were functional in their ancestors are called vestigial organ.
III. Evidences from vestigial organs: Organs of the body which are non-functional but they are functional in some other organisms are called vestigial organs:
Morphological evidence of evolution is provided by the presence of vestigial organs of body which are often undesired, degenerated and non-functional. These might have been large and functional in some other animals or in ancestors of those which now possess it in rudimentary forms. e.g„ vermiform appendix in man, muscles of external ear (pinna) in man, nictitating membrane or plica, semilunaris in human eye, wisdom teeth (third pair of molars) tail bone (coccyx) in man, wings of ostrich, hindlimbs in snakes, etc.
![]()
Question 7.
What do you mean by organic evolution? How do fossils exhibit evidence to prove organic evolution?
Answer:
Descent with modification in organism is known as organic evolution.
Evidences of organic evolution from fossils record : Fossils are treated as significant evidence of organic evolution. Fossils are the remains or impressions of ancient organisms preserved in the layers of rock and soil. Fossils only do not prove the theory of organic evolution, yet it evidently prove that gradually complexity increased in body organization. The complexity in the body of organization can be noticed as we study the upper layers. Thus, it can be concluded from above observations :
- The crust of the earth and the organisms living on it underwent change in the course of time.
- The organisms with simple structural organization originated earlier than the complex ones.
- Some of the organisms lived on the earth for short time and became extinct. This was a result of drastic changes in the climate on the earth.
Hence, forth fossils produce bonafide record of such plants and animals which had shown their existence once upon a time and now are extinct or not present exactly in the same form, thus, producing strong evidence in favour of organic evolution.