MP Board Class 11th Business Studies Important Questions Chapter 1 Nature And Purpose Of Business
Nature And Purpose Of Business Important Questions
Nature And Purpose Of Business Objective Type Questions
Question 1.
Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Which of the following does not characterise business activity –
(a) Production of goods and services
(b) Presence of risk
(c) Sale or Exchange of goods and services
(d) Salary or wages.
Answer:
(d) Salary or wages.
Question 2.
Which of the following cannot be classified as an auxiliary to trade –
(a) Mining
(b) Insurance
(c) Warehousing
(d) Transport.
Answer:
(a) Mining
Question 3.
The industries which provide support services to other industries are known as –
(a) Primary industries
(b) Secondary industries
(c) Commercial industries
(d) Tertiary industries.
Answer:
(d) Tertiary industries.
Question 4.
Which of the broad categories of industries covers oil refinery and sugar mills –
(a) Primary
(b) Secondary
(c) Tertiary
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(b) Secondary
![]()
Question 5.
Which of the following cannot be classified as an objective of business –
(a) Investment
(b) Productivity
(c) Innovation
(d) Profit Earning.
Answer:
(a) Investment
Question 6.
The occupation in which people work for others and get remunerated in return is known as –
(a) Business
(b) Employment
(c) Profession
(d) None of them.
Answer:
(b) Employment
Question 7.
Business risk is not likely to arise due to –
(a) Change in govt, policy
(b) Good management
(c) Employee dishonesty
(d) Power failure.
Answer:
(b) Good management
Question 8.
Free Guidance by a teacher to his son is –
(a) An economic activity
(b) Profession
(c) Employment
(d) A non – economic activity.
Answer:
(d) A non – economic activity.
Question 9.
Specialized knowledge and skill is needed in –
(a) Employment
(b) Non – Economic activity
(c) Profession
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Profession
Question 10.
Capital is not an essential element in –
(a) Employment
(b) Profession
(c) Business
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(a) Employment
Question 11.
The rework of risk is –
(a) Success
(b) Failure
(c) Profit
(d) Loss.
Answer:
(c) Profit
Question 12.
Economic activity –
(a) Business + Profession
(b) Profession + Employment
(c) Business + Employment
(d) Business + Profession + Employment.
Answer:
(d) Business + Profession + Employment.
Question 13.
It is not included in code of conduct –
(a) Rules
(b) Dishonesty
(c) Integrity
(d) Morality.
Answer:
(b) Dishonesty
Question 14.
Business is –
(a) Art
(b) Science
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b)
Question 15.
Which has the large scope –
(a) Trade
(b) Commerce
(c) Industry
(d) Business.
Answer:
(b) Commerce
![]()
Question 2.
Write true or false:
- Human activities directed towards acquisition of wealth are called economic activities.
- Activities performed for self-satisfaction and to fulfil social obligations are known as economic activities.
- All business risk are controllable.
- Activities based on specialized knowledge, training and experience is called profession.
- Risk element is compulsory for business.
- Only economic activities are included in business.
- Commerce is a indifferent part of business.
- Non – Economic activities are those which gives mental satisfaction.
- Doctors treats her mother is a economic activity.
- The main reason of risk in business is uncertainty of business.
- Business needs economic activities at regular interval.
- Creating new customer is a important objective of business.
- Teacher teaches his son at home is a economic activity.
- Employment needs capital.
- Postal Department is a part of Tertiary Sector.
Answer:
- True
- True
- False
- True
- True
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
- True
- True
- False
- False
- True.
Question 3.
Question (A)
Fill in the blanks:
- Business is a ……………. activities.
- Profit is the reward of …………….
- There are some ……………. of business towards society.
- ……………. activities measured in monetary terms.
- A human activities of business which is related with sale or purchase of goods is for earning …………….
- The economic activities on the basis of special knowledge, training and experiences are called …………….
- The risk element in business is called …………….
- Profession needs ……………. skill.
- For getting services on the basis of contract from men or Institution is called …………….
- In business all the ……………. services of men are included.
- Business is ……………. both.
- Business gives inspiration of …………….
- Business is undertaking within the boundries of a country is called …………….
Answer:
- Economic
- Risk
- Moral duties
- Economic
- Wealth
- Profession
- Business risk
- Specific
- Service
- Economic activities
- Art and science
- Skill
- Internal Trade.
Question (B)
Fill in the blanks:
- External Trade are ……………. types.
- …………… is a base of industry.
- Parameter of profession is …………….
- Services are provided for …………….
- Commerce, Industries and ……………. are the elements of business.
- ……………. is transferable.
Answer:
- 3
- Commerce
- Earning profit
- Payment
- Trade
- Business.
Question 4.
Give answer in one word/sentence:
Question 1.
Which work require specialize knowledge?
Answer:
Profession.
Question 2.
When trading is done by one country to another country by which name is called?
Answer:
Foreign trade.
Question 3.
What is result of Business risk?
Answer:
The result of Business risk is profit.
Question 4.
Which activity is related to service and welfare?
Answer:
Non – economic activities are related to service and welfare.
Question 5.
What is objective of Economic activities?
Answer:
The main objective of economic activities to earn profit and wealth.
Question 6.
What kind of activity is teaching of a teacher in school?
Answer:
It is economic activity.
![]()
Question 7.
What kind of activity is teaching of a teacher to his son?
Answer:
It is non – economic activity.
Question 8.
What is given to the person who render services is called?
Answer:
It is called as salary or wages.
Question 9.
What is last result of non – economic activities?
Answer:
Satisfaction is the last result of non – economic activities.
Question 10.
Why an entrepreneur voluntarily gets ready to have risk?
Answer:
An entrepreneur voluntarily gets ready to have risk in order to earn profit.
Question 11.
What kind of activity is Business?
Answer:
Economic activity.
Question 12.
By what the probability of loss in Business is called?
Answer:
Business risk.
Question 13.
What kind of Business is fishing?
Answer:
Primary Industry.
![]()
Question 14.
Which subsidiary Industry removes the problem of communication?
Answer:
Advertisement.
Question 15.
What is called as the person w ho takes risk in Business?
Answer:
Entrepreneur.
Question 16.
Which activities are not related to the wealth?
Answer:
Non – economic activities.
Question 17.
By what name exchange of goods and services for mutual benefit is called?
Answer:
Goods Exchange.
Question 18.
By what name the reward of risk is called?
Answer:
Profit.
Question 19.
By what name those activities which are done for earning Income?
Answer:
Economic Activities.
Question 20.
Which activity is the treatment of Doctor in the Hospital ?
Answer:
Economic Activity,
Nature And Purpose Of Business Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are Economic Activities?
Answer:
Those activities which are related to earning of money or wealth is called as Economic Activities, e.g. purchase and sale of goods, work of advocate, job in factory, etc.
Question 2.
What are Non – economic Activities ?
Answer:
Those activities which are not related to earning of money or wealth is called as Non – Economic activities, e.g., Teaching of teacher to his son.
Question 3.
Give any three examples of Economic Activities?
Answer:
The three examples of Economic Activities are:
- Working of Labour in factory.
- Working of Doctor in his clinic.
- Teaching by teacher in school,
Question 4.
Give any three examples of Non – economic Activities?
Answer:
The three examples of Non – economic Activities are:
- Helping old man to cross road.
- Teaching by teacher to his son.
- Cooking of food by house wife for his family.
- Care of child by mother.
![]()
Question 5.
Into how many categories Economic Activities are divided?
Answer:
They are divided into three categories:
- Business
- Profession
- Employment.
Question 6.
What do you mean by business?
Answer:
Production of goods, purchase and sale of goods and rendering services with objective of earning profit is called as business.
Question 7.
“Business is an Economic Activity.” Discuss?
Answer:
Business is such kind of Economic Activity whose main objective is exchange of goods and services continuously with bearing of risk. Hence, it is such economic activity which is related to earning of profit.
Question 8.
What do you mean by ‘Profession’?
Answer:
A profession is an occupation which requires specialized know ledge and skills and services are rendered personally against some remuneration for example, the services of doctors, lawyers, accountants, engineers, etc.
Question 9.
W hat do you mean by uncertainty of profit in the business?
Answer:
Uncertainty of profit means that profit which is not fixed when business is done for a particular period of time.
Question 10.
What do you mean by Employment?
Answer:
Employment is related to those jobs where people do work for other and get remuneration against it.
Question 11.
What is Industry?
Answer:
The place where increase in utility of commodity is done is called as Industry, e.g. Making of sugar from cane, Rearing of cattles for milk.
Question 12.
What do you mean by trade?
Answer:
Sale and purchase of goods for earning profit is called as trade.
Question 13.
What is commerce?
Answer:
Commerce is the sum total of those process which are engaged in the removal of the hindrances of person (Trade;, place (Transport and Insurance), time (Warehousing) and finance (Banking) in exchange of commodities.
Question 14.
List subsidiary activities or Auxiliaries to trade?
Answer:
Auxiliaries to trade are Transport, Bank, Insurance, Warehousing, Communication, Advertisement, Packaging, etc.
![]()
Question 15.
What do you mean by Innovation?
Answer:
Inclusion of new ideas or techniques in the work is called as Innovation.
Question 16.
What is warehousing?
Answer:
The process of keeping the produced goods safely is called as warehousing.
Question 17.
What is advertisement?
Answer:
Propoganda and spread of goods in order to increase the sales is called as advertisement.
Question 18.
What is transport?
Answer:
The process of transferring goods and human from one place to another is called .as transport.
Question 19.
What do you mean by business risk?
Answer:
That less profit or probability of having loss which occurs due to incontrollable factors of evidences in the business is called as business risk.
Question 20.
Give the meaning of Inland trade?
Answer:
The Business which is done within the borders of a country is called as Inland trade. In this the purchaser and seller belongs to the same country.
Question 21.
Explain the meaning of foreign trade?
Answer:
When the businessmen of one country have selling and purchasing of goods from the other country businessmen then it is called as foreign trade.
![]()
Question 22.
What is import trade?
Answer:
Purchase of goods from foreign countries is called as import trade, e.g., Purchase of goods by India from America.
Question 23.
What is export trade?
Answer:
Selling of goods to foreign countries is called as export trade, e.g.. Selling of goods by India to America.
Question 24.
What is Entreport trade ?
Answer:
The trade where goods are purchased from one country and then it is sold to other country is called as entreport trade.
Nature And Purpose Of Business Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
State the different types of economic activities?
Answer:
Economic activities are those by which we can earn our livelihood. Economic activities may. be further divided into three categories, namely business, profession and employment e.g.. a person running a garment business, a doctor operating in his clinic and a teacher teaching in a school, all three are doing so to earn their livelihood and are. therefore, engaged in an economic activity.
Question 2.
Explain the concept of business?
Answer:
The term ‘business’ is derived from the word ‘busy’. Thus, business means being busy. However, in a specific sense, business refers to any occupation in which people regularly engage in an activity with an objective of earning profit. The activity may consist of production or purchase of goods for sale, or exchange of goods or supply of services to satisfy the needs of other people in the society.
![]()
Question 3.
What are various types of industries?
Answer:
Industry refers to economic activities which are connected with conversion of resources into useful goods. Industries may be divided into three broad categories namely primary, secondary and tertiary:
1. Primary industries include all those activities which are connected with the extraction and production of natural resources and reproduction and development of living organisms, plants, etc.
2. Secondary industries are concerned with using or processing the materials which have already been extracted at the primary stage.
3. Tertiary industries are concerned with providing support services to primary and secondary industries. They also include activities relating to trade.
Question 4.
How would you classify business activities ?
Answer:
Various business activities may be classified into two broad categories:
Industry and commerce. Industry is concerned with the production or processing of goods and materials. Industries may be divided into three broad categories namely primary, secondary and tertiary. Commerce includes all those activities which are necessary for facilitating the exchange of goods and services. Commerce includes two types of activities, viz.
- Trade and
- Auxiliaries.
Question 5.
What is the role of profit in business?
Answer:
Every business operates with an aim to earn more than what has been invested and profit is the excess of revenue over cost. Profit plays an important role in business.
- It is a source of income for business persons.
- It can be a source of finance for meeting expansion requirements of business.
- It indicates the efficient working of business.
- It can be taken as society’s approval of the utility of business.
- It builds up the reputation of a business enterprise.
Question 6.
What is business risk? What is its nature?
Answer:
The term ‘business risk’ refers to the possibility of inadequate profits or even losses due to uncertainties or unexpected events. Business risks are of two types speculative and pure speculative risks involve both the possibility of gall as well as the possibility of loss speculative risks arise due to changes in market conditions, changes in prices or changes in fashion and tastes of customers. Pure risks involve only the possibility of loss or no loss. The chances of fire, theft or strike are examples of pure risks.
Nature of business risks can be understood in terms of the following characteristics:
- Business risks arise due to uncertainties.
- Risk is an essential part of every business.
- Degree of risk depends mainly upon the nature and size of business.
- Profit is the reward for risk taking.
![]()
Question 7.
“Business, Commerce and Industry are inter – related”. Discuss?
Answer:
In commerce all those activities which helps in the purchase and sale of goods are included. Business is the main organ of the commerce. Business commerce and industry have separate existence but then also directly or indirectly they are inter-related to each other. Commerce and Business is impossible without the industry because exchange of goods and services are possible only when they are produced.
Similarly industries are useless without Business and Commerce. Until the produced goods and services are not made available to the customers their production is of no use and will not generate any profit. This all is possible only the commerce, Hence it can be said that Business, Commerce and Industry are inter related to each other.
Question 8.
“Maximum profitability is not only the objective of the business”. Discuss?
Answer:
There is no doubt that maximum profit earning is the main objective for keeping business in existence, for its expansion and development and for its fame and goodwill but this only should not be the objective of the business as it should be appropriate keeping in view social objectives, human objectives and national objectives.
Question 9.
Write characteristics of Economic Activities?
Answer:
Following are the characteristics of Business activities:
1. Economic objective:
Every economic activity have the objective of Earning or spending money. These activities can be measured with money.
2. Social Activities:
Man is a social animal. It has no existence other than society. Social rituals always guide us rather than when we go at wrong deeds. Hence, they cannot be overlooked hence man do his economic work in context to social needs.
3. Legality:
Only those activities which are done as per the rules of state and society will only be included in the economic activities. They should be always done along with values, justice and public welfare. Earning from theft, robbery and gambling cannot be considered as economic activities.
Question 10.
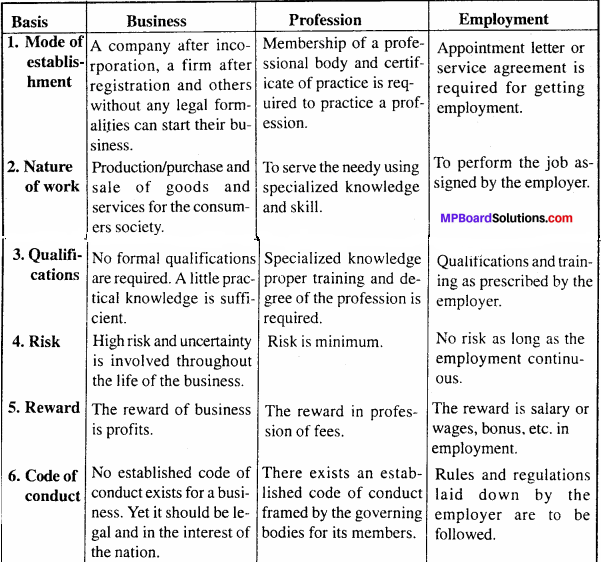
Compare business with profession and employment?
Answer:
Economic activities may be divided into three major categories:
1. Business:
Business refers to those economic activities, which are connected with the production or purchase and sale of goods or supply of services with the main object of earning profit. People engaged in business earn income in the form of profit.
2. Profession:
Profession includes those activities, which require special knowledge and skill to be applied by individuals in their occupation. Those engaged in professions are known as professionals and are generally subject to guidelines or codes of conduct laid down by professional bodies, e.g. lawyers are engaged in the legal profession, governed by the Bar Council of India and Chartered Accountants belonging to the accounting profession are subject to the regulations of the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India.
3. Employment:
Employment refers to the occupation in which people work for others and get remunerated in return. Those who are employed by others are known as employees. Thus, people who work in factories, offices of banks, insurance companies or government department, etc. at various posts are the employees of these organizations. They receive wages and salaries.
Comparison of Business, Profession and Employment:
Nature And Purpose Of Business Long Answer Type Questions – I
Question 1.
Explain the characteristics of business?
Answer:
Business refers to any occupation in which people regularly engage in an activity with an objective of earning profit. The activity may consist of production or purchase of goods for sale or exchange (If goods or supply of services to satisfy the needs of other people in the society), Business has the following characteristics:
1. Economic Activity:
Business is considered to be an economic activity because it is undertaken with the aim of earning money or livelihood and not because of any sentimental reason like love, affection or sympathy.
2. Production or Procurement of Goods and Services:
Goods are offered to consumers after they are either produced or procured by business enterprises. Thus, every business enterprise either manufactures the goods. It deals in or it acquires them from other producers, to be further sold to consumers or users.
3. Sale or Exchange of Goods and Services:
Business involves transfer or exchange of goods and services for value addition. If goods are produced for self – consumption and not for selling purpose, it cannot be called a business activity, cooking food at home for the family is not business, but cooking food and selling it to others in a restaurant is business. Thus, one essential characteristic of business is that there should be sale or exchange of goods or services between the seller and the buyer.
4. Regular Dealings in Goods and Services:
Business involves dealings in goods or services on a regular basis. Therefore, one single transaction of sale or purchase does not constitute business e.g., if a person sells his/her old washing machine even at a profit. It will not be considered a business activity. But if he/she sells washing machines regularly it will be termed as a business,
5. Profit Earning:
One of the main objectives of business is to earn profit. No business can survive for long without earning profit. It is a source of income for business persons and a source of finance for meeting expansion requirements of business. Hence, businessmen make all possible efforts to maximize profits, by increasing the sales revenue or reducing costs.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain with examples the various types of industries?
Answer:
Industries may be divided into three broad categories namely primary, secondary and tertiary.
1. Primary Industries:
These include all those activities, which are connected with the extraction and production of natural resources and reproduction and development of living organisms, plants, etc.
These industries may be further sub – divided as follows:
(a) Extractive Industries:
These industries extract or draw out products from natural sources. Extractive industries are suppliers of basic raw materials that are mostly products of the geographical or natural environment products of these.
(b) Genetic Industries:
These industries are concerned with breeding of plants and animals for their use in further reproduction seeds and nursery companies can lead breeding farms, poultry farms, and fish hatchery are examples of genetic industries.
2. Secondary Industries:
These are concerned with using and processing the materials which have already been extracted by the primary sector to produce goods for final consumption or for further processing by other industrial units e.g. the iron ore extracted by mining which is a primary industry, is processed into steel and hence, steel industry is a secondary industry. Secondary industries may be further divided as follows:
(a) Manufacturing Industries:
These industries are engaged in producing goods for intermediate or final consumption through processing of raw materials and thus creating form utilities. Manufacturing industries may be further divided into four categories on the basis of method of operation for production.
- Analytical industry which analyses and separates different elements from the same materials, e.g. oil refinery.
- Synthetical industry which combines various ingredients into a new product, e.g. cement industry.
(b) Construction Industries:
These industries are involved in the construction of buildings, dams, bridges, roads, tunnels and canals. Engineering and architectural skills play an important role in construction industries. These industries are important for infrastructure development.
3. Tertiary Industries:
These comprise of support services to primary and secondary industries as well as activities relating to trade. These industries provide service facilities. These may be considered as a part of commerce because as auxiliaries to trade they assist trade. Transport, banking, insurance, warehousing, communication. Packaging and advertising are examples of tertiary industries.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain with importance of Industries?
Answer:
Following are the importance of the Industries:
1. Economic Development of the Nation:
The economic Development of a country completely depends on the establishment of industries. Industrially developed nations are considered rich.
2. Increase in National income:
Industries help to utilize the resources of a country to the fullest possible extent. This increases the national income of the country.
3. Increase in Employment Opportunities:
The establishment of maximum number of large scale and small – scale industries ensures generation of large scale employment opportunities.
4. Capital formation:
Increase in income leads to savings. By the small savings only big capitals are formed.
5. Encourages Research and Development:
Development of industries lead to new discoveries. New methods of production and new machines are invented for the same purpose.
6. Increase in trade:
New industries will lead to increase in selling and purchases of goods. Moreover there will be increase in the allied activities like banking, insurance, transportation, marketing etc.
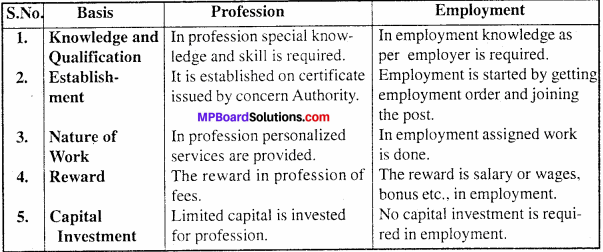
Question 4.
Differentiate between Profession and Employment.
Answer:
Differences between Profession and Employment:
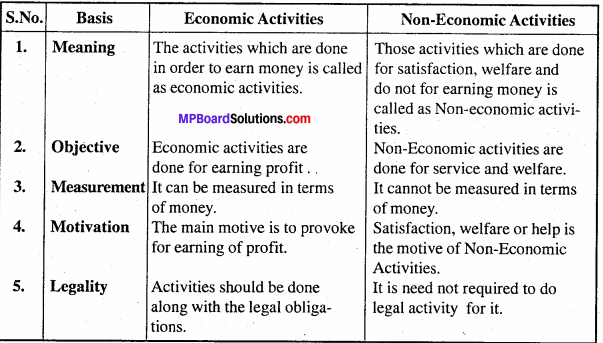
Question 5.
Differentiate between Economic Activities and Non – Economic Activities?
Answer:
Differences between Economic Activities and Non – Economic Activities:
Question 6.
What are auxiliaries to trade? Explain any five auxiliaries in brief?
Answer:
Commerce includes two types of activities, viz. (i) Trade and (ii) Auxiliaries to trade. Buying and selling of goods is termed as trade. On the other hand, activities that are required to facilitate the purchase and sale of goods are called services or auxiliaries to trade. The various activities included in commerce are discussed below.
1. Trade:
The hindrance of persons is removed by trade thereby making goods available to the consumers from the producers. Trade is an essential part of commerce. It refers to sale, transfer or exchange of goods. It helps in making the goods produced available to ultimate consumers or users. Businessmen are engaged in trading activities as middlemen like wholesalers and retailers to make the goods produced at a large scale in one place, available to consumers in different markets. Trade may be internal or external.
2. Auxiliaries to Trade:
Activities which are meant for assisting trade are known as auxiliaries to trade. These activities are generally, referred to as services because these are in the nature of support service facilitating the activities relating to industry and trade. These activities help in removing various hindrances which arise in connection with the production and distribution of goods. Auxiliaries to trade are briefly discussed below.
(a) Transport and Communication:
Transport removes the hindrances of place. Transport facilitates through road, rail or coastal shipping facilitate movement of raw material to the place of production and the finished products from factories to the place of consumption. Along with the transport facility, there is also a need for communication facilities to enable the producers, traders and consumers to exchange information with one another. Thus, postal services and telephone facilities are also regarded as auxiliaries to business activities.
(b) Banking and Finance:
Capital required to acquire assets and meeting the day-to¬day expenses is provided by banking and financing institutions. Commercial banks lend money to business organizations by providing; loans and advances. Banks also undertake collection of cheque, remittance of funds to different places, and discounting of bills on behalf of traders. In foreign trade, payments are arranged by commercial banks on behalf of importers and exporters.
(c) Insurance:
The risk of loss or damage to the factory building, machinery, furniture, goods held in stock or goods in course of transport due to theft, fire, accidents, etc. is removed by insurance of goods. By payment of a nominal premium, the amount of loss or damage and compensation for injury, if any can be recovered from the insurance company.
Nature And Purpose Of Business Long Answer Type Questions – II
Question 1.
Differentiate between Trade, Industry and Commerce.
Answer:
Differences between Trade, Industry and Commerce:
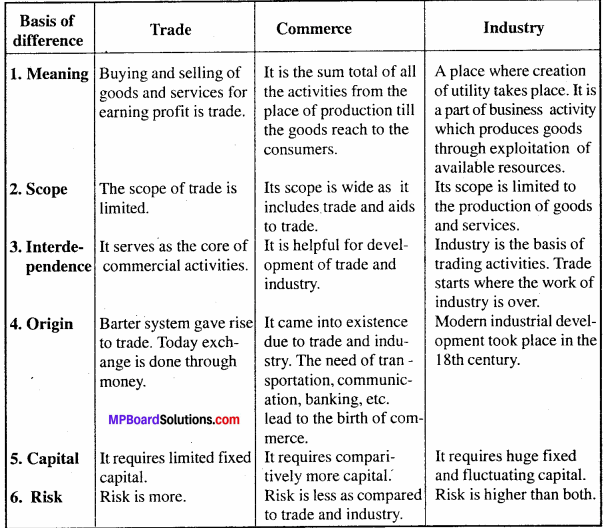
Question 2.
Differentiate between Business, Profession and Employment?
Answer:
Differences between Business Profession and Employment:

Question 3.
What are multiple objectives of a Business? Explain any five such objectives.
Answer:
Objectives are needed in every area where performance and results affect the survival and prosperity of business. Five of the objectives of business are described below:
1. Profit Maximization:
Profit is defined as excess of revenue over cost profitability refers to profit in relation to capital investment. Although earning profit cannot be the only objective of business, its importance cannot be ignored. Every business makes an attempt to reap maximum profit as possible in the given market conditions. Profit may be regarded as an essential objective of business for various reasons:
- It is a source of income for business persons.
- It can be a source of finance for meeting expansion requirements of business.
- It indicates the efficient working of business.
2. Market Standing:
Market standing refers to the position of an enterprise in relation to its competitors. A business enterprise must aim at standing on stronger footing. In terms of offering competitive products to its customers and provide customer satisfaction.
3. Innovation:
Innovation is the introduction of new ideas or methods. There are two kinds of innovation in every business.
(i) Product Innovation:
In product innovation a new product or service or an improved version of existing product is developed.
(ii) Process Innovation:
This involves innovation in the methods, skills and activities needed to produce or supply products.
4. Productivity:
Productivity is calculated by comparing the value of outputs with the value of inputs. It is used as a measure of efficiency. Higher productivity leads to reduction in costs as the same amount of output is produced with lesser amount of inputs. This ensures survival and growth of the enterprise.
5. Social Responsibility:
Every business operates within a society. It uses the resources of the society and depends on the society for its functioning. This creates an obligation on the part of business to look after the welfare of society. So, all the activities of the business should be such that they will not harm, rather they will protect and contribute to the interests of the society.
![]()
Question 4.
What factors are important to be considered while starting a business? Explain.
Answer:
Business firms encounter some basic problems while starting a business. Various decisions have to be taken regarding the business while starling it. Some of the basic factors to be considered while starting a business are as follows:
1. Selection of Line of Business:
The first thing to be decided by any entrepreneur of a new business is the nature and type of business to be undertaken. One should enter an industry which is in growth phase and thus, has a higher possibility of profits. Technical knowledge and interest the entrepreneur has for producing a particular product is also important in this regard.
2. Size of the Firm:
Size of the firm refers to the scale of its operation. Business can be started at a large scale if the entrepreneur is confident that the demand for the proposed product is likely to be high over time and he has the necessary skills and capital for business. Business should be started at a small or medium scale if the market conditions are uncertain and risks are high.
3. Form of Ownership:
There are various forms of ownership in a business organization like sale proprietorship, partnership or a joint stock company. The choice of the suitable form of ownership will depend on such factors as the capital requirements, liability of owners, division of profit, transferability of interest and so on.
4. Location of Business:
Enterprise Plant location is an important factor to be considered at the start of the business. Availability of raw materials and labour, power supply; and services like banking, transportation, communication, warehousing, etc. are important factors while making a choice of location.
5. Plant Layout:
Plant layout refers to a layout plan showing the arrangement of physical facilities such as machines and equipments for production. It should be drawn by the entrepreneur after deciding about the scale of operation and physical facilities to be acquired.
6. Tax Planning:
Every business has to pay certain taxes as levied by the government. Tax planning and management for reducing tax liability as far as possible is acceptable both legally and ethically. The entrepreneur must consider in advance the tax liability under various tax laws and its impact on business decisions.
Question 5.
Explain the nature of Business risk.
Answer:
Nature or Characteristics of Business risks:
Following are the few of the basic characteristics of business risks:
1. Uncertainty:
Uncertainty is an important feature of any business concern, e.g., change in production, wrong estimate of demand sudden hike in the prices, technological changes, changes in government policies, fluctuation in demand and supply, natural calamities are the few examples which influences the business.
2. Profit is Reward of Business Risks:
The principle of no risk no gain is applicable practically to all types of business. An entrepreneur invests capital in the business, does labour day and night and as a consideration for the same he gets his reward, i.e., profit.
3. Business Risks cannot be Eliminated:
In today’s computer age forecast can be done of weather, demand financial status, etc. which may help to reduce the business risks but it cannot be eliminated totally.
4. Degree of Risk Depends on Nature of Business:
The nature of business and the volume of production purchases, sales, etc. determines the degree of risk for any business. Degree of risk is high where changes taken place frequently. For example, in fashion industry, the items (product) are very costly and the taste of people changes frequently. Thus, there exists a high degree of risk in such business.
5. Quantum of Risk on Basis of Time:
The degree of risks is influenced by time factor also. A business may have to incure huge losses when there is political instability, terrorism communal riots, natural calamity, etc.
![]()
Question 6.
Explain the functions of Commerce.
Answer:
Functions of Commerce:
The various functions of commerce can be stated below:
1. Removal of Hindrances of Persons:
Hindrances of persons refers to the lack of communication between producers and consumers. Producers always search for a customer, who can pay a handsome price for his product. Similarly, consumers are always in search of products which are suitable to their purchasing power.
Hence, there is a need of persons who can buy the products from producers and sell them to the ultimate consumers. Traders have emerged to fill the gap between producer and consumers. Wholesalers, retailers and agents operate to remove the hindrance of person.
2. Removal of Hindrance of Exchange:
Purchaser and seller generally reside away from each other. After the completion of transaction the seller wants the payment at his place of convenience and purchaser like to pay from where he lies. This hindrance is removed by banks and insurance companies. The payment is done through bank drafts, bills of exchanges, cheques, etc. which fall within the scope of commerce.
3. Removal of Hindrance of Time:
There is always a time lag between the production and consumption of goods. Purchaser demands the immediate supply of goods, whereas it is obvious for the seller to take some time to supply goods. Thus, it becomes essential for the seller to produce goods and keep it safe.
The function of storage is performed by the warehouses which remove the hindrances of time by balancing the time lag between production and consumption, thus, creating time utility. Here, insurance play a vital role by providing risk cover for the loss of goods due to theft or fire.
4. Removal of Hindrance of Place and Distance:
Various fastest means of communication (Telephone, telegram, e – mail, etc.) helps to remove the hindrance of distance. Two traders residing at distant place can contact through the various means of communication for dealings. The goods produced at a place needs to be transported to the place of its demand.
Here, various mode of transport (Roadways, Railways and Waterways) help to remove the hindrance of place. Here again, insurance provides the risk cover during transit and storage