MP Board Class 12th Chemistry Solutions Chapter 15 Polymers
Polymers NCERT Intext Exercises
Question 1.
What are polymers ?
Answer:
Polymers are high molecular mass substances (103-107u) formed by the combi-nation of a large number of simple molecules. They are also called macro molecules. For example, polyethene, bakelite, PVC, teflon etc.
Question 2.
How are polymers classified on the basis of structure ?
Answer:
On the basis of structure, polymers are classified as:
- Linear polymers: e.g. polyethene, nylons, polyvinylchloride etc.
- Branched chain polymers: e.g. low density polythene, glycogen.
- Cross-linked polymers: e.g. bakelite, melamine, etc.
Question 3.
Write the names of monomers of the following polymers:
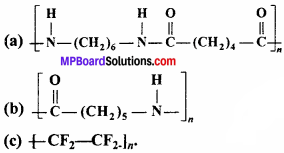
Answer:
- Hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid
- Caprolactum
- Tetrafluoroethene.
Question 4.
Classify the following as addition and condensation polymers: Terylene, Bakelite, Polyvinyl chloride, Polythene.
Answer:
- Terylene: Condensation polymer
- Bakelite: Condensation polymer
- Polyvinyl chloride: Addition polymer
- Polyethene: Addition polymer.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain the difference between Buna-N and Buna-S.
Answer:
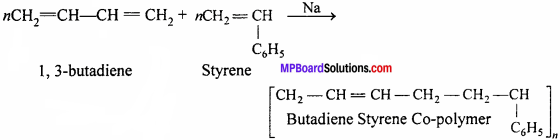
Buna-N is a co-polymer of 1,3-butadiene and acrylonitrile Buna-S is a co-polymer of 1,3-butadiene and styrene.
Question 6.
Arrange the following polymers in increasing order of their inter molecular forces:
- Nylon 6,6, Buna-S, Polythene.
- Nylon 6, Neoprene, Polyvinyl chloride.
Answer:
- Buna-S < Polyethene < Nylon-6,6.
- Neoprene < Polyvinyl chloride < Nylon-6.
Polymers NCERT Text-Book Exercises
Question 1.
Explain the terms polymer and monomer.
Answer:
Polymers are high molecular mass substances (103-107u) formed by the combi-nation of a large number of simple molecules. They are also called macromolecules. For example, polyethene, bakelite, PVC, teflon etc.
Monomer:
Monomer is a simple molecule capable of undergoing polymerization to form polymers. For example, polyethene is a polymer and its simple molecule ethene is a monomer.

Question 2.
What are natural and synthetic polymers ? Give two examples of each type.
Answer:
Natural polymers:
Natural polymers are high molecular mass macro molecules and are found in nature mainly in plants and animals. For example, protein, nucleic acids, starch, cellulose etc.
Synthetic polymer:
Synthetic polymers are man-made high molecular mass macro molecules. For example, plastics (Polyethene, P.V.C.), synthetic fibres (Polyesters, Nylon-6,6), synthetic rubber (Neoprene, Buna-S) etc.
Question 3.
Distinguish between the terms homopolymer and copolymer and give an example of each.
Answer:
Homo polymers are the polymers which are made by addition polymerization of single type of monomeric species.

Co-polymers are the polymers which are made by addition polymerization from two different monomers.
Question 4.
How do you explain the functionality of a monomer ?
Answer:
Functionality means the number of bonding sites in a molecule. For example, the functionality of ethene, propene, styrene, acrylonitrile is one while that of 1,3 – butadiene, adipic acid, terephthalic acid, hexamethylene diamine is two.
Question 5.
Define the term polymerization.
Answer:
Polymerization is a process of formation of a high molecular mass polymer from one or more types of monomers. Polymerization leads to linkage together of several repeating structural units with covalent bonds.
![]()
Question 6.
Is (NH – CHR – CO)n a homopolymer or copolymer ?
Answer:
It is a homopolymer because the repeating structural unit has only one type of monomer unit, i.e., NH2 – CHR – COOH.
Question 7.
In which classes, the polymers are classified on the basis of molecular forces ?
Answer:
On the basis of molecular forces present between the chains of various polymers, these are classified as:
- Elastomers
- Fibres
- Thermoplastics
- Thermo setting plastics.
Question 8.
How can you differentiate between addition and condensation polymeriza-tion ?
Answer:
Addition polymerization:
The molecules of the same or different monomers add together to form a macromolecule. Without elimination of any thing the addition polymers are formed by monomers which are unsaturated compound. For example, formation of polyethene from ethene.
Condensation polymerization:
Two or more bi-functional molecules undergo a se-ries of condensation reactions with the elimination of some simple molecules like H2O, R – OH, NH3, HCl or CO2 etc., to form a macromolecule (Polymer). For example, Nylon-6,6 is a condensation polymer of hexamethylene diamine and adipic acid formed by the elimination of water molecule.
![]()
Question 9.
Explain the term co-polymerization and give two examples.
Answer:
When two or more different monomers unite together to polymerize, the result- product is called a co-polymer and the process is termed as copolymerization. Thus, a co-polymer contains a large number of units of each monomer used in the same polymeric chain. For example, Buna-S and Buna-N whereas Buna-S is a copolymer of 1,3-butadiene and styrene while Buna-N is a co-polymer of 1,3-butadiene and acrylonitrile.
Question 10.
Write the free radical mechanism for the polymerization of ethene.
Answer:
In the presence of Benzoyl peroxide the polymerization of ethane can be under¬stand by the free radical mechanism.
Chain initiation step:
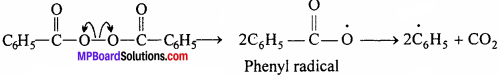
Chain propagation step:
C6H5 + CH2 = CH2 → C6H5 – CH2 – CH2
Chain termination step:
C6H5 – CH2– CH2 + CH2 = CH2 → C6H5 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 → C6H5(- CH2 – CH2-)n CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2(- CH2 – CH2 – )KC6H5 Polythene
Question 11.
Define thermoplastics and thermosetting polymers with two examples of each.
Answer:
Thermoplastics are polymers which can be easily softened repeatedly on heating and hardened on cooling. Therefore, it can be used again and again. For example, polyethene and polyvinyl chloride. Thermosetting polymers are those which undergo permanent change on heating. They become hard and infusible on heating and cannot be softened again. For example, Bakelite, and Melamine formaldehyde.
Question 12.
Write the monomers used for getting the following polymers:
- Polyvinyl chloride
- Teflon
- Bakelite.
Answer:
- Vinyl chloride (CH2 = CH – Cl)
- Tetrafluoroethylene (CF2 = CF2)
- Phenol (C6H5OH) and Formaldehyde (HCHO).
Question 13.
Write the name and structure of one of the common initiators used in free radical addition polymerization.
Answer:
Benzoyl peroxide:

Question 14.
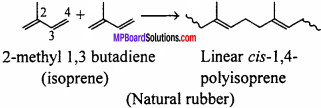
How does the presence of double bonds in rubber molecules influence their structure and reactivity ?
Answer:
From the structural point of view, the natural rubber is a linear cis- 1,4-poly iso- prene. In this polymer the double bonds are located between C2 and C3 of isoprene units. This cis-configuration about double bonds do not allow the chains to come closer for effective interactions and hence inter molecular forces are quite-weak. Therefore, natural rubber has coiled structure and show elasticity.
Question 15.
Discuss the main purpose of vulcanization of rubber.
Answer:
The main purpose of vulcanization of rubber is to improve the following draw-back of natural rubber:
- At high temperature (T >335K) natural rubber become soft.
- At low temperature (T< 283K) natural rubber becomes brittle.
- Natural rubber is soluble in non-polar solvents.
- It is non-resistant to attack by oxidizing agents.
Question 16.
What are the monomeric repeating units of Nylon-6 and Nylon-6,6 ?
Answer:
Nylon-6: Caprolactum Nylon-6,6: hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid.
![]()
Question 17.
Write the names and structures of the monomers of the following poly mers:
(i) Buna-S
(ii) Buna-N
(iii) Dacron
(iv) Neoprene.
Answer:
Names and structures of the monomers:
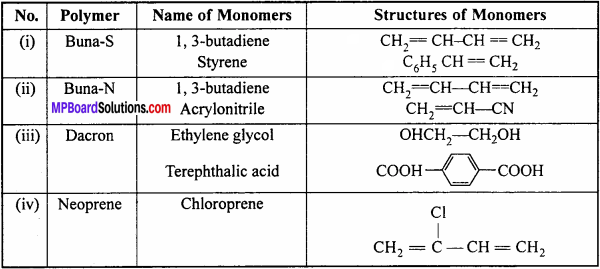
Question 18.
Identify the monomer in the following polymeric structures:
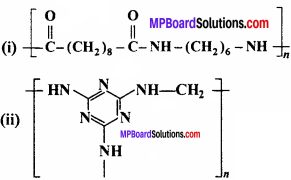
Answer:
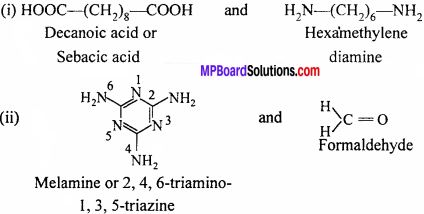
Question 19.
How is dacron obtained from ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid ?
Answer:
Dacron is obtained by the polymerization of ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid.
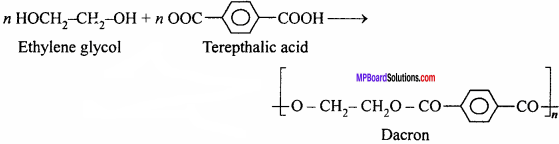
Question 20.
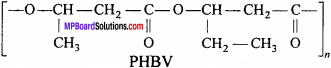
What is a biodegradable polymer ? Give an example of a biodegradable aliphatic polyester.
Answer:
The polymers which are degraded by micro-organism within a suitable period of time so that the polymers and their degraded products do not cause any serious affects on the environment are called biodegradable polymers. An example of biodegradable aliphatic polyester is PHBV. (Poly-β-hydroxy butyrate – CO – β – hydroxyvalerate)
Polymers Other Important Exercises
Polymers Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Which of the following is false:
(a) Artificial silk is derived from cellulose
(b) Nylon-6,6 is an example of elastomer
(c) The repeat unit in natural rubber is isoprene
(d) Both starch and cellulose are polymers of glucose.
Answer:
(b) Nylon-6,6 is an example of elastomer
Question 2.
Formation of polyethylene from calcium carbide takes place as follows:
CaC2 + 2H2O → Ca(OH)2 + C2H2
C2H2 + H2 → C2H4
nC2 H4 → (- CH2 – CH2 -)n
The amount of polyethylene obtained from 64-0 kg CaC2 is:
(a) 7 kg
(b) 14 kg
(c) 21 kg
(d) 28 kg.
Answer:
(d)28 kg.
Question 3.
Which of the following statements about low density polythene is false:
(a) Its synthesis requires high pressure
(b) It is a poor conductor of electricity
(c) Its synthesis requires dioxygen or a peroxide initiator as a catalyst
(d) It is used in the manufacture of buckets, dustbin etc.
Answer:
(d) It is used in the manufacture of buckets, dustbin etc.
![]()
Question 4.
Nylon is an example of:
(a) Polyamide
(b) Polythene
(c) Polyester
(d) Polysaccharide.
Answer:
(a) Polyamide
Question 5.
Natural rubber has:
(a) Alternate cis- and tnms-configuration
(b) Random cis- and /ram-configuration
(c) All cis-configuration
(d) All trans-configuration.
Answer:
(c) All cis-configuration
Question 6.
Which of the following is not a condensation polymer :
(a) Melamine
(b) Glyptal
(c) Dacron
(d) Neoprene.
Answer:
(d) Neoprene.
Question 7.
Which is a monomer of neoprene in the following :

Answer:
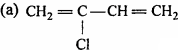
Question 8.
Which of the following is a biodegradable polymer:
(a) Polythene
(b) Bakelite
(c) PHBV
(d) P.V.C.
Answer:
(c) PHBV
Question 9.
Which of the following has ester linkage:
(a) Nylon
(b) Bakelite
(c) Terylene
(d) P.V.C.
(e) Rubber.
Answer:
(c) Terylene
![]()
Question 10.
Teflon is a polymer of:
(a) Tetrafluoroethylene
(b) Tetraiodoethylene
(c) Tetrabromoethylene
(d) Tetrachloroethylene.
Answer:
(a) Tetrafluoroethylene
Question 11.
Nylon threads are made up of:
(a) Polyamide polymer
(b) Polyethylene polymer
(c) Polyvinyl polymer
(d) Polyester polymer.
Answer:
(a) Polyamide polymer
Question 12.
Bakelite is a polymer of:
(a) HCHO and acetic acid
(b) HCHO and phenol
(c) C2H5OH and phenol
(d) CH3COOH and benzene,
Answer:
(b) HCHO and phenol
Question 13.
Which of the following is a biodegradable polymer:
(a) Cellulose
(b) Polyethene
(c) Polyvinylchloride
(d) Nylon-6.
Answer:
(a) Cellulose
Question 14.
Nylon-6,6 is not a:
(a) Condensation polymer
(b) Copolymer
(c) Polyamide
(d) Homopolymer.
Answer:
(d) Homopolymer.
![]()
Question 15.
Which of the following is a chain-growth polymer:
(a) Starch
(b) Nucleic acid
(c) Poly styrene
(d) Protein
Answer:
(c) Poly styrene
Question 2.
Fill in the blanks:
- …………… Is used for the preparation of chloroprene.
- Charge on polymers is ……………
- Molecular mass of polymers is ……………
- Glucose is a monomer of ……………
- Cellulose is a …………… polymer.
- Polymer of ethylene glycol and phthalic acid is ……………
- Rubber is a …………… polymer.
- Vulcanisation of rubber is an example of ……………
- Bakelite is a …………… polymer.
- Polymer used for making pipes is ……………
- Nylon 6 is also called ……………
- Teflon is a polymer of ……………
Answer:
- Synthetic rubber
- Nil (zero)
- High
- Cellulose and starch
- Natural
- Glyptal
- Natural
- Elastomer
- Heat resistant
- PVC
- Perlon-L
- Tetra fluoro ethylene.
Question 3.
Match the following:

Answer:
- (d) Polyethylene glycol phthalate
- (a) Adipic acid and hexa methylene diamine
- (c) Caprolactum
- (f) Lucite
- (b) Melamine
- (g) Polytetrafluoroethene
- (e) Dacron
- (h) Bakelite.
![]()
Question 4.
Answer in one word / sentence:
- Give two examples of natural polymer.
- Give two examples of addition polymer.
- Give two examples of condensation polymer.
- Write chemical name of Buna rubber.
- What is Buna-S ?
- Give an example of synthetic rubber.
- Monomer of polythylene is.
- Give the name of polymer used for formation of tyre thread.
- Name the polymerisation which takes place by addition of two or more than two different monomers.
- Name the polymer which is formed by condensation of ethylene glycol and dimethyl terephthalic acid.
Answer:
- Natural polymer-Rubber, starch
- (i) Polythene
(ii) Polypropylene - (i) Nylon
(ii) Bakelite - Styrene Butadiene rubber
- It is a co-polymer of Butadiene and styrene. Bu is for Butadiene Na for sodium and S-for styrene
- Styrene Butadiene rubber (S.B.R.)
- Ethylene
- Terylene
- Co-polymerisation
- Terylene.
![]()
Polymers Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Can a copolymer be formed both in addition and condensation polymeri-zation ?
Answer:
Yes, it can be formed in both the cases, e.g., buna-S is a copolymer of styrene, 1,3 – butadiene and sodium and is an addition polymer. Nylon-6,6 is a condensation co-polymer in which monomers are different, i.e., adipic acid and hexamethylene diamine.
Question 2.
What is the difference between two notations: nylon-6 and nylon-6,6 ?
Answer:
Nylon-6 is obtained from caprolactum which is obtained from cyclohexane. It has only one compound having 6 carbon atom.
Nylon-6,6 refers to polymer obtained from 6 carbon atom of dicarboxylic acid (adipic acid) and 6 carbon atoms of diamine.
Question 3.
Arrange the following polymers in the increasing order of their intermo – lecular forces. Also classify them as addition and condensation polymer. Nylon-6,6, Buna-S, Polythene.
Answer:
- Polythene < buna-S < nylon-6,6.
- Nylon – 6,6 – condensation polymer
- buna – S, polythene – addition polymer.
Question 4.
How do thermoplastic polymer differ from thermosetting polymer ?
Answer:
Difference between Thermoplastic polymer and Thermosetting polymer:
Thermoplastic:
- These are linear polymers.
- Weak van der Waals’ force is present in the form of intermolecular force which on heating becomes soft and melts.
- It can be remoulded into different shapes again and again. Example: Polystyrene, P.V.C., terylene etc.
Thermosetting:
- These are cross-linked polymers.
- Due to presence of chemically cross – linked bonds thermo setting polymers become non-fusible and do not melt on heating.
- They become hard at the time of mould ing and therefore cannot be remoulded. Example: Formaldehyde, resin, glyptal etc.
![]()
Question 5.
Are polyesters and polyacrylates same ? Justify your answer.
Answer:
Polyesters and polyacrylates are different types of polymer and differ in following ways:
- Polyacrylates are homopolymer, while the polyesters are co-polymer in nature.
- The mode of synthesis of polyacrylates is addition polymerization, while those of polyester is condensation polymerization.
- Polymerization occurs across C = C bond in polyacrylates whereas, in polyesters it is through ester linkage.
Question 6.
Why should one always use the purest form of monomer in free radical polymerization reaction ?
Answer:
In free radical polymerization, the impurities can act as chain transfer agent and may combine with the free radical to slow down the reaction or even stop the reaction.
Question 7.
List some important differences between Natural rubber and Vulcanization of rubber.
Answer:
Differences between Natural rubber and Vulcanisation of rubber:
Natural rubber:
- It is soft and sticky.
- It has low tensile strength.
- It has low elasticity.
- It can be used over a narrow range of temperature (10°C to60°C).
Vulcanisation of rubber:
- It is hard and non-sticky.
- It has high tensile strength.
- It has high elasticity.
- It can be used over a wide range of temperature (40°C to 100°C).
Question 8.
What are polythene ? Write its two uses.
Answer:
It is prepared by heating ethylene at about 473 K under high pressure (1500-2000 atm) in presence of a very small amount of oxygen.
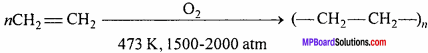
Uses:
- It is used for packaging.
- It is used as an insulator for electrical wires and cables.
- In the manufacture of pipes, bottles, etc.
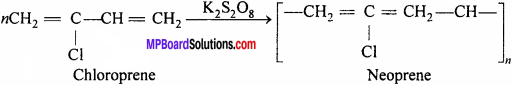
Question 9.
What is neoprene rubber ? Write its uses.
Answer:
Neoprene is a thermoplastic polymer of 2 – chloro – 1, 3 – butadiene (Chloroprene).
Method of preparation: By polymerisation of chloroprene in presence of potassium persulphate.
Uses:
- For making petrol delivery pipes.
- For making conveyer belts used in coal mines.
Question 10.
What is PVC ? Write its uses.
Answer:
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) is a higher polymer of vinyl chloride.
Preparation:
It is prepared by heating vinyl chloride in an inert solvent in the presence of benzoyl peroxide
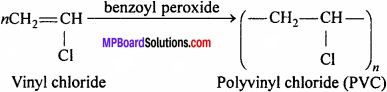
Uses:
It is used for making plastic pipes, gramophone records, toys, buckets, electric insulators, raincoat, hand bag and water proof substances
Question 11.
What is teflon ? Write its uses.
Answer:
It is a polymer obtained by the polymerization of tetrafluoroethylene in presence of benzoyl peroxide.
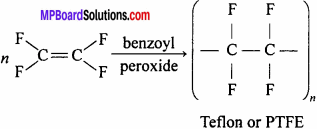
Uses: For making gasket, packing of pump, valve seal, bearing, etc.
![]()
Question 12.
What is cellulose ? Write its uses.
Answer:
Cellulose is a natural polysaccharide, molecular formula of cellulose is (C6H10O5)n. It is the main constituent of cell wall of plants and is also found in the tissues of some animals. Wood contain 60% and cotton 90% of cellulose. It is an organic compound found in abundance in nature.
Uses:
It is used to manufacture semi synthetic polymer, artificial thread and plastic.
Question 13.
What is Zieglar – Natta catalyst ? Write its uses.
Answer:
Zieglar – Natta catalyst:
Mixture of titanium tetrachloride and aluminium compound in an inert solvent (hexane) is called Zieglar – Natta catalyst.
Uses:
(i) At low pressure and temperature polythene is formed from ethylene.
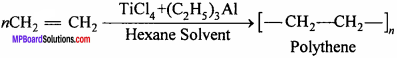
It is used for making toys, radio, T.V., cabinet.
(ii) At low temperature and pressure, propylene in presence of Zieglar – Natta catalyst form polypropylene
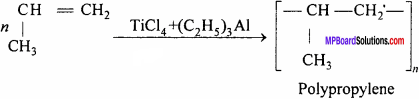
It is used for making bottles, pipes, gramophone records.
Question 14.
Differentiate between Nylon – 6 and Nylon-6,6.
Answer:
Difference between Nylon-6 and Nylon-6,6 polymer:
Nylon-6:
- This is prepared by the condensation of caprolactam molecules.
- Caprolactam contains a chain of 6 atoms hence this polymer is nylon-6.
- It is used in sheets, bristles for brushes. Crinkled nylon is also used in elastic hosiery.
Nylon-6,6:
- This is obtained by the condensation of hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid monomers.
- Adipic acid and hexamethylenedi amine both the compounds contain a chain of 6 carbons hence the polymer is called nylon-6, 6.
- It is used in manufacture of tyres, cords, fabrics and ropes.
Question 15.
Describe the preparation, properties and uses of teflon.
Answer:
Teflon or Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE):
This is obtained by the polymer – ization of tetrafluoroethylene. Tetrafluoroethylene is heated under pressure in the presence of ammonium peroxosuiphate.
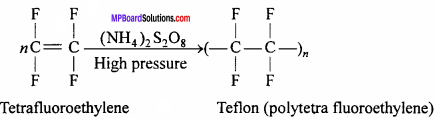
Properties:
- It is hard, heat resistant and chemically inert. It melts at 330 °C. It is unaffected by concentrated acids (cone. HNO3, cone. H2SO4, cone. HCl), aqua regia and concentrated sodium hydroxide solution even at high temperature.
- It is bad conductor of electricity.
Uses:
- It is used in making cans used to store concentrated acid, aqua regia etc.
- It is used as a non sticky coating on utensils.
Question 16.
How is bakelite prepared ? Write its uses also.
Answer:
Bakelite is cross – linked polymer. It is prepared by condensation of phenol and formaldehyde in presence of alkali.
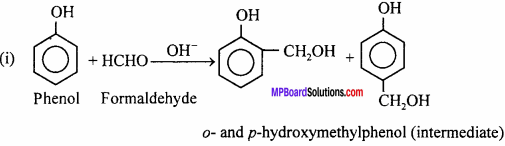
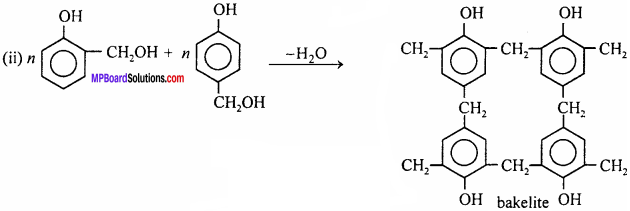
Uses:
Soft bakelite formed due to less polymerization are used as binder in wooden items, in varnishes and liquors. Hard bakelite are formed by high degree of polymerization and are used for manufacture of electrical goods, comb, fountain pens, gramophone records, table tops like pharmica, etc.
![]()
Question 17.
Write the method of preparation, properties and uses of Nylon-6,6.
Answer:
Preparation:
Nylon is a polymer containing amide![]() Nylon-6,6 is prepared by the polymerization of hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid. The meaning of 6,6 is that in the polymer chain both acid and diamine molecules contain 6-6 carbon atoms.
Nylon-6,6 is prepared by the polymerization of hexamethylenediamine and adipic acid. The meaning of 6,6 is that in the polymer chain both acid and diamine molecules contain 6-6 carbon atoms.
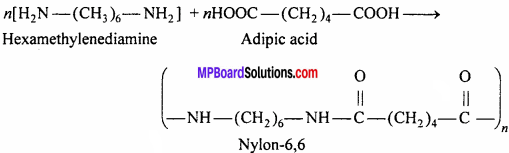
Properties:
- Nylon threads possess high tensile strength.
- They are hard.
- They are elastic in nature.
- Structure of nylon is like protein.
Uses:
- It is used for coating of wire, cables and other electrical goods because PVC is a good insulator of electricity.
- It is used for making plastic pipes, gramophone records, hand bags, raincoats, inflatable toys, etc.
- For making vinyl flooring, shower, curtains, false ceiling, wall covering, doors and windows.
- For making shoes heals and foot wear.
- For making sheets of tank-linkings, raincoats, lacquers, rods, tubes, packings, table cloths, light fittings, safety helmets, refrigeration components, trays, cycles, motorcycle mudguards, flexible articles such as toys, insulators, leather clothes, dolls, dipped goods such as protective gloves.
- It is used in manufacture of types cords, fabrics and ropes.
![]()
Polymers Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are natural polymer ? Explain some polymers with example.
Answer:
Natural polymers:
Those polymers which are found in nature (generally in plants and animals) are called natural polymers. The followings are their example:
(a) Polysaccharides:
Starch and cellulose are important example of polysaccharides. They are the polymers of glucose. Cellulose is the main structural material of plants. Plants store their food in the form of starch.
(b) Proteins:
Proteins are polymers of a-amino acids. They are the main constituents of animal cells. Natural silk, wool and leather are some examples.
(c) Nucleic acids:
The polymers of nucleic acids are called nucleotides. Their impor-tant examples are RNA and DNA.
(d) Natural rubber:
Natural rubber is prepared from latex which is obtained from rubber tree. It is a polymer of 2-methyl-1, 3-butadiene (isoprene). It may be noted that polymers like polysaccharides, nucleic acids, proteins, etc. which control various life processes in plants and animals are also called biopolymers.
![]()
Question 2.
On the basis of structure polymers are of how many types ? Explain.
Answer:
Classification based on structure:
This classification is based upon how the monomeric units are linked together. The polymers of this class are of three types:
(i) Linear polymers:
In this type of polymers, the monomer units are linked together to form long linear chains. These linear chains are placed one above the other and are closely packed in space. If A is the monomeric unit then linear chain is formed as given in Fig.
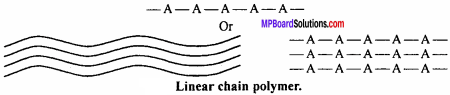
Characteristics:
Due to close packed structure, they have high densities, high tensile strength and high melting point, e.g., polythene, nylon, polystyrene, etc.
(ii) Branched chain polymers:
In this type of polymers, the monomer units combine to form a long chain which is called the main chain. Many side chains are connected to the main chain. The side chains of different lengths constitute branches, e.g., A is the monomeric unit which forms a straight linear chain (main chain). Side chain of A is connected to main chain as shown in Fig. They are not closely packed.
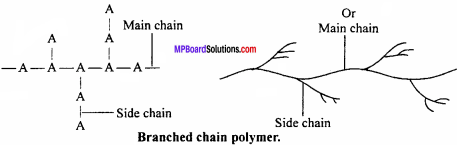
Characteristics:
Due to irregular packed structure, branched chain polymers have low densities, low tensile strength and low melting point, e.g., low density polythene, amylopectin, glycogen, etc.
(iii) Cross-linked polymers:
In these polymers, the monomer units combine to form a three-dimensional network.
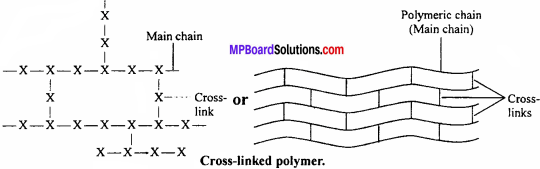
Characteristics:
They are hard, rigid and brittle due to cross-linked structure, e.g., bakelite, melamine, etc.